Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

`a,`
\(x^2-3x\ne0\)
`<=>x(x-3)`\(\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\x-3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne0\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\)
`b,`
đặt `A=(x^2-6x+9)/(x^2-3x)`
`A= ((x-3)^2)/(x(x-3))`
`A= (x-3)/x`
`c, `
để `x=5`
`=> A= (x -3)/x=(5-3)/5= 2/5`

a) ĐKXĐ:
\(x^2-1\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm1\)
b) \(A=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1}{x^2-1}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x^2-2\cdot x\cdot1+1^2}{x^2-1^2}\)
\(A=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(A=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
c) Thay x = 3 vào A ta có:
\(A=\dfrac{3-1}{3+1}=\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
a) ĐKXĐ:
\(9x^2-y^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left(3x\right)^2-y^2\ne0\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-y\right)\left(3x+y\right)\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x\ne\pm y\)
b) \(B=\dfrac{6x-2y}{9x^2-y^2}\)
\(B=\dfrac{2\cdot3x-2y}{\left(3x\right)^2-y^2}\)
\(B=\dfrac{2\left(3x-y\right)}{\left(3x+y\right)\left(3x-y\right)}\)
\(B=\dfrac{2}{3x+y}\)
Thay x = 1 và \(y=\dfrac{1}{2}\) và B ta có:
\(B=\dfrac{2}{3\cdot1+\dfrac{1}{2}}=\dfrac{2}{3+\dfrac{1}{2}}=\dfrac{2}{\dfrac{7}{2}}=\dfrac{4}{7}\)

a) Phân thức 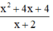 xác định
xác định
⇔ x + 2 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ -2
Vậy điều kiện xác định của phân thức là x ≠ -2.
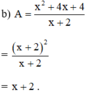
c) A = 1 ⇔ x + 2 = 1 ⇔ x = -1 ≠ -2 (Thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy với x = -1 thì A = 1.
d) A = 0 ⇔ x + 2 = 0 ⇔ x = -2 (Không thỏa mãn điều kiện)
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x để A = 0.

a) x ≠ -5.
b) Ta có P = ( x + 5 ) 2 x + 5 = x + 5
c) Ta có P = 1 Û x = -4 (TMĐK)
d) Ta có P = 0 Û x = -5 (loại). Do vậy x ∈ ∅ .

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-2\)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x^2-4x+8}{x^3+8}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2}{x+2}\)
c) Vì x=2 thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ
nên Thay x=2 vào biểu thức \(\dfrac{2}{x+2}\), ta được:
\(\dfrac{2}{2+2}=\dfrac{2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: Khi x=2 thì giá trị của biểu thức là \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
d) Để \(\dfrac{2}{x+2}=2\) thì x+2=1
hay x=-1(nhận)
Vậy: Để \(\dfrac{2}{x+2}=2\) thì x=-1

a) \(\frac{2x^2-4x+8}{x^3+8}\Rightarrow\) ĐKXĐ: \(x^3+8\ne0 \Leftrightarrow x^3\ne-8 \Leftrightarrow x\ne-2 \)
b) \(\frac{2x^2-4x+8}{x^3+8}=\frac{2\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=\frac{2}{x+2}\)
c) \(\frac{2}{x+2}\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=\frac{2}{2+2}=\frac{1}{2}\)
d) \(\frac{2}{x+2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-1\)
uum, mik nghĩ phần C chỗ x+2=1 thì phải gt tại sao x+2=1 thì đúng hơn
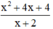

a, ĐKXĐ : \(x^2+2x+1\ne0=>\left(x+1\right)^2\ne0\)
=> \(x\ne-1\)
b, Ta có \(B=\frac{x^2+2x+1}{x^2-1}\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{x+1}{x-1}\)
c, Đề P =0
<=> \(\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
=> x=-1
a/ x khác cộng trừ 1
b/ B= 1/(x-1)
c/ vô nghiệm