
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)Đk:\(sinx\ne1\)
Pt\(\Leftrightarrow sin^2x+sinx=-2\left(sinx-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin^2x+3sinx-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sinx=\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{17}}{2}\left(tm\right)\\sinx=\dfrac{-3-\sqrt{17}}{2}\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=arcc.sin\left(\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{17}}{2}\right)+k2\pi\\x=\pi-arc.sin\left(\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{17}}{2}\right)+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)(\(k\in Z\))
b)Đk:\(sinx\ne1\)
Pt \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1-2sin^2x+sinx}{sinx-1}+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-\left(sinx-1\right)\left(2sinx+1\right)}{sinx-1}+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2sinx+1\right)+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sinx=0\) (tm)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=k\pi,k\in Z\)
Vậy...

Để giải phương trình cos(2x) - sin(x) = 0, ta có thể sử dụng các công thức lượng giác để đưa phương trình về dạng phù hợp.
Bước 1: Sử dụng công thức cos(2x) = 2cos^2(x) - 1, phương trình trở thành 2cos^2(x) - 1 - sin(x) = 0.
Bước 2: Sử dụng công thức sin^2(x) + cos^2(x) = 1, ta có thể thay thế cos^2(x) bằng 1 - sin^2(x), phương trình trở thành 2(1 - sin^2(x)) - 1 - sin(x) = 0.
Bước 3: Giải phương trình 2 - 2sin^2(x) - 1 - sin(x) = 0.
Bước 4: Đặt sin(x) = t, phương trình trở thành 2 - 2t^2 - 1 - t = 0.
Bước 5: Rút gọn phương trình, ta có -2t^2 - t + 1 = 0.
Bước 6: Giải phương trình bậc hai trên, ta có thể sử dụng công thức hoặc phân tích thành nhân tử để tìm giá trị của t.
Bước 7: Giải phương trình -2t^2 - t + 1 = 0, ta tìm được hai giá trị t = -1 và t = 1/2.
Bước 8: Đặt sin(x) = -1 và sin(x) = 1/2, ta tìm được hai giá trị x = -π/2 và x = π/6.
Vậy, phương trình cos(2x) - sin(x) = 0 có hai nghiệm là x = -π/2 và x = π/6.
ĐKXĐ: 1-sin x<>0
=>sin x<>1
=>x<>pi/2+k2pi
cos2x/1-sinx=0
=>cos2x=0
=>2x=pi/2+kpi
=>x=pi/2+kpi/2
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(x\in\left\{pi+k2pi;\dfrac{3}{2}pi+k2pi;2pi+k2pi\right\}\)

ĐK: \(x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi;x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{2sin^2x+cos4x-cos2x}{\left(sinx-cosx\right)sin2x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2x+cos4x-cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2sin^2x-1+cos4x-cos2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos^22x-2cos2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cos2x=0\\cos2x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\\2x=k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x=k\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đối chiếu điều kiện ta được \(x=-\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\)


Đ á p á n B P T đ ã c h o t ư ơ n g đ ư ơ n g : 4 . cos 2 2 x + 8 sin 2 x - 7 = 0 ⇔ 4 . 1 - sin 2 2 x + 8 . sin 2 x - 7 = 0 ⇔ - 4 . sin 2 2 x + 8 . sin 2 x - 3 = 0 ⇔ sin 2 x = 1 2 ⇔ x = π 12 + k π ( k ∈ ℤ ) hoặc x = 5 π 12 + kπ ( k ∈ ℤ )

\(cos2x+cosx+1=sin2x+sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos^2x-sin^2x+cosx+cos^2x+sin^2x=2sinx.cosx+sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2cos^2x+cosx=2sinx.cosx+sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cosx\left(2cosx+1\right)=sinx\left(2cosx+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2cosx+1\right)\left(sinx-cosx\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2cosx+1=0\\sinx=cosx\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}cosx=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\tanx=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\pm\dfrac{\pi}{3}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left|cosx\right|-\left|sinx\right|-\left(\left|cosx\right|-\left|sinx\right|\right)\left(\left|cosx\right|+\left|sinx\right|\right)\sqrt{1+sin2x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\left|cosx\right|-\left|sinx\right|\right)\left(1-\left(\left|cosx\right|+\left|sinx\right|\right)\sqrt{1+sin2x}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left|cosx\right|=\left|sinx\right|\Leftrightarrow cos2x=0\left(1\right)\\\left(\left|cosx\right|+\left|sinx\right|\right)\sqrt{1+sin2x}=1\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
\(\left(2\right)\Leftrightarrow\left|cosx\right|+\left|sinx\right|=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{1+sin2x}}\) (với \(sin2x\ne-1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow1+2\left|sinx.cosx\right|=\dfrac{1}{1+sin2x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+\left|sin2x\right|=\dfrac{1}{1+sin2x}\)
TH1: \(-1< sin2x< 0\Rightarrow1-sin2x=\dfrac{1}{1+sin2x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1-sin^22x=1\Rightarrow sin2x=0\) (loại)
TH2: \(0\le sin2x\le1\Rightarrow1+sin2x=\dfrac{1}{1+sin2x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+sin2x=1\Leftrightarrow sin2x=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)
Vậy \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x=\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bạn tự tìm số giá trị nhé
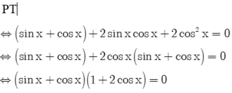

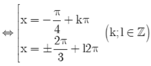
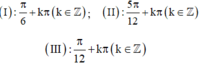
cos 2 x - sin x - 1 = 0 ⇔ 1 - 2 sin 2 x - sin x - 1 = 0 ⇔ sin x ( 2 sin x + 1 ) = 0