

Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


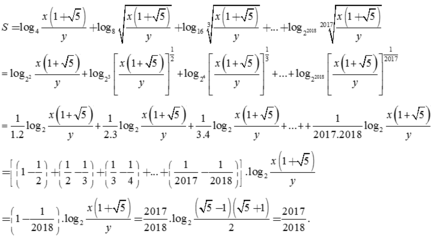

Đáp án B
Ta có log(x + 2y) = log x + log y
<=> log 2 (x+2y) = log 2xy
<=> 2 (x+2y) = 2xy (*).
Đ ặ t a = x > 0 b = 2 y > 0 , khi đó
* ⇔ 2 a + b = a b
và P = a 2 1 + b + b 2 1 + a ≥ a + b 2 a + b + 2
Lại có a b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇒ 2 a + b ≤ a + b 2 4 ⇔ a + b ≥ 8 .
Đặt t = a + b, do đó
P ≥ f t = t 2 t + 2 .
X é t h à m s ố f t = t 2 t + 2 t r ê n [ 8 ; + ∞ )
c ó f ' t = t 2 + 2 t t + 2 2 > 0 ; ∀ ≥ 8
Suy ra f(t) là hàm số đồng biến trên [ 8 ; + ∞ )
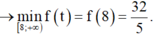
Vậy gía trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P là 32 5 .

\(log_xy=log_yx=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Rightarrow\left(log_xy\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(log_x\left(x-y\right)\) tồn tại \(\Rightarrow x-y\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne y\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(log_x\left(x-y\right)=log_y\left(x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=x\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2-2x-1=0\)
Pt này nghiệm xấu, đề bài có vấn đề

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne y\)
\(log_xy=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Leftrightarrow log_x^2y=1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\left(l\right)\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=log_{x^{-1}}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=1\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^2-1=0\Rightarrow x^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=\frac{1}{x^2}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+xy+y^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}+1+\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}+1\)

Nếu một trong các số \(x+y-z;y+z-x;z+x-y\) bằng 0 thì cả 3 số đều bằng 0 và dẫn đến \(x=y=z=0\), mâu thuẫn
Từ giả thiết ta có : \(\begin{cases}x\log y\left(y+z-x\right)=y\log x\left(z+x-y\right)\\y\log z\left(z+x-y\right)=z\log y\left(x+y-z\right)\\z\log x\left(x+y-z\right)=x\log z\left(y+z-x\right)\end{cases}\)
Xét đẳng thức thứ nhất ta có :
\(x\log y\left(y+z-x\right)=y\log x\left(z+x-y\right)\Leftrightarrow x\log y=y\log x.\frac{z+x-y}{y+z-x}\) \(\Leftrightarrow x\log y+y\log x=y\log x\left(\frac{z+x-y}{y+z-x}+1\right)\Leftrightarrow x\log y+z\log x=y\log x\frac{2z}{y+z-x}\)
Biến đổi tương tự với đẳng thức thứ hai ta có :
\(y\log z+z\log y=z\log y\frac{2z}{z+z-y}\)
Ta thấy rằng : \(x^y.y^x=y^z.z^y\Leftrightarrow x\log y+y\log x=y\log z+z\log y\)
Do đó ta cần có :
\(y\log x\frac{2z}{y+z-x}=z\log y\frac{2z}{z+x-y}\Leftrightarrow y\log x\left(z+x-y\right)=x\log y\left(y+z-x\right)\), đúng
Do đó ta được : \(x^yy^x=y^z.z^y\)
Chứng minh tương tự ta có : \(y^zz^y=z^x.x^z\)
=> Điều phải chứng minh

Đáp án D
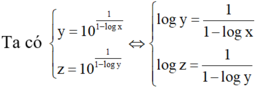
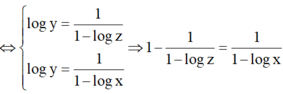
⇔ log z - 1 log z = 1 1 - log x
⇔ 1 - log x = log z log z - 1
⇔ log x = - 1 log z - 1 ⇔ x = 10 1 1 - log z .