
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)\(đkx\ge1,x\ne-1\)
\(\sqrt{\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=4x-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)(nhận)
Vậy S=\(\left\{1\right\}\)
c)đk\(25x^2-10x+1=\) \(\left(5x-1\right)^2\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{1}{5}\)
\(\sqrt{25x^2-10x+1}+2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(5x-1\right)^2}+2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-1+2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{7}\)(nhận)
Vậy S=\(\left\{\dfrac{2}{7}\right\}\)
c: Ta có: \(\sqrt{25x^2-10x+1}+2x=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|5x-1\right|=1-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x-1=1-2x\left(x\ge\dfrac{1}{5}\right)\\5x-1=2x-1\left(x< \dfrac{1}{5}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{7}\left(nhận\right)\\x=0\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

Câu 4:
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3>=0\\23-2x>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x< =\dfrac{23}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>3/2<=x<=23/2
\(A=\sqrt{2x-3}+\sqrt{23-2x}\)
=>\(A^2=1\cdot\sqrt{2x-3}+1\cdot\sqrt{23-2x}< =\left(1^2+1^2\right)\cdot\left(2x-3+23-2x\right)\)
=>\(A^2< =2\cdot20=40\)
=>\(-2\sqrt{10}< =A< =2\sqrt{10}\)
Vậy: \(A_{max}=2\sqrt{10}\) khi 2x-3=23-2x
=>4x=26
=>x=6,5


a, \(AC=\sqrt{BC^2-AB^2}=16\left(cm\right)\)
\(AH=\dfrac{AB\cdot AC}{BC}=9,6\left(cm\right)\\ \sin ABC=\dfrac{AC}{BC}=\dfrac{4}{5}\approx\sin53^0\Rightarrow\widehat{ABC}\approx53^0\)
b, Áp dụng HTL: \(AN\cdot AC=AH^2\)
Áp dụng PTG: \(AH^2=AC^2-HC^2\)
Suy ra đpcm
c, Vì \(\widehat{AMH}=\widehat{ANH}=\widehat{MAN}=90^0\) nên AMHN là hcn
Do đó AH=MN
Áp dụng HTL: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AN\cdot NC=HN^2\\AM\cdot MB=HM^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Áp dụng PTG: \(HN^2+HM^2=MN^2=AH^2\)
Suy ra đpcm

4:
c; =>|x-1|+|x+2|=3
TH1: x<-2
Pt sẽ là -x-2+1-x=3
=>-2x-1=3
=>-2x=4
=>x=-2(loại)
TH2: -2<=x<1
Pt sẽ là x+2+1-x=3
=>3=3(luôn đúng)
TH3: x>=1
Pt sẽ là x-1+x+2=3
=>2x-1=3
=>2x=4
=>x=2(nhận)

1.
Ta có: $4x^2+4x+3=(4x^2+4x+1)+2=(2x+1)^2+2\geq 0+2=2$
$\Rightarrow A=\frac{6}{4x^2+4x+3}\leq \frac{6}{2}=3$
Vậy $A_{\max}=3$. Giá trị này đạt tại $2x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1}{2}$
2.
$6+4x+x^2=(x^2+4x+4)+2=(x+2)^2+2\geq 0+2=2$
$\Rightarrow \frac{4}{6+4x+x^2}\leq \frac{4}{2}=2$
$\Rightarrow \frac{-4}{6+4x+x^2}\geq -2$
$\Rightarrow B\geq -2$
Vậy $B_{\min}=-2$. Giá trị này đạt tại $x+2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-2$

Bài 3:
\(a,\) Gọi \(\left(d\right):y=ax+b\) là đt cần tìm
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\0a+b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left(d\right):y=2x+1\)
\(b,\) PT hoành độ giao điểm:
\(-x^2=2x+1\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\Leftrightarrow y=-1\Leftrightarrow A\left(-1;-1\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-1;-1\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm (P) và (d)
Bài 4:
PT có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=16-3m\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{16}{3}\)
Áp dụng Viét: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{8}{3}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Mà \(x_1^2+x_2^2=\dfrac{82}{9}\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=\dfrac{82}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{64}{9}-\dfrac{2m}{3}=\dfrac{82}{9}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2m}{3}=-2\Leftrightarrow m=-3\left(tm\right)\)

