Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1.
Đặt \(x^2-2x+m=t\), phương trình trở thành \(t^2-2t+m=x\)
Ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x+m=t\\t^2-2t+m=x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-t\right)\left(x+t-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=t\\x=1-t\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=x^2-2x+m\\x=1-x^2+2x-m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-x^2+3x\\m=-x^2+x+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của \(y=-x^2+x+1\) và \(y=-x^2+3x\):
\(-x^2+x+1=-x^2+3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
Đồ thị hàm số \(y=-x^2+3x\) và \(y=-x^2+x+1\):
Dựa vào đồ thị, yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi \(m< \dfrac{5}{4}\)
Mà \(m\in\left[-10;10\right]\Rightarrow m\in[-10;\dfrac{5}{4})\)
Có cách nào lm bài này bằng cách lập bảng biến thiên k ạ

a: ĐKXĐ của A là x<>1; x<>-3
ĐKXĐ của B là x<>4
ĐKXĐ của C là x<>0; x<>2
ĐKXĐ của D là x<>3
ĐKXĐ của E là x<>0; x<>2
b: \(A=\dfrac{2x\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{2x}{x-1}\)
Để A=0 thì 2x=0
=>x=0
\(B=\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)^2}=\dfrac{x+4}{x-4}\)
Để B=0 thì x+4=0
=>x=-4
\(C=\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x+2}{x-2}\)
Để C=0 thì x+2=0
=>x=-2
\(D=\dfrac{\left(x+4\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)}=\dfrac{x+4}{x^2+3x+9}\)
Để D=0 thi x+4=0
=>x=-4
\(E=\dfrac{2x\left(x^2+2x+1\right)}{2x\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{x-2}\)
Để E=0 thì (x+1)^2=0
=>x=-1

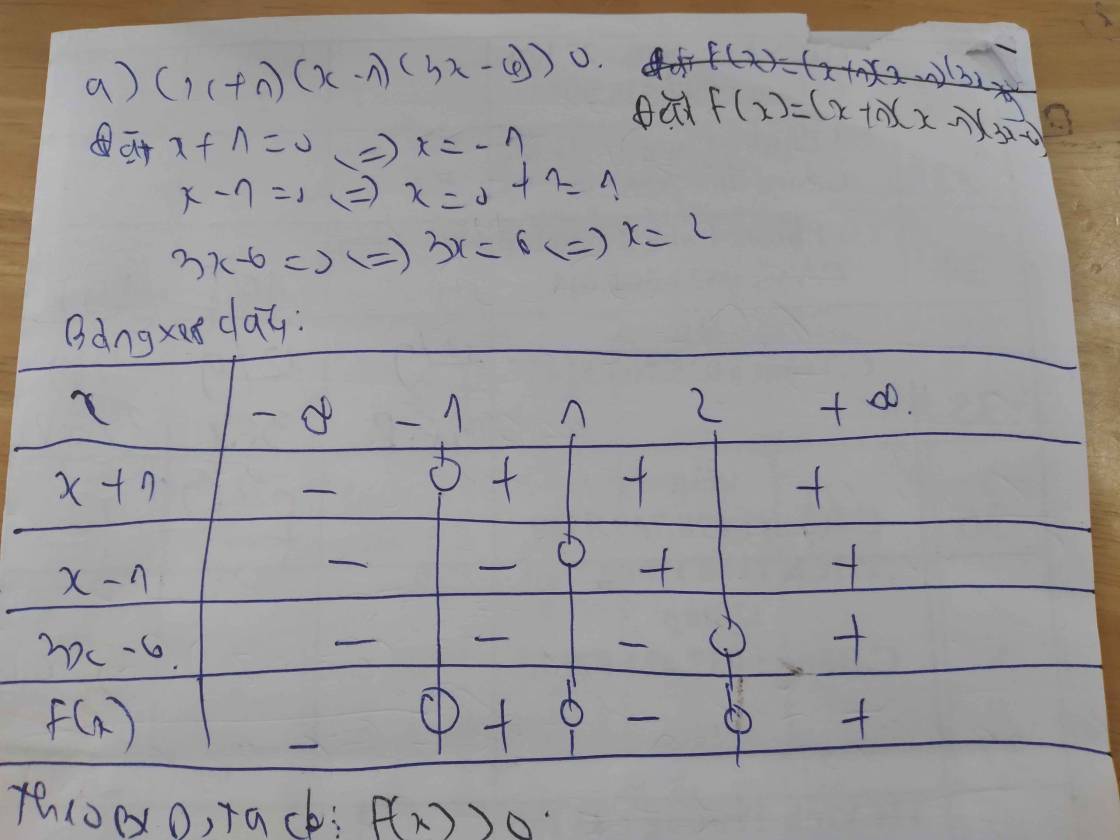
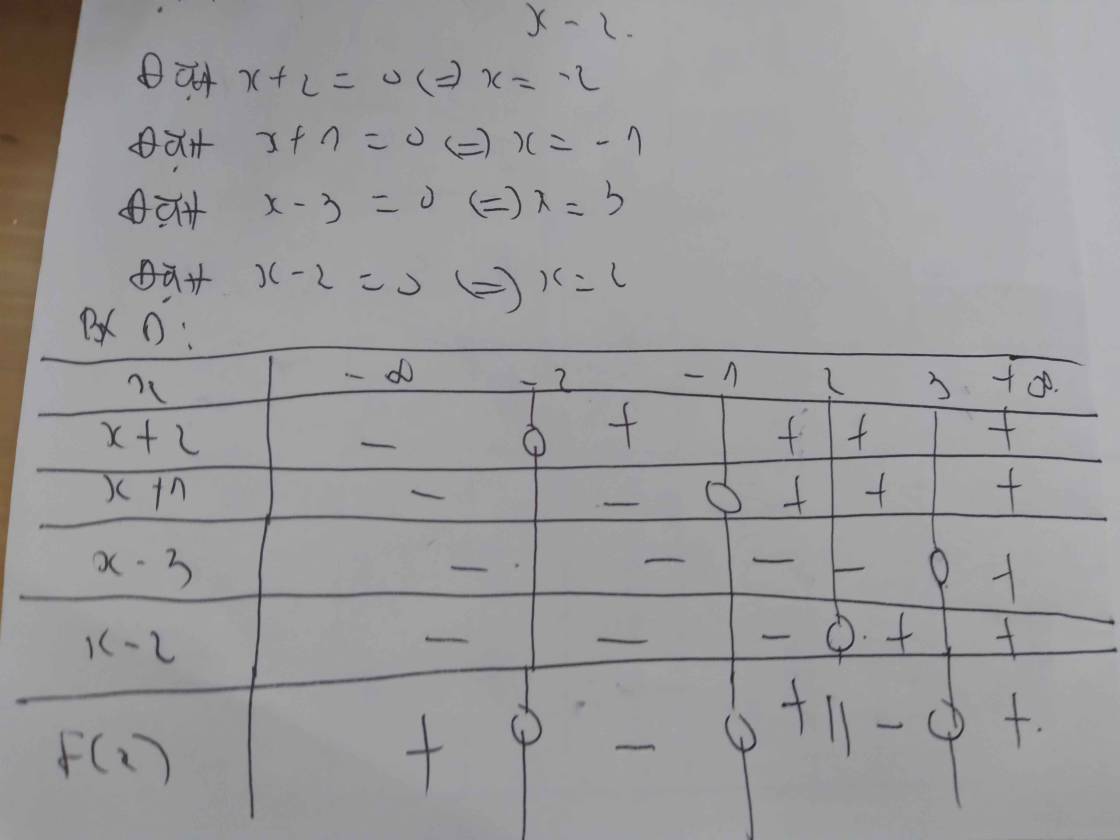
a) \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)\left(3x-6\right)>0\)
Lập bảng xét dấu ta được kết quả :
\(Bpt\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-1< x< 1\\x>2\end{matrix}\right.\)
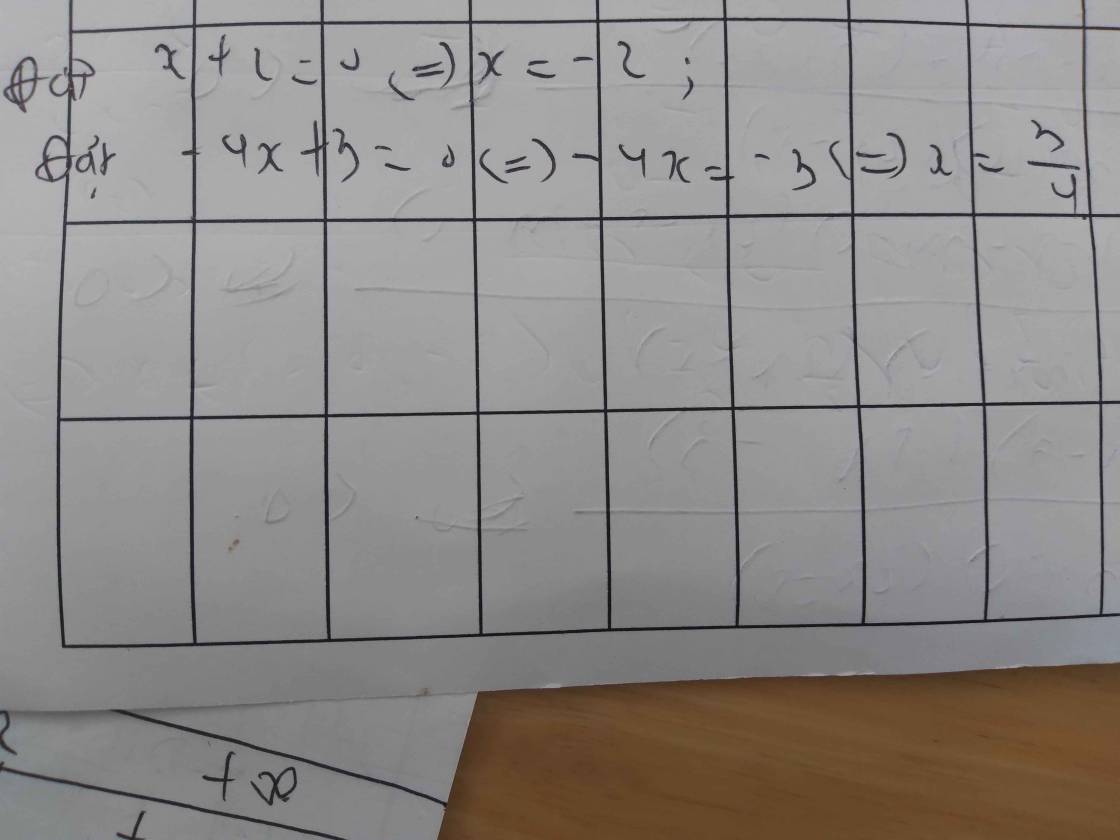
b) \(\dfrac{x+3}{x-2}\le0\)
Lập bảng xét dấu ta được kết quả :
\(Bpt\Leftrightarrow-3\le x< 2\)
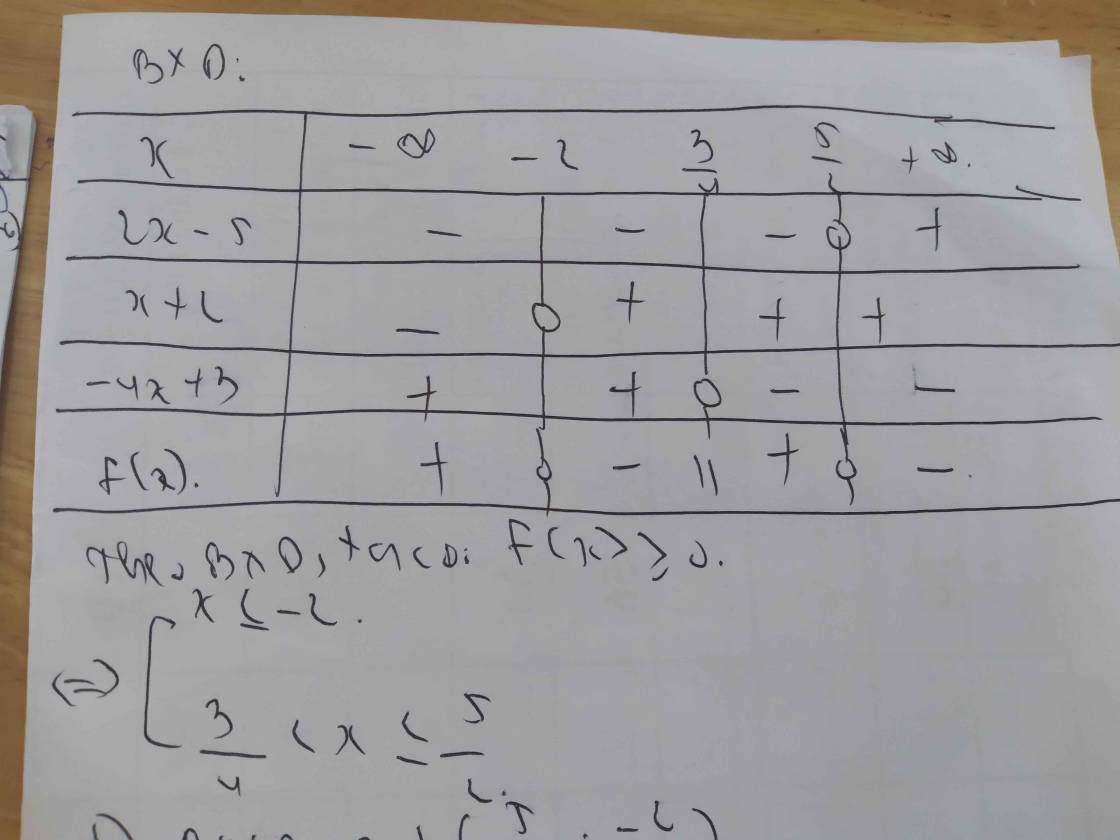
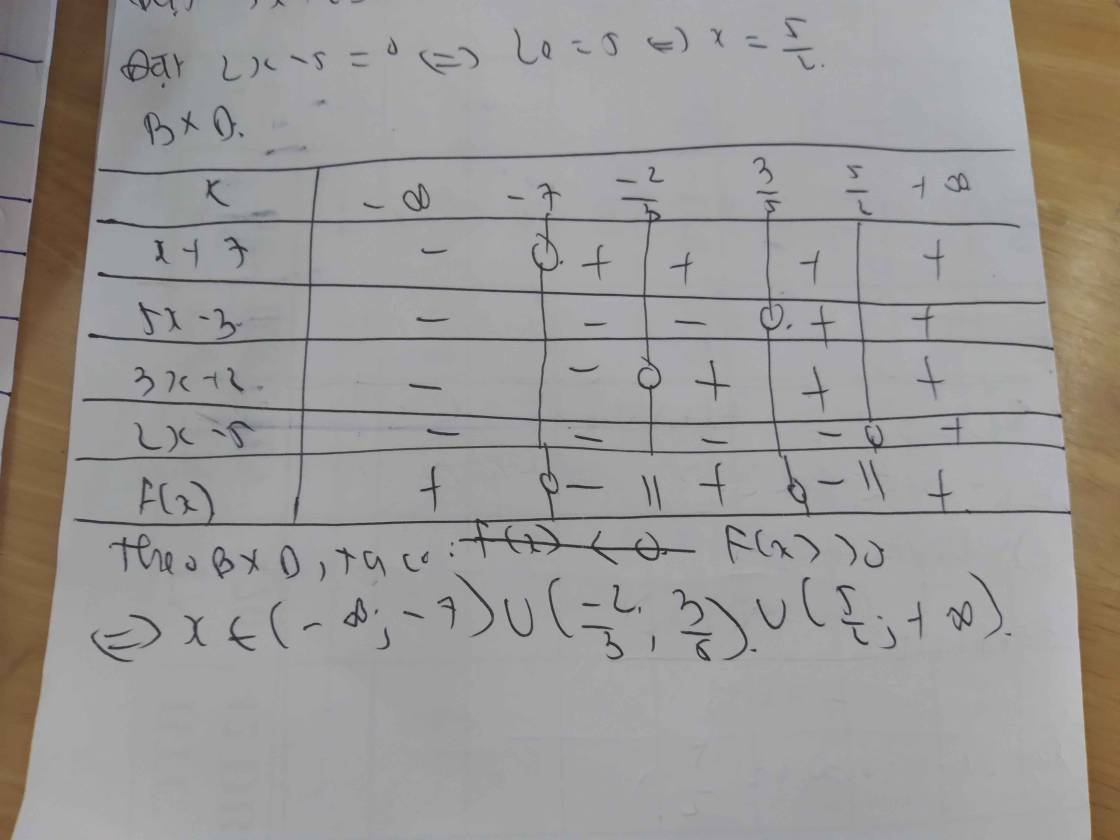
