
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,A=x^2+y^2\\=x^2-2xy+y^2+2xy\\=(x-y)^2+2xy\\=2^2+2\cdot1\\=4+2\\=6\)
\(b,x+y=1\\\Leftrightarrow (x+y)^3=1^3\\\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2y+3xy^2+y^3=1\\\Leftrightarrow x^3+3xy(x+y)+y^3=1\\\Leftrightarrow x^3+3xy\cdot1+y^3=1\\\Rightarrow A=1\)
a) Ta có:
\(x-y=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-y\right)^2=2^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-2xy+y^2=4\)
Mà: \(xy=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2+y^2\right)-2\cdot1=4\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2=4+2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+y^2=6\)
b) Ta có:
\(x+y=1\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+y\right)^3=1^3\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3+3x^2y+3xy+y^3=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3+3xy\left(x+y\right)+y^3=1\)
Mà: x + y = 1
\(\Rightarrow x^3+3xy\cdot1+y^3=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x^3+3xy+y^3=1\)

Sửa đề: \(P=x^{2008}+y^{2009}+z^{2010}\)
Ta có: x+y+z=1
nên \(\left(x+y+z\right)^3=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+y^3+z^3+3\left(x+y\right)\left(y+z\right)\left(x+z\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+y\right)\left(y+z\right)\left(z+x\right)+1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+y\right)\left(y+z\right)\left(x+z\right)=0\)
mà 3>0
nên \(\left(x+y\right)\left(y+z\right)\left(x+z\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+y=0\\y+z=0\\x+z=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-y\\y=-z\\x=-z\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x=-y vào biểu thức \(x+y+z=1\), ta được:
\(-y+y+z=1\)
hay z=1
Thay x=-y và z=1 vào biểu thức \(x^2+y^2+z^2=1\), ta được:
\(\left(-y\right)^2+y^2+1=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2+y^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2y^2=0\)
hay y=0
Vì x=-y
và y=0
nên x=0
Thay x=0; y=0 và z=1 vào biểu thức \(P=x^{2008}+y^{2009}+z^{2010}\), ta được:
\(P=0^{2008}+0^{2009}+1^{2010}=1\)
Vậy: P=1
nma ở trên cm y=-z mà. Nếu ở thay y=0 và z=1 vào thì nghĩa là 0 = -1 hả

\(A=x^2+y^2+z^2-yz-4x-3y+2027\)
\(\Rightarrow4A=4x^2+4y^2+4z^2-4yz-16x-12y+8108=4x^2-16x+16+3y^2+12y+12+y^2-4yz+4z^2+8080=4\left(x-2\right)^2+3\left(y+2\right)^2+\left(y-2z\right)^2+8080\)
Vì \(4\left(x-2\right)^2\ge0\)
\(3\left(y+2\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\left(y-2z\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow4A\ge8080\Rightarrow A\ge2020\)
\(ĐTXR\Leftrightarrow x=2,y=-2,z=-1\)

x 2 – 2xy – 4 z 2 + y 2 = ( x 2 – 2xy + y 2 ) – 4 z 2
= x - y 2 - 2 z 2 = (x – y + 2z)(x – y – 2z)
Thay x = 6; y = -4; z= 45 vào biểu thức ta được:
[ 6- (- 4) + 2.45]. [6- (-4) – 2.45]
= (6 + 4 + 90)(6 + 4 – 90) = 100.(-80) = -8000

Tìm giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức:
a) Ta có:
\(M=2x^2+4x+7\)
\(M=2\cdot\left(x^2+2x+\dfrac{7}{2}\right)\)
\(M=2\cdot\left(x^2+2x+1+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(M=2\cdot\left[\left(x+1\right)^2+2,5\right]\)
\(M=2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\)
Mà: \(2\left(x+1\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) nên:
\(M=2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\ge5\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(2\left(x+1\right)^2+5=5\Leftrightarrow2\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x+1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy: \(M_{min}=5\) khi \(x=-1\)
b) Ta có:
\(N=x^2-x+1\)
\(N=x^2-2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(N=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Mà: \(\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2\ge0\forall x\) nên \(N=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\forall x\)
Dấu '=" xảy ra:
\(\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{1}{2}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: \(N_{min}=\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Tìm giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức
a) Ta có:
\(E=-4x^2+x-1\)
\(E=-\left(4x^2-x+1\right)\)
\(E=-\left[\left(2x\right)^2-2\cdot2x\cdot\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{1}{16}+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\)
\(E=-\left[\left(2x-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\)
Mà: \(\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\ge\dfrac{15}{16}\forall x\) nên
\(\Rightarrow E=-\left[\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]\le-\dfrac{15}{16}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(-\left[\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2+\dfrac{15}{16}\right]=-\dfrac{15}{16}\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2-\dfrac{15}{16}=-\dfrac{15}{16}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(2x+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow2x-\dfrac{1}{4}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
Vậy: \(E_{max}=-\dfrac{15}{16}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{1}{16}\)
b) Ta có:
\(F=5x-3x^2+6\)
\(F=-3x^2+5x-6\)
\(F=-\left(3x^2-5x-6\right)\)
\(F=-3\left(x^2-\dfrac{5}{3}x-2\right)\)
\(F=-3\left[\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2-\dfrac{97}{36}\right]\)
\(F=-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}\)
Mà: \(-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2\le0\forall x\) nên:
\(F=-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}\le\dfrac{97}{36}\forall x\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra:
\(-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2+\dfrac{97}{36}=\dfrac{97}{36}\Leftrightarrow-3\left(x-\dfrac{5}{6}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{5}{6}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)
Vậy: \(F_{max}=\dfrac{97}{36}\) khi \(x=\dfrac{5}{6}\)

\(A=x^2+y^2+\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2-2xy+2.\dfrac{1}{2}x-2.\dfrac{1}{2}.y+\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(A=\left(x-y+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}\ge\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(A_{min}=\dfrac{3}{4}\) khi \(x-y+\dfrac{1}{2}=0\)
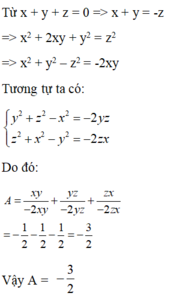
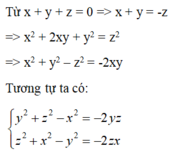
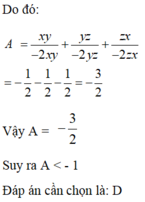
Ta có: \(\left(a-b\right)^2+\left(b-c\right)^2+\left(c-a\right)^2\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2+2b^2+2c^2-2ab-2bc-2ca\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2+2b^2+2c^2\ge2ab+2bc+2ca\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)\ge a^2+b^2+c^2+2\left(ab+bc+ca\right)=\left(a+b+c\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2+b^2+c^2\ge\frac{\left(a+b+c\right)^2}{3}\)
Khi đó \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+y^2+z^2\ge\frac{\left(x+y+z\right)^2}{3}=\frac{1}{3}\)