
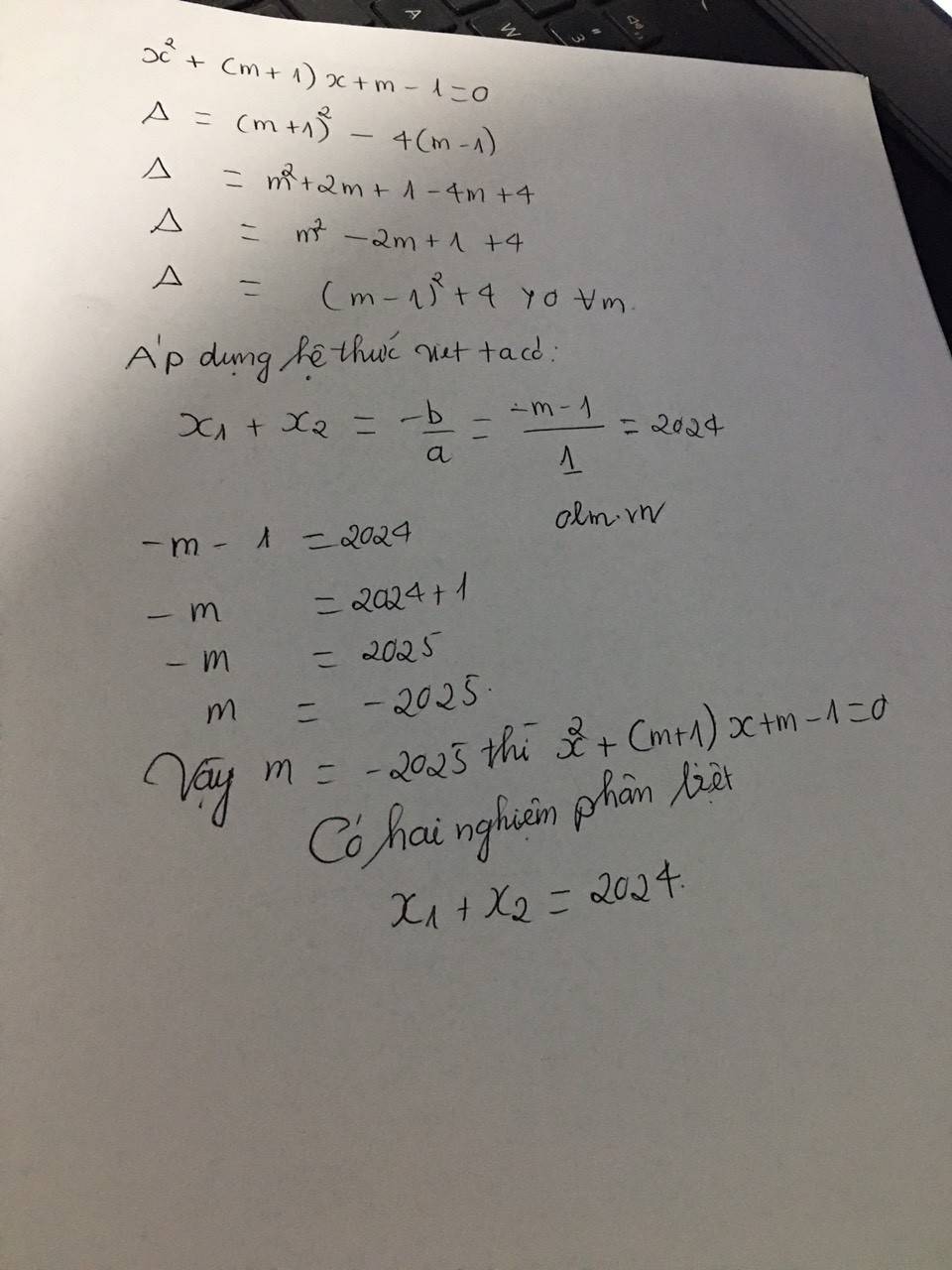
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

