
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x}=\dfrac{1}{x}\left(đk:x\ne0,x\ne2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)x-2}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x^2-2x}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-2=x^2-2x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=2\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Cho mình sửa lại nhé:
\(\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}-\dfrac{2}{x^2-2x}=\dfrac{1}{x}\left(đk:x\ne0,x\ne2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)x-2}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x-2}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x-2=x-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=-1\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\dfrac{1}{a}-\dfrac{a-4}{4a}=6\)
\(ĐK:x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4-\left(a-4\right)}{4a}=\dfrac{24a}{4a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-\left(a-4\right)=24a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4-a+4=24a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8=25a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a=\dfrac{8}{25}\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{\dfrac{8}{25}\right\}\)

`[x-4]/[x+4]-x/[x-4]=[3x-14]/[x^2-16]` `ĐK: x \ne +-4`
`<=>[(x-4)^2-x(x+4)]/[(x-4)(x+4)]=[3x-14]/[(x-4)(x+4)]`
`=>x^2-8x+16-x^2-4x=3x-14`
`<=>3x+8x+4x=16+14`
`<=>15x=30`
`<=>x=2` (t/m)
Vậy `S={2}`
`(x - 4)/(x + 4) - x/(x - 4) = (3x - 14)/(x^2 - 16)`
`=>` `x = 2`

<=>(x+1)3+x=x3+3x2+4x+1
=>x(x-1)2+5=x3-2x2+x+5
=>x3+3x2+4x+1=x3-2x2+x+5
=>x=\(\pm\frac{\sqrt{89}}{10}-\frac{3}{10}\)

Bài 8:
a: Khi a=1 thì phương trình sẽ là \(\left(1-4\right)x-12x+7=0\)
=>-3x-12x+7=0
=>-15x+7=0
=>-15x=-7
hay x=7/15
b: Thay x=1 vào pt, ta được:
\(a^2-4-12+7=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-3\right)\left(a+3\right)=0\)
hay \(a\in\left\{3;-3\right\}\)
c: Pt suy ra là \(\left(a^2-16\right)x+7=0\)
Để phương trình đã cho luôn có một nghiệm duy nhất thì (a-4)(a+4)<>0
hay \(a\notin\left\{4;-4\right\}\)

Ta có:
(2 - 3x)(x + 8) = (3x - 2)(3 - 5x)
⇔ (2 - 3x)(x + 8) - (3x - 2)(3 - 5x) = 0
⇔ (2 - 3x)(x + 8) + (2 - 3x)(3 - 5x) = 0
⇔ (2 - 3x)(x + 8 + 3 - 5x) = 0
⇔ (2 - 3x)(11 - 4x) = 0
⇔ 2 - 3x = 0 hay 11 - 4x = 0
⇔ 2 = 3x hay 11 = 4x
⇔ x = \(\dfrac{2}{3}\) hay x = \(\dfrac{11}{4}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của pt S = \(\left\{\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{11}{4}\right\}\)
<=> (2-3x ) (x+8) + (2-3x ) (3-5x)=0
<=> (2-3x ) ( x+8 + 3-5x ) =0
<=> (2-3x ) ( 11 - 4x ) = 0
=> 2-3x =0 hoặc 11-4x =0
3x = 2 4x =11
x = 2/3 x = 11/4

c: ĐKXĐ: x<>8
\(\dfrac{3}{2x-16}+\dfrac{3x-20}{x-8}+\dfrac{1}{8}=\dfrac{13x-102}{3x-24}\)
=>\(\dfrac{9}{6\left(x-8\right)}+\dfrac{18x-120}{6\left(x-8\right)}-\dfrac{26x-204}{6\left(x-8\right)}=\dfrac{-1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{18x-111-26x+204}{6\left(x-8\right)}=\dfrac{-1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{-8x+93}{6x-48}=\dfrac{-1}{8}\)
=>\(\dfrac{8x-93}{6x-48}=\dfrac{1}{8}\)
=>8(8x-93)=6x-48
=>64x-744-6x+48=0
=>58x=696
=>x=12
d: ĐKXĐ: x<>1; x<>-1
\(\dfrac{6}{x^2-1}+5=\dfrac{8x-1}{4x+4}+\dfrac{12x-1}{4x-4}\)
=>\(\dfrac{24}{4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{20\left(x^2-1\right)}{4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(8x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)+\left(12x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
=>8x^2-9x+1+12x^2+12x-x-1=24+20x^2-20
=>20x^2+2x=20x^2+4
=>2x=4
=>x=2(loại)
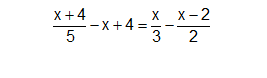

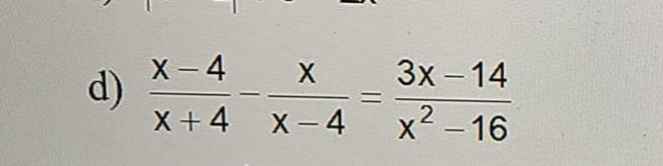
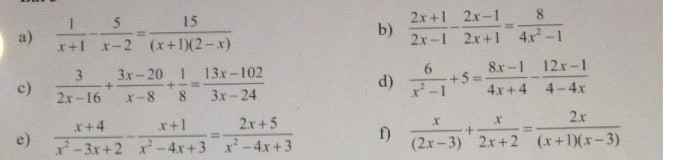
\(\dfrac{x+4}{5}-x+4=\dfrac{x}{3}-\dfrac{x-2}{2}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{x+4}{5}-\dfrac{5x}{5}+\dfrac{20}{5}=\dfrac{2x}{6}-\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{6}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\dfrac{-4x+24}{5}=\dfrac{-x+6}{6}\Leftrightarrow6\cdot\left(-4x+24\right)=5\cdot\left(-x+6\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)-24x+144=-5x+30\(\Leftrightarrow\)-24x+5x=30-144\(\Leftrightarrow\)-19x=-114\(\Leftrightarrow\)x=6