d) \(\dfrac{2x-5}{3x+2}< \dfrac{3x+2}{2x-5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-5}{3x+2}-\dfrac{3x+2}{2x-5}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2x-5\right)^2-\left(3x+2\right)^2}{\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-5\right)}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2x-5+3x+2\right)\left(2x-5-3x-2\right)}{\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-5\right)}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-\left(5x-3\right)\left(x+7\right)}{\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x-5\right)}< 0\)
Lập bảng xét dấu ta được kết quả :
\(Bpt\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-7< x< -\dfrac{2}{3}\\\dfrac{5}{3}< x< \dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Điều kiện: x 3 − 4 x 2 + 5 x − 2 ≥ 0 2 − x ≥ 0 ⇔ x − 1 2 x − 2 ≥ 0 x ≤ 2 ⇔ x = 1 x = 2
Thay x = 1 và x = 2 vào phương trình thấy chỉ có x = 1 thỏa mãn.
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm duy nhất.
Đáp án cần chọn là: B

1.
\(x^4-6x^2-12x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-2x^2+1-4x^2-12x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)^2=\left(2x+3\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-1=2x+3\\x^2-1=-2x-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2-2x-4=0\\x^2+2x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\pm\sqrt{5}\)
3.
ĐK: \(x\ge-9\)
\(x^4-x^3-8x^2+9x-9+\left(x^2-x+1\right)\sqrt{x+9}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x+9}+x^2-9\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+9}+x^2-9=0\left(1\right)\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x+9}=t\left(t\ge0\right)\Rightarrow9=t^2-x\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow t+x^2+x-t^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+t\right)\left(x-t+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-t\\x=t-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\sqrt{x+9}\\x=\sqrt{x+9}-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

a, ĐKXĐ : \(D=R\)
BPT \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+5x+4< 5\sqrt{x^2+5x+4+24}\)
Đặt \(x^2+5x+4=a\left(a\ge-\dfrac{9}{4}\right)\)
BPTTT : \(5\sqrt{a+24}>a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+24\ge0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a\ge0\\25\left(a+24\right)>a^2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-24\le a< 0\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a^2-25a-600< 0\\a\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}-24\le a< 0\\0\le a< 40\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-24\le a< 40\)
- Thay lại a vào ta được : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+5x-36< 0\\x^2+5x+28\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9< x< 4\)
Vậy ....
b, ĐKXĐ : \(x>0\)
BĐT \(\Leftrightarrow2\left(\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}\right)< x+\dfrac{1}{4x}+1\)
- Đặt \(\sqrt{x}+\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x}}=a\left(a\ge\sqrt{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2=x+\dfrac{1}{4x}+1\)
BPTTT : \(2a\le a^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a\le0\\a\ge2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\ge2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2\ge4\)
- Thay a vào lại BPT ta được : \(x+\dfrac{1}{4x}-3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-12x+1\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=(0;\dfrac{3-2\sqrt{2}}{2}]\cup[\dfrac{3+2\sqrt{2}}{2};+\infty)\)
Vậy ...