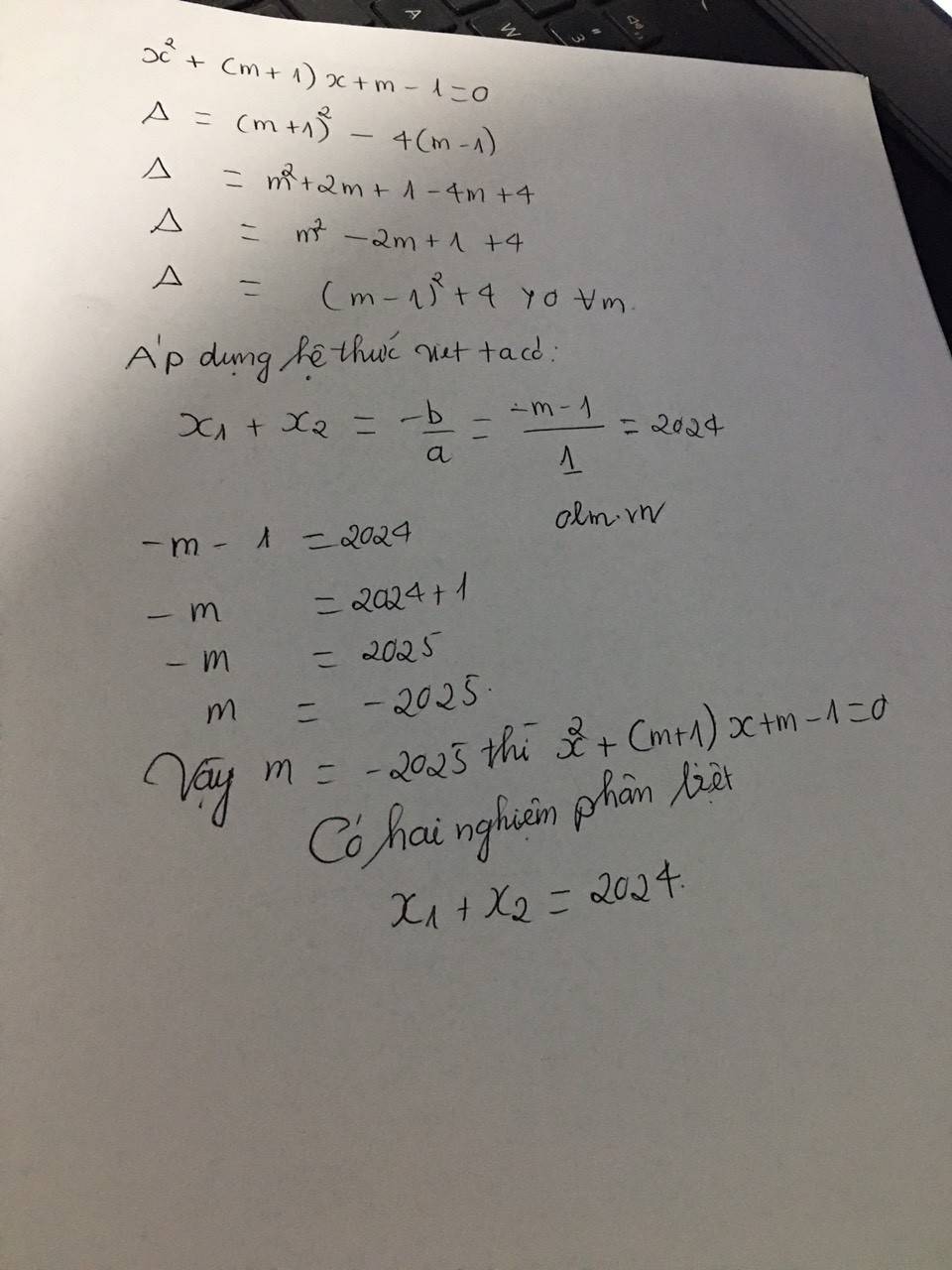

\(x^2-2\left(2m+1\right)x+4m^2+4m=0\)
Để pt có hai ng pb\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4>0\left(lđ\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\)Pt luôn có hai ng pb với mọi m
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{2\left(2m+1\right)+\sqrt{4}}{2}=2m+2\\x_2=\dfrac{2\left(2m+1\right)-\sqrt{4}}{2}=2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Có \(\left|x_1-x_2\right|=x_1+x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2m+2-2m\right|=2m+2+2m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2=4m+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
Vậy...