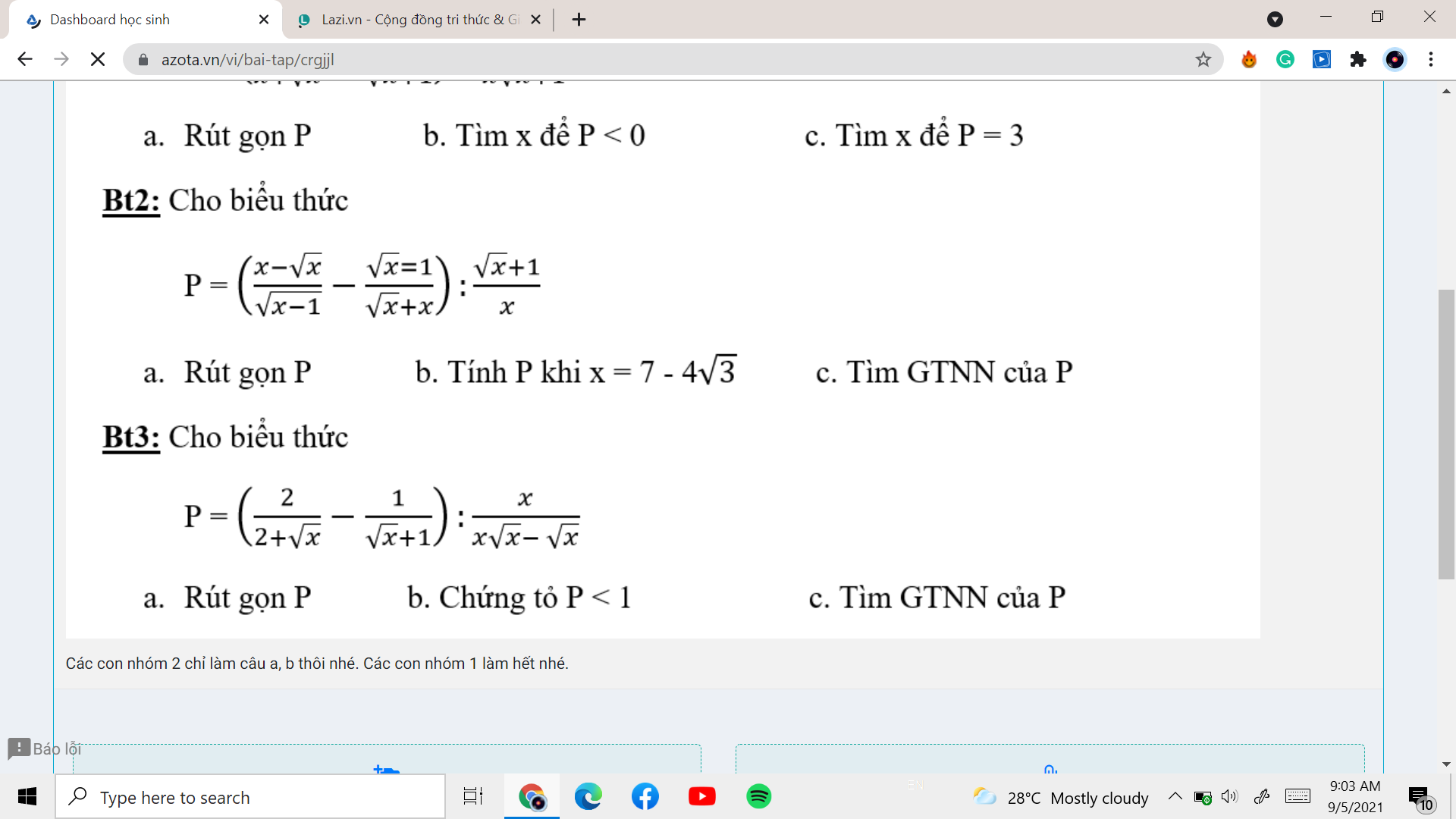
Bài 3:
a: Ta có: \(P=\left(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}+2}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}+1}\right):\dfrac{x}{x\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+2-\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-1}{\sqrt{x}+2}\)