Đặt x2−2x+m=tx2−2x+m=t, phương trình trở thành t2−2t+m=xt2−2t+m=x
Ta có hệ {x2−2x+m=tt2−2t+m=x{x2−2x+m=tt2−2t+m=x
⇒(x−t)(x+t−1)=0⇒(x−t)(x+t−1)=0
⇔[x=tx=1−t⇔[x=tx=1−t
⇔[x=x2−2x+mx=1−x2+2x−m⇔[x=x2−2x+mx=1−x2+2x−m
⇔[m=−x2+3xm=−x2+x+1⇔[m=−x2+3xm=−x2+x+1
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của y=−x2+x+1y=−x2+x+1 và y=−x2+3xy=−x2+3x:
−x2+x+1=−x2+3x−x2+x+1=−x2+3x
⇔x=12⇒y=54⇔x=12⇒y=54
Đồ thị hàm số y=−x2+3xy=−x2+3x và y=−x2+x+1y=−x2+x+1:


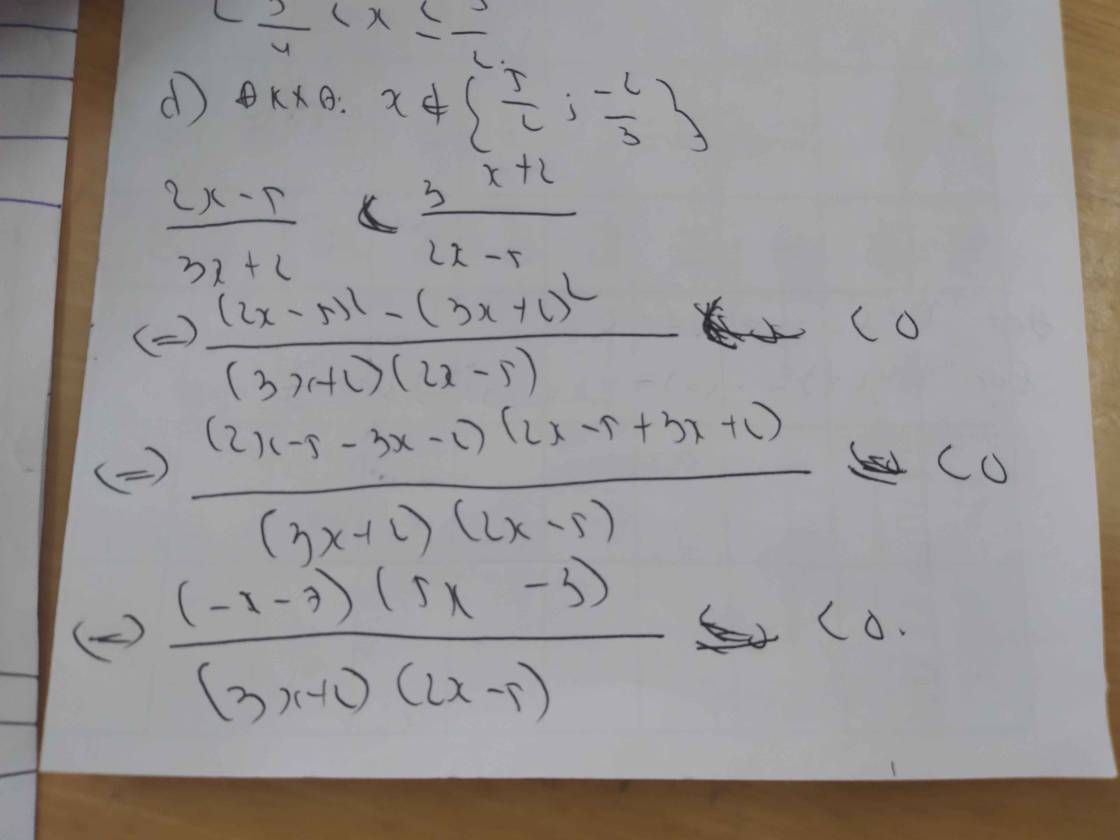

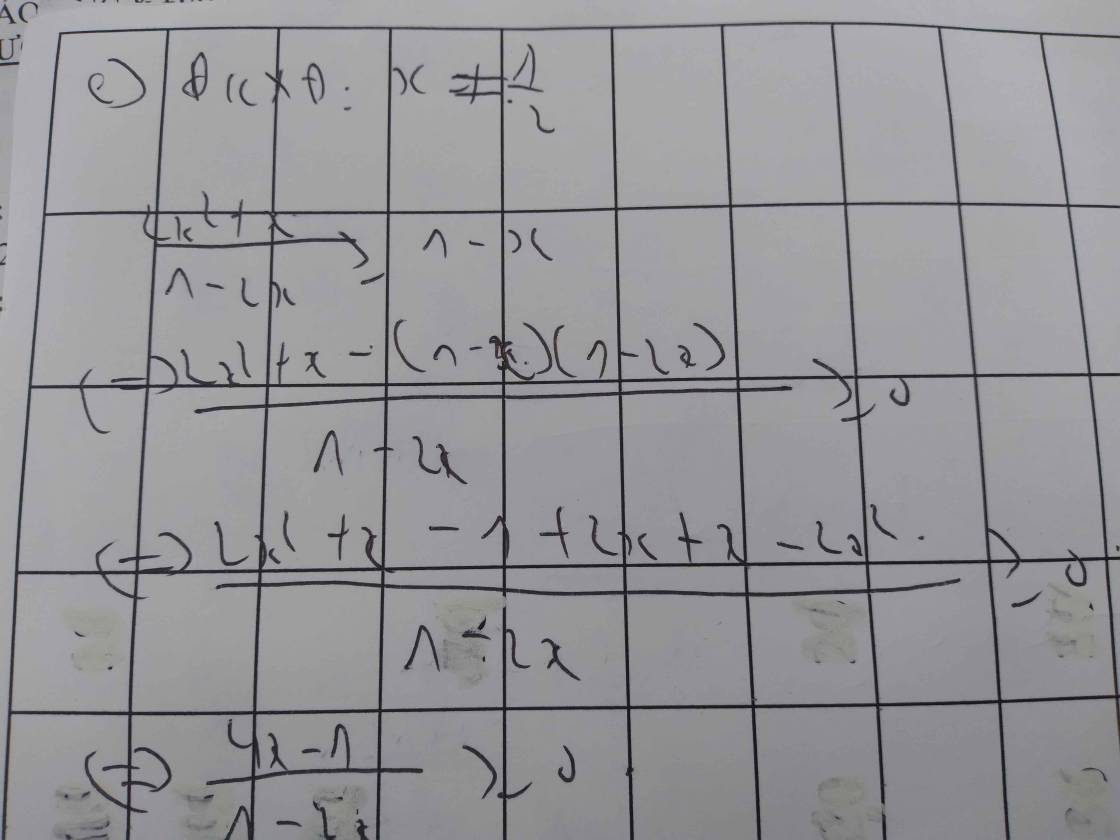

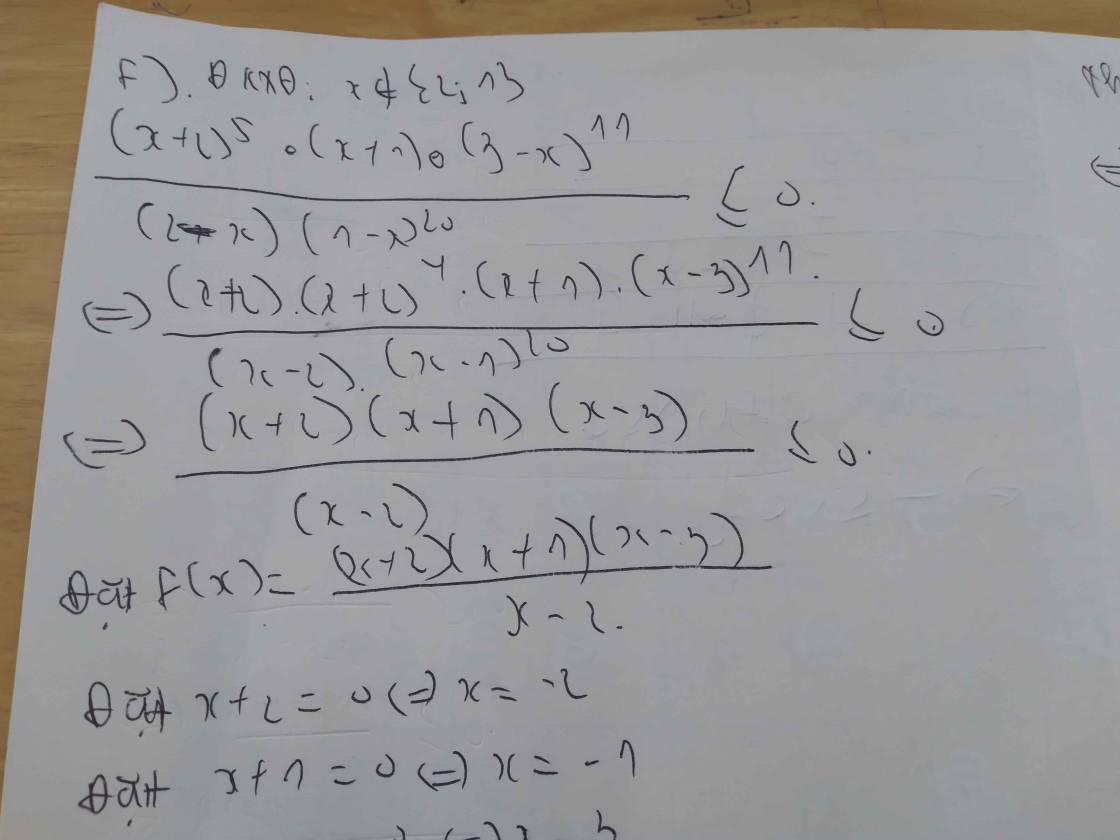
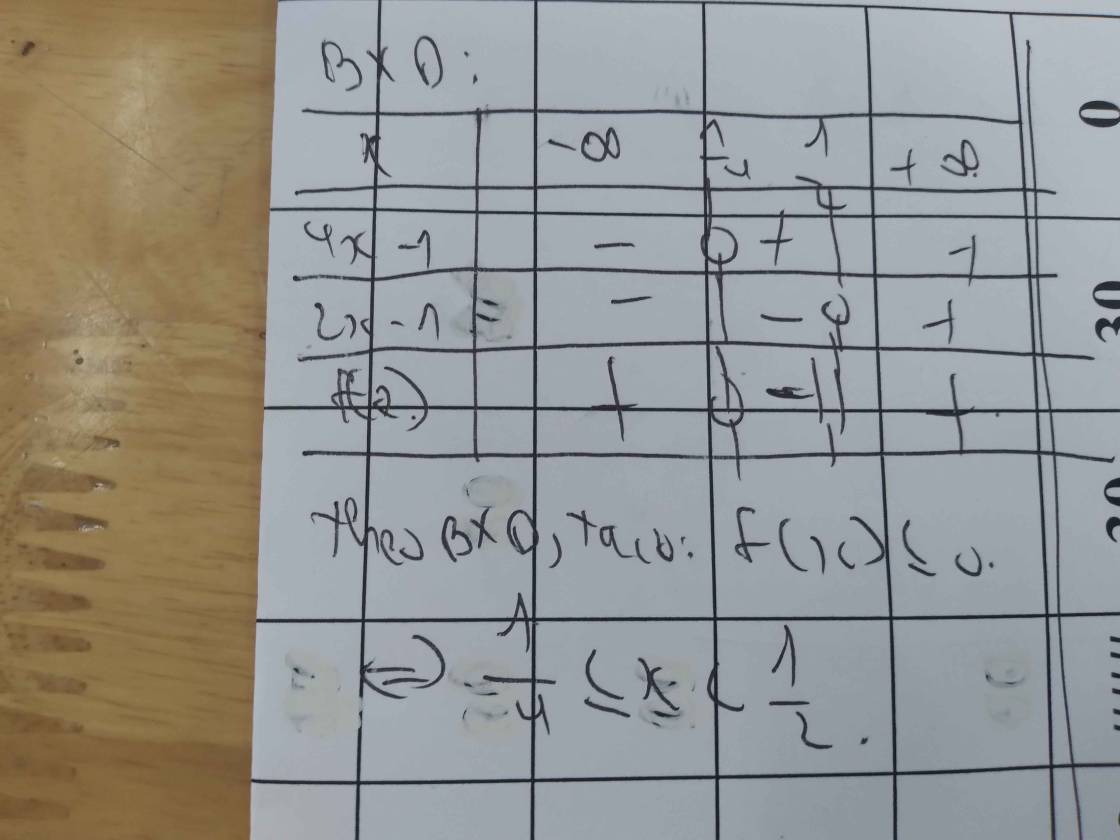


mấy bài này , e ko chắc lắm đâu , coi lại rồi xem có j sai k nhé ! Sai thì ns vs e để e còn sửa
a) \(pt\Leftrightarrow14x^2-6x-8=0\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-1\right)\left(7x+4\right)=0\)
b) \(-3x^4-10x^3+32x^2=0\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(2-x\right)\left(3x+16\right)=0\)
c) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^5-5x^4-5\right)}{x^4-x+1}=0\)