Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: f(2)=2*2^2-3*2+4=8-6+4=2+4=6
b: h(x)=-2x^2+x-1+f(x)
=-2x^2+x-1+2x^2-3x+4
=-2x+3

a: F(x)=3x^3-2x^2+5x-7
G(x)=3x^3-2x^2+5x+7x^2+3=3x^3+5x^2+5x+3
Bậc của F(x),G(x) đều là 3
b: N(x)=G(x)-F(x)
\(=3x^3+5x^2+5x+3-3x^3+2x^2-5x+7=7x^2+10\)
M(x)=2F(x)+G(x)
\(=6x^3-4x^2+10x-14+3x^3+5x^2+5x+3\)
\(=9x^3+x^2+15x-11\)
c: x^2-3x=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=3
\(M\left(0\right)=9\cdot0^3+0^2+15\cdot0-11=-11\)
\(M\left(3\right)=9\cdot3^3+3^2+15\cdot3-11=286\)
d: N(x)=7x^2+10>=10
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=0

Bài 1:
Theo đề, ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=1\\2a+b=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=3\\b=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(A=\left|x+\frac{2}{3}\right|\)
Ta có: \(\left|x+\frac{2}{3}\right|\ge0\forall x\)
\(A=0\Leftrightarrow\left|x+\frac{2}{3}\right|=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{2}{3}\)
Vậy \(A_{min}=0\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{2}{3}\)
\(B=\left|x\right|+\frac{1}{2}\)
Ta có: \(\left|x\right|\ge0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left|x\right|+\frac{1}{2}\ge\frac{1}{2}\forall x\)
\(B=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\left|x\right|=0\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Vậy \(B_{min}=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
Câu c,d tương tự
P/S tất cả những bài trên chỉ tìm được min, ko tìm được max.

Sửa đề: f(x) = x² - 4x + 3
a) f(0) = 0 - 4.0 + 3 = 3
f(1) = 1 - 4.1 + 3 = 0
f(3) = 9 - 4.3 + 3 = 0
b) x = 1 và x = 3 là nghiệm của đa thức f(x) vì f(1) = 0 và f(3) = 0

a,f(x)+g(x)= (x2 + 3x - 5 ) +(x2 + 2x + 3)
= x2 +3x-5 +x2 +2x+3
= (x2+x2) +(3x+2x) +(-5+3)
= 2x2 +5x -2
b, f(x)-g(x)=(x2 + 3x - 5 ) -(x2 + 2x + 3)
= x2 + 3x - 5 -x2 - 2x - 3
= (x2-x2) + (3x-2x) +(-5-3)
= X-8
HỌC TỐT :D

Vì \(\hept{\begin{cases}|x-3|\\|4+x|\end{cases}\ge0}\) nên minH = 0

câu 4: b, đề bài là tính giá trị của A tại x =-1/2;y=-1
Tk
Bài 2
a) F(x)-G(x)+H(x)= \(x^3-2x^2+3x+1-\left(x^3+x-1\right)+\left(2x^2-1\right)\)
= \(x^3-2x^2+3x+1-x^3-x+1+2x^2-1\)
= \(x^3-x^3-2x^2+2x^2+3x-x+1+1-1\)
= 2x + 1
b) 2x + 1 = 0
2x = -1
x=\(\dfrac{-1}{2}\)
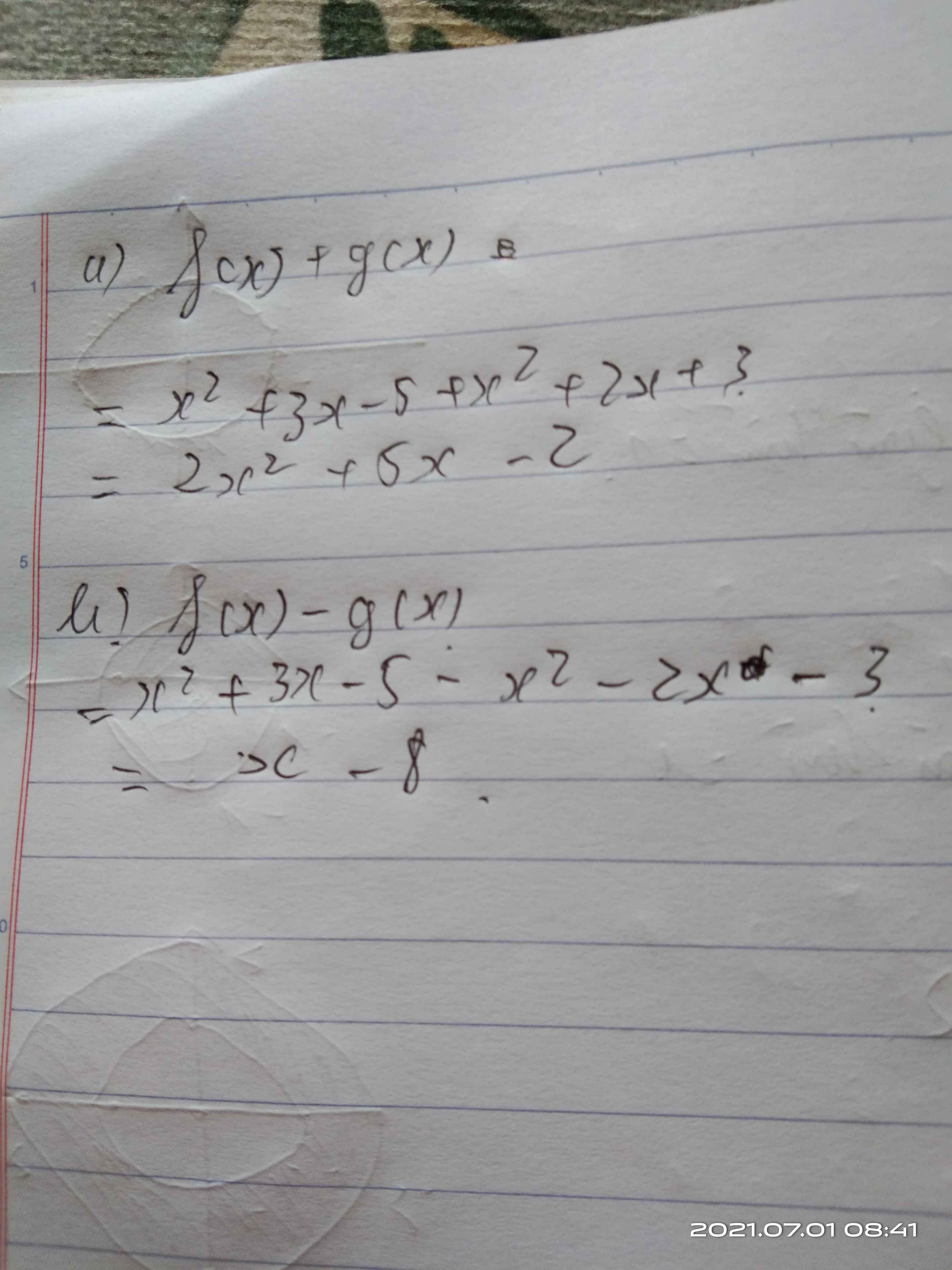
\(h\left(x\right)=f\left(x\right)+g\left(x\right)+1=3x^2-30x+75+2\left|x-5\right| \)
\(=3\left(x^2-2.x.5+25\right)+2\left|x-5\right|+1=3\left(x-5\right)^2+2\left|x-5\right|+1\ge1\)
Giá trị nhỏ nhất của H(x bằng 1 khi và chỉ khi \(\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-5\right)^2=0\\\left|x-5\right|=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}x=5\)