Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1;0\right\}\)
b: \(K=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1-x^2+2x-1+x^2-4x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+2003}{x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+2003}{x}=\dfrac{x+2003}{x}\)
c: Để K là số nguyên thì \(x\inƯ\left(2003\right)\)
hay \(x\in\left\{2003;-2003\right\}\)

a) ĐKXĐ \(\hept{\begin{cases}x-1\ne0\\x+1\ne0\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne-1\\x\ne0\end{cases}}\)
b)\(\left(\frac{x+1}{x-1}-\frac{x-1}{x+1}+\frac{x^2-4x-1}{x^2-1}\right)\frac{x+2003}{x}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2+x^2-4x-1}{\left(x-1\right).\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x+2003}{x}\)
\(\frac{\left(x+1-x+1\right)\left(x+1+x-1\right)+x^2-4x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x+2003}{x}\)
\(\frac{4x+x^2-4x-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x+2003}{x}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x+2003}{x}=\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{x+2003}{x}\)
\(=\frac{x+2003}{x}\)
c) Ta có \(K=\frac{x+2003}{x}\)
Để K nguyên thì x + 2003 ⋮ x
Ta có x ⋮ x => 2003 ⋮ x
=> x thuộc Ư(2003) = { 1; -1; 2003; -2003 }
Vậy khi x thuộc { 1; -1; 2003; -2003 } thì K nguyên

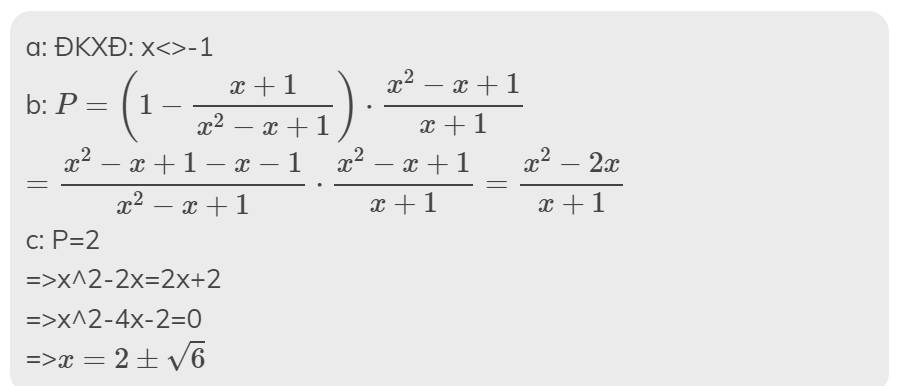
a: ĐKXĐ: x<>-1
b: \(P=\left(1-\dfrac{x+1}{x^2-x+1}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x+1-x-1}{x^2-x+1}\cdot\dfrac{x^2-x+1}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{x+1}\)
c: P=2
=>x^2-2x=2x+2
=>x^2-4x-2=0
=>\(x=2\pm\sqrt{6}\)

a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{-\dfrac{1}{2};\dfrac{1}{2};-2\right\}\)
b: \(B=\dfrac{4x^2+4x+1-4-4x^2+4x-1}{\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{2x+1}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{8x-4}{2x-1}\cdot\dfrac{1}{x+2}=\dfrac{4}{x+2}\)

a) Biểu thức A xác định `<=>x^2-1 ne 0 <=> (x-1)(x+1) ne 0 <=> x ne +-1`
b) `A=(x^2-3x-4)/(x^2 -1) = (x^2+x-4x-4)/(x^2-1) = (x(x+1)-4(x+1))/(x^2-1)`
`= ((x+1)(x-4))/((x+1)(x-1))=(x-4)/(x-1)`
c) `A` là số nguyên `<=> (x-4) vdots\ (x-1)`
`<=>[(x-1)-3] vdots\ (x-1)`
`<=> -3\ vdots\ (x-1)`
`<=> (x-1)\ in\ Ư(-3)`
`<=>(x-1)\ in\ {-3;-1;3;1}`
`<=>x\ in\ {-2;0;4;2}`
Vậy...
a: ĐKXĐ: x<>1; x<>-1
b: \(A=\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{x-4}{x-1}\)
c: Để A là số nguyên thì x-1-3 chia hết cho x-1
=>\(x-1\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{2;0;4;-2\right\}\)

a) Phân thức A được xác định khi: \(x^2-1\ne0\Rightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\ne0\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+1\ne0\\x-1\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne1\\x\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vây ĐKXĐ của A là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne1\\x\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
b)Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)}\)
Vậy \(A=\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne1\\x\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) Ta có A=2 <-> \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}=2\Leftrightarrow x+1=2\left(x-1\right)\Leftrightarrow x+1=2x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1-2x+2=0\Leftrightarrow3-x=0\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy khi x=3 thì A=2