=>căn 2x1=x2-1
=>2x1=x2^2-2x2+1
=>x2^2-2(x1+x2)+1=0
=>x2^2-2(2m+1)+1=0
=>x2^2=4m+2-1=4m+1
=>\(x_2=\pm\sqrt{4m+1}\)
=>\(x_1=2m+1\pm\sqrt{4m+1}\)
x1*x2=m^2-m
=>m^2-m=4m+1\(\pm2m+1\)
=>m^2-5m-1=\(\pm2m+1\)
TH1: m^2-5m-1=2m+1
=>m^2-7m-2=0
=>\(m=\dfrac{7\pm\sqrt{57}}{2}\)
TH2: m^2-5m-1=-2m-1
=>m^2-3m=0
=>m=0; m=3

\(x^2-x+1-m=0\left(1\right)\\ \text{PT có 2 nghiệm }x_1,x_2\\ \Leftrightarrow\Delta=1-4\left(1-m\right)\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m-3\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\\ \text{Vi-ét: }\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=1\\x_1x_2=1-m\end{matrix}\right.\\ \text{Ta có }5\left(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}\right)-x_1x_2+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow5\cdot\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}-x_1x_2+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{1-m}+m-1+4=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{1-m}+m+3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow5+\left(1-m\right)\left(m+3\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2+2m-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+4m-8=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)\left(m+4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2\left(n\right)\\m=-4\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy $m=2$

\(\text{Δ}=\left(2m-1\right)^2-8\left(m-1\right)\)
\(=4m^2-4m+1-8m+8\)
\(=4m^2-12m+9=\left(2m-3\right)^2\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì 2m-3<>0
hay m<>3/2
Theo đề, ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1-4x_2=11\\x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-2m+1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1-4x_2=11\\2x_1+2x_2=-2m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x_1-4x_2=11\\4x_1+4x_2=-4m+2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x_1=-4m+13\\4x_2=3x_1-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-4m+13}{7}\\4x_2=\dfrac{-12m+36}{7}-\dfrac{77}{7}=\dfrac{-12m-41}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-4m+13}{7}\\x_2=\dfrac{-12m-41}{28}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo Vi-et, ta được: \(x_1x_2=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(4m-13\right)\left(12m+41\right)}{196}=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4m-13\right)\left(12m+1\right)=98\left(m-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow48m^2+4m-156m-13-98m+98=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow48m^2-250+85=0\)
Đến đây bạn chỉ cần giải pt bậc hai là xong rồi
\(\Delta=\left(2m-1\right)^2-8\left(m-1\right)=4m^2-12m+10\)
\(=\left(2m-3\right)^2+1>0\)
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm pb
Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{1-2m}{2}\left(1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có \(3x_1-4x_2=11\left(3\right)\)
Từ (1) ; (3) ta có hệ \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4x_1+4x_2=2-4m\\3x_1-4x_2=11\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x_1=13-4m\\x_2=\dfrac{1-2m}{2}-x_1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{13-4m}{7}\\x_2=\dfrac{1-2m}{2}-\dfrac{13-4m}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_2=\dfrac{7-14m-26+8m}{14}=\dfrac{-19-6m}{14}\)
Thay vào (2) ta được \(\left(\dfrac{13-4m}{7}\right)\left(\dfrac{-19-6m}{14}\right)=\dfrac{m-1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=4,125\)

Δ=(2m-6)^2-4(m^2+3)
=4m^2-24m+36-4m^2-12=-24m+24
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì -24m+24>0
=>m<1
x1^2+x2^2=36
=>(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2=36
=>(2m-6)^2-2(m^2+3)=36
=>4m^2-24m+36-2m^2-6-36=0
=>2m^2-24m-6=0
=>m^2-12m-3=0
=>\(m=6-\sqrt{39}\)

Lời giải:
Để pt có 2 nghiê pb thì:
$\Delta'=1-(m-3)>0\Leftrightarrow m< 4$
Áp dụng định lý Viet: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x_1+x_2=2\\ x_1x_2=m-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó:
\(x_1^2-2x_2+x_1x_2=-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2-2(2-x_1)+x_1(2-x_1)=-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1=-2\Leftrightarrow x_2=2-x_1=4\)
$m-3=x_1x_2=(-2).4=-8$
$\Leftrightarrow m=-5$ (tm)