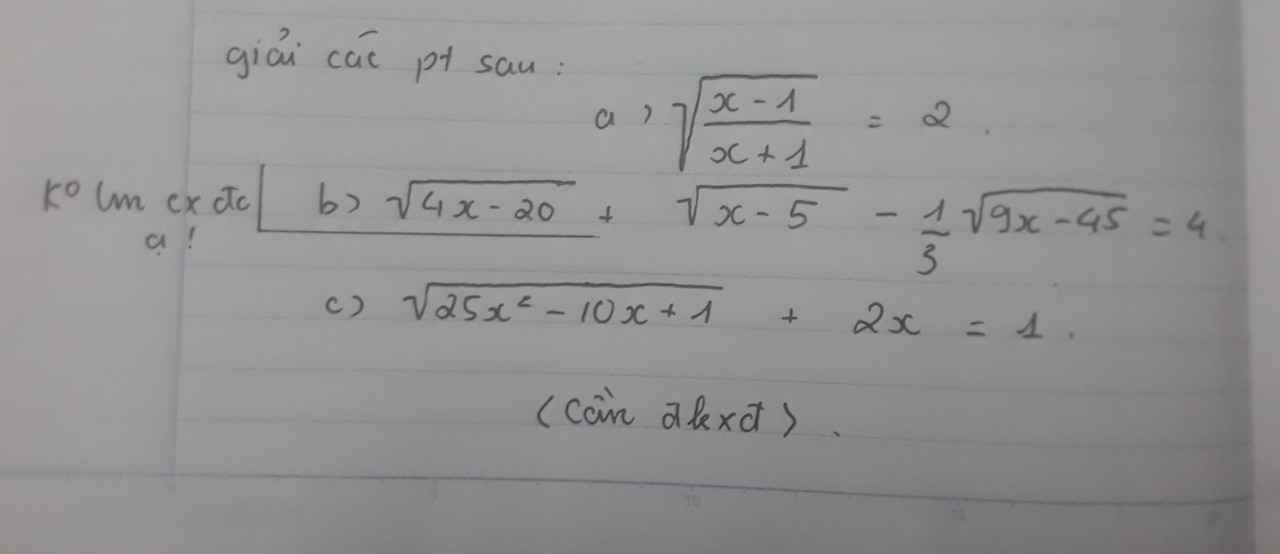
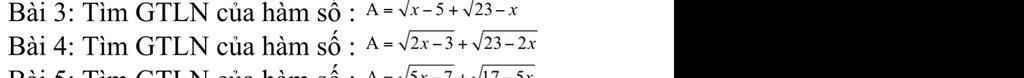


 bài 4 câu c thôi ạ
bài 4 câu c thôi ạ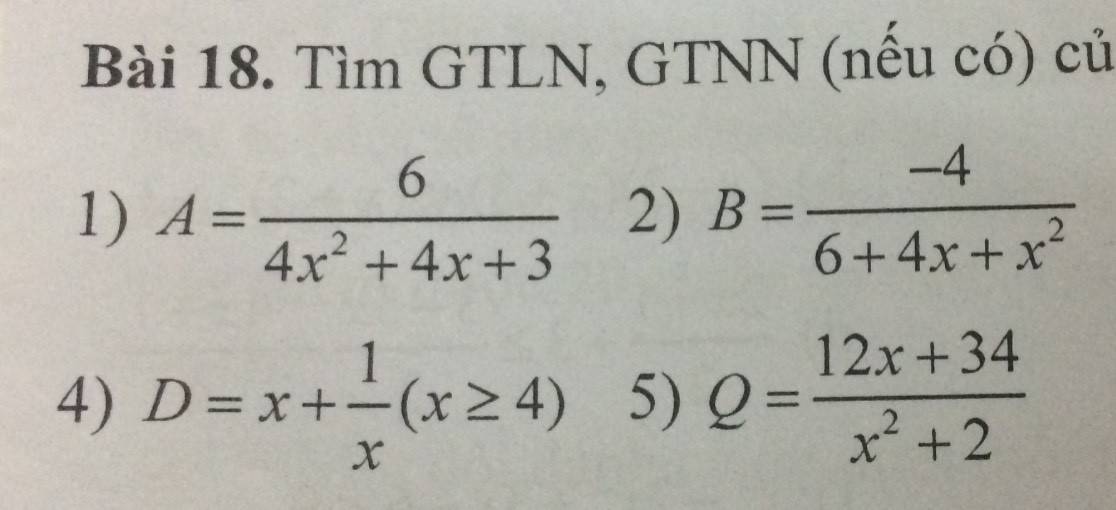

c. \(\left(x+2\right)^4-6\left(x+2\right)^2+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^4-\left(x+2\right)^2-5\left(x+2\right)^2+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^2\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-1\right]-5\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-1\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-1\right]\left[\left(x+2\right)^2-5\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2+\sqrt{5}\right)\left(x+2-\sqrt{5}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+3=0\\x+1=0\\x+2+\sqrt{5}=0\\x+2-\sqrt{5}=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=-1\\x=-\sqrt{5}-2\\x=\sqrt{5}-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-3;-1;-\sqrt{5}-2;\sqrt{5}-2\right\}\)
lm cho em câu 4 nữa đc ko