Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \(f\left( 1 \right) = 3.1 = 3;f\left( { - 2} \right) = 3.\left( { - 2} \right) = - 6;f\left( {\dfrac{1}{3}} \right) = 3.\dfrac{1}{3} = 1\).
b) Ta có: \(f\left( { - 3} \right) = 3.\left( { - 3} \right) = - 9;f\left( { - 1} \right) = 3.\left( { - 1} \right) = - 3\)
\(f\left( 0 \right) = 3.0 = 0;f\left( 2 \right) = 3.2 = 6;f\left( 3 \right) = 3.3 = 9\);
Ta lập được bảng sau
\(x\) | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
\(y\) | –9 | -6 | –3 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 9 |

a) Đại lượng \(y\) là hàm số của đại lượng \(x\) vì với mỗi giá trị của \(x\) ta chỉ xác nhận được duy nhất một giá trị \(y\) tương ứng.
b) \(f\left( 2 \right) = {2^2} = 4;f\left( { - 3} \right) = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} = 9\)
Ta có: \(f\left( { - 2} \right) = {\left( { - 2} \right)^2} = 4;f\left( { - 1} \right) = {\left( { - 1} \right)^2} = 1\)
\(f\left( 0 \right) = {0^2} = 0;f\left( 1 \right) = {1^2} = 1\)
\(f\left( 2 \right) = {2^2} = 4;f\left( 3 \right) = {3^2} = 9\)
\(x\) | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
\(f\left( x \right)\) | 9 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 9 |

a: F=9/25x^2y^4*20/27x^3y=4/15x^5y^5
Bậc: 10
b: y=-x/3 và x+y=2
=>x+y=2 và -1/3x-y=0
=>x=3 và y=-1
Khi x=3 và y=-1 thì F=4/15*(-3)^5=-324/5

\(a,=5^3:5^2=5\\ b,=\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^{5-3}=\left(\dfrac{3}{4}\right)^2=\dfrac{9}{16}\\ c,=1728-512=1216\\ d,=x^{10}:x^8=x^2\\ e,=\left(-x\right)^{5-3}=\left(-x\right)^2=x^2\\ f,=\left(-y\right)^{5-4}=-y\)

a) \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{3}x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-5\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\Rightarrow x\left(x^2-\dfrac{1}{9}\right)=0\Rightarrow x\left(x-\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\left(x+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=\dfrac{1}{3}\\x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e) \(\Rightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x+2-x+2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(x+2\right).4=0\Rightarrow x=-2\)
f) \(\Rightarrow x\left(2x-3\right)+2\left(2x-3\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(2x-3\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
g) \(\Rightarrow2\left(3x-2\right)^2-\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x+2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(3x-2\right)\left(3x-6\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{2}{3}\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
h) \(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=-1\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
i) \(\Rightarrow4x\left(x+1\right)+5\left(x+1\right)=0\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(4x+5\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=-\dfrac{5}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = {\left( { - 3} \right)^2} + 4 = 9 + 4 = 13\);
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = {\left( { - 2} \right)^2} + 4 = 4 + 4 = 8\);
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = {\left( { - 1} \right)^2} + 4 = 1 + 4 = 5\);
\(f\left( 0 \right) = {0^2} + 4 = 0 + 4 = 4\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = {1^2} + 4 = 1 + 4 = 5\).

\(=\left(\dfrac{1+2\left(x-y\right)\left(2x-2y+1\right)-2x+2y-1}{2x-2y+1}\right):\dfrac{\left(2x-2y\right)\left(2x-2y+1\right)-4x^2+8xy-4y^2}{2x-2y+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{1+\left(2x-2y\right)^2+2x-2y-2x+2y-1}{2x-2y+1}\cdot\dfrac{2x-2y+1}{\left(2x-2y\right)^2+2x-2y-4x^2+8xy-4y^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2x-2y\right)^2}{4x^2-8xy+4y^2+2x-2y-4x^2+8xy-4y^2}=2x-2y\)
=2(x-y) luôn là số chẵn

+ Với \(x = - 3\)\( \Rightarrow f\left( { - 3} \right) = 4.\left( { - 3} \right) - 1 = - 13;g\left( { - 3} \right) = - 0,5.\left( { - 3} \right) + 8 = 9,5\);
+ Với \(x = - 2\)\( \Rightarrow f\left( { - 2} \right) = 4.\left( { - 2} \right) - 1 = - 9;g\left( { - 2} \right) = - 0,5.\left( { - 2} \right) + 8 = 9\);
+ Với \(x = - 1\)\( \Rightarrow f\left( { - 1} \right) = 4.\left( { - 1} \right) - 1 = - 5;g\left( { - 1} \right) = - 0,5.\left( { - 1} \right) + 8 = 8,5\);
+ Với \(x = 0\)\( \Rightarrow f\left( 0 \right) = 4.0 - 1 = - 1;g\left( 0 \right) = - 0,5.0 + 8 = 8\);
+ Với \(x = 1\)\( \Rightarrow f\left( 1 \right) = 4.1 - 1 = 3;g\left( 1 \right) = - 0,5.1 + 8 = 7,5\);
+ Với \(x = 2\)\( \Rightarrow f\left( 2 \right) = 4.2 - 1 = 7;g\left( 2 \right) = - 0,5.2 + 8 = 7\);
+ Với \(x = 3\)\( \Rightarrow f\left( 3 \right) = 4.3 - 1 = 11;g\left( 3 \right) = - 0,5.3 + 8 = 6,5\).
Ta có bảng sau:
\(x\) | –3 | –2 | –1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
\(y = f\left( x \right) = 4x - 1\) | –13 | –9 | –5 | –1 | 3 | 7 | 11 |
\(y = g\left( x \right) = - 0,5x + 8\) | 9,5 | 9 | 8,5 | 8 | 7,5 | 7 | 6,5 |
a) Ta có:
\(f\left( {\dfrac{1}{5}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{1}{5}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{4}{5}}} = 5:\dfrac{4}{5} = 5.\dfrac{5}{4} = \dfrac{{25}}{4};\)
\(f\left( { - 5} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 5} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 20}} = \dfrac{{ - 1}}{4};\)
\(f\left( {\dfrac{4}{5}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{4}{5}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{{16}}{5}}} = 5:\dfrac{{16}}{5} = 5.\dfrac{5}{{16}} = \dfrac{{25}}{{16}}\)
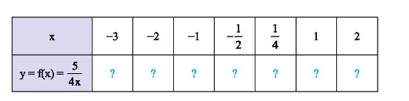
b) Ta có:
\(f\left( { - 3} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 3} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 12}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{{12}};\)
\(f\left( { - 2} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 2} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 8}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{8};\)
\(f\left( { - 1} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - 1} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 4}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{4};\)
\(f\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\left( { - \dfrac{1}{2}} \right)}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{{ - 4}}{2}}} = \dfrac{5}{{ - 2}} = \dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}\);
\(f\left( {\dfrac{1}{4}} \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.\dfrac{1}{4}}} = \dfrac{5}{{\dfrac{4}{4}}} = \dfrac{5}{1} = 5\);
\(f\left( 1 \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.1}} = \dfrac{5}{4}\);
\(f\left( 2 \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4.2}} = \dfrac{5}{8}\)
Ta có bảng sau:
\(x\)
–3
–2
–1
\( - \dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
1
2
\(y = f\left( x \right) = \dfrac{5}{{4x}}\)
\(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{{12}}\)
\(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{8}\)
\(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{4}\)
\(\dfrac{{ - 5}}{2}\)
5
\(\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\dfrac{5}{8}\)