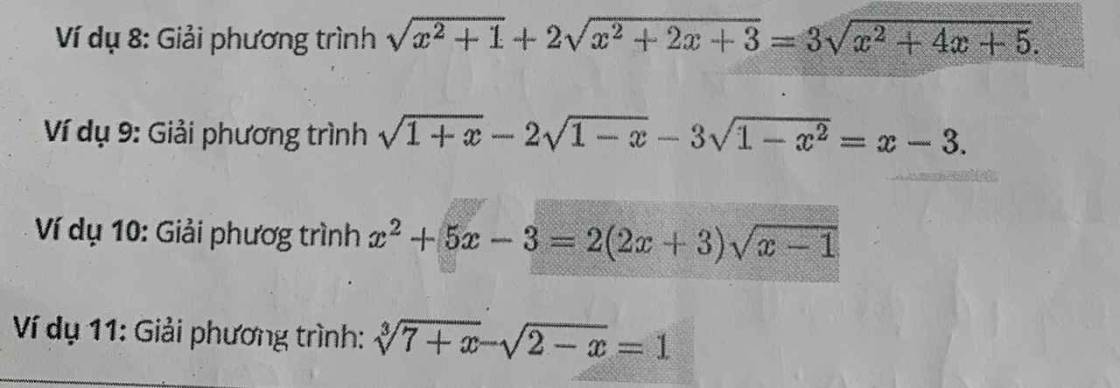Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


1. \(\dfrac{4x}{4x^2-8x+7}+\dfrac{3x}{4x^2-10x+7}=1\)
Dễ thấy \(x=0\) ko phải là nghiệm của pt
Chia tử và mẫu cho x, ta được:
\(\dfrac{4}{4x-8+\dfrac{7}{x}}+\dfrac{3}{4x-10+\dfrac{7}{x}}=1\) (*)
Đặt \(t=4x+\dfrac{7}{x}-8\) thì:
(*) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4}{t}+\dfrac{3}{t-2}=1\)
Quy đồng lên tìm được t, sau đó dễ dàng tìm được x.


câu 1:
a2+b2+c2+42 = 2a+8b+10c
<=> a2-2a+1+b2 -8b+16+c2-10c+25=0
<=> (a-1)2+(b-4)2+(c-5)2=0
<=>a=1 và b=4 và c=5
=> a+b+c = 10
ta có 2(a2+b2)=5ab
<=> 2a2+2b2-5ab=0
<=> 2a2-4ab-ab+2b2=0
<=> 2a(a-2b)-b(a-2b)=0
<=> (a-2b)(2a-b)=0
<=> a=2b(thỏa mãn)
hoặc b=2a( loại vì a>b)
với a=2b =>P=5b/5b=1

Ta thừa nhận định lý f(x) chia hết cho x-a thì f(a) =0 ( mình đang vội khỏi chứng minh nhé, nếu thắc mắc phiền bạn xem SGK 9 nha)
Thay 1 vào x, ta có
f(x) =14+12+a=0
2+a=0 suy ra a=-2

câu 14 : chọn đáp án \(B\) vì \(\left|\overrightarrow{b}\right|=\sqrt{\left(1\right)^2+\left(-1\right)^2}=\sqrt{2}\ne0\)
câu 18 : ta có tọa độ trọng tâm \(G\) của tam giác \(ABC\)
là \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_G=\dfrac{x_A+x_B+x_C}{3}\\y_G=\dfrac{y_A+y_B+y_C}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_G=\dfrac{2+3-7}{3}\\y_G=\dfrac{1-1+3}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_G=\dfrac{-2}{3}\\y_G=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy tọa độ trọng tâm \(G\) là \(G\left(\dfrac{-2}{3};1\right)\) \(\Rightarrow\) chọn đáp án \(B\)
câu 19 : đặt tọa độ của điểm \(D\) là \(D\left(x_D;y_D\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(1;-7\right)\\\overrightarrow{DC}=\left(4-x_D;3-y_D\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
ta có \(ABCD\) là hình bình hành \(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{DC}\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1=4-x_D\\-7=3-y_D\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_D=3\\y_D=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
vậy tọa độ điểm \(D\) là \(D\left(3;10\right)\) \(\Rightarrow\) chọn đáp án \(A\)




8.
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=a>0\\\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}=b>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=x^2+1\)
Pt trở thành:
\(\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}+2a=3b\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2a^2-b^2}=3b-2a\)
\(\Rightarrow2a^2-b^2=4a^2-12ab+9b^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2-12ab+10b^2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=b\\a=5b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\\\sqrt{x^2+2x+3}=5\sqrt{x^2+4x+5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2x+3=x^2+4x+5\\x^2+2x+3=25\left(x^2+4x+5\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\24x^2+98x+122=0\left(vn\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
9.
ĐKXĐ: \(-1\le x\le1\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=a\ge0\\\sqrt{1-x}=b\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow a^2+2b^2=3-x=-\left(x-3\right)\)
Pt trở thành:
\(a-2b-3ab=-\left(a^2+2b^2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+a^2-3ab+2b^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-2b+\left(a-b\right)\left(a-2b\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a-2b\right)\left(a-b+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=2b\\a+1=b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{1+x}=2\sqrt{1-x}\\\sqrt{1+x}+1=\sqrt{1-x}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}1+x=4\left(1-x\right)\\x+2+2\sqrt{1+x}=1-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5x=3\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{3}{5}\\-1-2x=2\sqrt{1+x}\left(1\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Xét (1) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1-2x\ge0\\\left(-1-2x\right)^2=4\left(1+x\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^2=\dfrac{3}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\)
Vậy \(x=\left\{\dfrac{3}{5};-\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right\}\)