
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}< \dfrac{1}{3}\left(đk:x\ne1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x-9< x-1\Leftrightarrow5x< 8\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{8}{5}\) và ĐK \(x\ne1\)
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{x-1}>\dfrac{1}{3}\left(đk:x\ne1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 6x-9\Leftrightarrow5x>8\Leftrightarrow x>\dfrac{8}{5}\) và ĐK \(x\ne1\)

\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

\(\dfrac{x}{2x-6}-\dfrac{x}{2x+2}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\left(ĐKXĐ:x\ne-1,x\ne3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{2\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x}{2\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}-\dfrac{x\left(x-3\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{2x\cdot2}{2\left(x+1\right)\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-x\left(x-3\right)=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x=4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-x^2+3x-4x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=0\)
Phương trình có vô số nghiệm , trừ x = -1,x = 3
Vậy ...
\(\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< \dfrac{9x+1}{3}-\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12\cdot\dfrac{12x+1}{12}< 12\cdot\dfrac{9x+1}{3}-12\cdot\dfrac{8x+1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 4\left(9x+1\right)-3\left(8x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 36x+4-24x-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x+1< 12x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-12x< 1-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x< 0\)
Vậy S = {x | x \(\in R\)}

a) |3x| = x + 6 (1)
Ta có 3x = 3x khi x ≥ 0 và 3x = -3x khi x < 0
Vậy để giải phương trình (1) ta quy về giải hai phương trình sau:
+ ) Phương trình 3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x ≥ 0
Ta có: 3x = x + 6 ⇔ 2x = 6 ⇔ x = 3 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = 3 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
+ ) Phương trình -3x = x + 6 với điều kiện x < 0
Ta có -3x = x + 6 ⇔ -4x + 6 ⇔ x = -3/2 (TMĐK)
Do đó x = -3/2 là nghiệm của phương trình (1).
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình đã cho S = {3; -3/2}
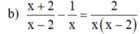
ĐKXĐ: x ≠ 0, x ≠ 2
Quy đồng mẫu hai vễ của phương trình, ta được:
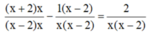
![]()
![]()
![]()
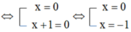
![]()
Vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là S = {-1}
c) (x + 1)(2x – 2) – 3 > –5x – (2x + 1)(3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 2x + 2x – 2 – 3 > –5x – (6x – 2x2 + 3 – x)
⇔ 2x2 – 5 ≥ –5x – 6x + 2x2 – 3 + x
⇔ 10x ≥ 2 ⇔ x ≥ 1/5
Tập nghiệm: S = {x | x ≥ 1/5}

a: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{x-2}=\dfrac{2x-1}{x-2}-\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{x-2}\)
=>3=2x-1-x^2+2x
=>3=-x^2+4x-1
=>x^2-4x+1+3=0
=>x^2-4x+4=0
=>x=2(loại)
b: =>(x+2)(2x-4)=x(2x+3)
=>2x^2-4x+4x-8=2x^2+3x
=>3x=-8
=>x=-8/3(nhận)

\(\left(x-1\right)^3-\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x-5\right)+\left(2x-3\right)^3-\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x-5\right)+\left(3x-5\right)^3-\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\left(x-1\right)^2-\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x-5\right)\right)+\left(2x-3\right)\left(\left(2x-3\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-5\right)\right)+\left(3x-5\right)\left(\left(3x-5\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-3\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(7-5x\right)+\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)^2+\left(3x-5\right)\left(x-2\right)\left(7x-11\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\left(x-1\right)\left(7-5x\right)+\left(2x-3\right)\left(x-2\right)+\left(3x-5\right)\left(7x-11\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(18x^2-63x+54\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\18x^2-63x+54=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
aGiải phương trình |x-1|+|x-2|=|2x-3|
b)Giải phương trình 1/(x−2 )+ 2/(x−3) − 3/(x−5) = 1/(x^2 −5x+6)


a: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{y+5}{y\left(y-5\right)}-\dfrac{y-5}{2y\left(y+5\right)}=\dfrac{y+25}{2\left(y-5\right)\left(y+5\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(y+5\right)^2-\left(y-5\right)^2=y^2+25y\)
=>\(2y^2+20y+50-y^2+10y-25=y^2+25y\)
=>30y+25=25y
=>5y=-25
=>y=-5(loại)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)+x\left(x-3\right)=4x\)
=>x^2+x+x^2-3x-4x=0
=>2x^2-6x=0
=>2x(x-3)=0
=>x=0(nhận) hoặc x=3(loại)
c: =>x^2-9-6(2x+7)=-13(x+3)
=>x^2-9-12x-42+13x+39=0
=>x^2+x-6=0
=>(x+3)(x-2)=0
=>x=2(nhận) hoặc x=-3(loại)

a: |x+9|=2
=>x+9=2 hoặc x+9=-2
=>x=-7 hoặc x=-11
b: |2x-3|=x-3
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\\left(2x-3-x+3\right)\left(2x-3+x-3\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=3\)

\(\left(x-2\right)^3\)+\(\left(x+1\right)^3\)+\(\left(1-2x\right)^3\) = 0
\(x^3-6x^2+12x-8+x^3+3x^2+3x+1+1-6x+12x^2-8x^3\text{=}0\)
\(-6x^3+9x^2+9x-6\text{=}0\)
\(\left(-6x^3-6\right).\left(9x^2+9x\right)\text{=}0\)
\(6\left(-x^2-1\right)+9x\left(x+1\right)\text{=}0\)
\(6\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)+9x\left(x+1\right)\text{=}0\)
\([6(x-1)+9x].\left(x+1\right)\text{=}0\)
\(\left(6x-6+9x\right).\left(x+1\right)\text{=}0\)
\(\left(15x-6\right)\left(x+1\right)\text{=}0\)
\(TH1:15x-6\text{=}0\)
\(15x\text{=}6\)
\(x\text{=}\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(TH2:x+1\text{=}0\)
\(x\text{=}-1\)
Vậy phương trình một ẩn x có tập nghiệm S \(\in(\dfrac{2}{5};-1)\)
bạn mở rộng, bỏ ngoặc, rút gọn có đa thức 6x3 . ... Đa thức này có nghiệm là - 1, nhẩm ra , bạn chia đa thức 6 x3 .... với (x + 1)
\(\left(x-3\right)^3=\left(2x+1\right)^3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-3=2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-4\)