Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

b: \(\Leftrightarrow3n^3+n^2+9n^2+3n-3n-1-4⋮3n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n+1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{0;-1;1\right\}\)

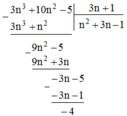
Ta có: 3 n 3 + 10 n 2 - 5 = 3 n + 1 n 2 + 3 n - 1 - 4
Để phép chia đó là chia hết thì 4 ⋮ 3n + 1⇒ 3n + 1 ∈ Ư(4)
3n + 1 ∈ {-4; -2; -1; 1; 2; 4}
3n + 1 = -4⇒ 3n = -5⇒ n = 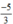 ∉ Z : loại
∉ Z : loại
3n + 1 = -2⇒ 3n = -3⇒ n = -1 ∈ Z
3n + 1 = -1⇒ 3n = -2⇒ n = 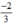 ∉ Z : loại
∉ Z : loại
3n + 1 = 1⇒ 3n = 0⇒ n = 0 ∈ Z
3n + 1 = 2⇒ 3n = 2⇒ n = 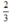 ∉ Z : loại
∉ Z : loại
3n + 1 = 4⇒ 3n = 3⇒ n = 1 ∈ Z
Vậy n ∈ {-1; 0; 1} thì 3 n 3 + 10 n 2 - 5 chia hết cho 3n + 1.

a: \(\Leftrightarrow3n^3+n^2+9n^2+3n-3n-1-4⋮3n+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3n+1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
mà n là số nguyên
nên \(n\in\left\{0;-1;1\right\}\)
b: \(\Leftrightarrow10n^2-10n+11n-11+1⋮n-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n-1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
hay \(n\in\left\{2;0\right\}\)
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^3+5x^2+x^2-x+5+n-5⋮x^2-x+5\)
=>n-5=0
hay n=5

\(a,A=\left(x^2-4xy+4y^2\right)+10\left(x-2y\right)+25+\left(y^2-2y+1\right)+2\\ A=\left(x-2y\right)^2+10\left(x-2y\right)+5+\left(y-1\right)^2+2\\ A=\left(x-2y+5\right)^2+\left(y-1\right)^2+2\ge2\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y-5\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\Leftrightarrow3x^3+10x^2-5+n=\left(3x+1\right)\cdot a\left(x\right)\)
Thay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\Leftrightarrow3\left(-\dfrac{1}{27}\right)+10\cdot\dfrac{1}{9}-5+n=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{1}{9}+\dfrac{10}{9}-5+n=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-4+n=0\Leftrightarrow n=4\)
\(c,\Leftrightarrow2n^2-4n+5n-10+3⋮n-2\\ \Leftrightarrow2n\left(n-2\right)+5\left(n-2\right)+3⋮n-2\\ \Leftrightarrow n-2\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{-1;1;3;5\right\}\)

Bài 3:
Ta có: \(2n^2+n-7⋮n-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2n^2-4n+5n-10+3⋮n-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow n-2\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
hay \(n\in\left\{3;1;5;-1\right\}\)

a) Cho x2 - x + 5=0 =>x={ \(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}i;\frac{1}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}i\) }
Thay giá trị của x là \(\frac{1}{2}+\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}i\)hoặc \(\frac{1}{2}-\frac{\sqrt{19}}{2}i\) vừa tìm được vào x4 - x3 + 6x2- x sẽ luôn được kết quả là -5
=>-5 +a=0 => a=5
b) Cho x+2=0 => x=-2
Thay giá trị của x vào biểu thức 2x3 - 3x2 + x sẽ được kết quả là -30
=> -30 + a=0 => a=30
a) Cho 3n +1 =0 => n= \(\frac{-1}{3}\)
Thay n= \(\frac{-1}{3}\)vào biểu thức 3n3 + 10n2 -5 sẽ được kết quả -4
Vậy n = -4
b) Cho n-1=0 => n=1
Thay n=1 vào biểu thức 10n2 + n -10 sẽ được kết quả là 1
Vậy n = 1

\(a,n^3-2n^2+3n+3=n^3-n^2-n^2+n+2n-2+5\\ =\left(n-1\right)\left(n^2-n+2\right)+5\\ \Leftrightarrow n^3-2n^2+3n+3⋮\left(n-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow5⋮n-1\\ \Leftrightarrow n-1\in\left\{-5;-1;1;5\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow n\in\left\{-4;0;2;6\right\}\)
\(b,\Leftrightarrow x^4+6x^3+7x^2-6x+a\\ =x^4+3x^3-x^2+3x^3+9x^2-3x-x^2-3x+1-1+a\\ =\left(x^2+3x-1\right)\left(x^2+3x-1\right)-1+a\\ =\left(x^2+3x-1\right)^2+a-1\)
Để \(x^4+6x^3+7x^2-6x+a⋮x^2+3x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a-1=0\Leftrightarrow a=1\)

Mình chỉ làm mẫu một câu thôi, mấy câu này giống nhau về cách làm :))
a) Thực hiện phép chia đa thức 3n3 + 10n2 - 5 cho đa thức 3n + 1 được thương là n2 + 3n - 1 và dư -4
Vậy để 3n3 + 10n2 - 5 ⋮ 3n + 1 thì -4 ⋮ 3n + 1
=> 3n + 1 thuộc Ư(4) = { 1; 2; 4; -1; -2; -4 }
=> n thuộc { 0; 1/3; 1; -2/3; -1; -5/3 }
Mà n nguyên => n thuộc { 0; 1; -1 }
b) d) tương tự
c) hơi khác mình làm nốt
Thực hiện phép chia đa thức x4 - x3 + 6x2 - x + n cho đa thức x2 - x + 5 ta được số dư là n - 5
Để phép chia trên là phép chia hết thì số dư phải bằng 0
=> n - 5 = 0
<=> n = 5
Vậy n = 5

a: =>\(n+2\in\left\{1;-1;7;-7\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{-1;-3;5;-9\right\}\)
b: =>n-3+4 chia hết cho n-3
=>\(n-3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{4;2;5;1;7;-1\right\}\)
c: =>3n^3+n^2+9n^2-1-4 chia hết cho 3n+1
=>\(3n+1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{0;-\dfrac{2}{3};\dfrac{1}{3};-1;1;-\dfrac{5}{3}\right\}\)
d: =>10n^2-10n+11n-11+1 chia hết cho n-1
=>\(n-1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(n\in\left\{2;0\right\}\)
Bài làm
a) Đặt t = x2 + x + 1
bthuc <=> t( t + 1 ) - 12
= t2 + t - 12
= t2 - 3t + 4t - 12
= t( t - 3 ) + 4( t - 3 )
= ( t - 3 )( t + 4 )
= ( x2 + x + 1 - 3 )( x2 + x + 1 + 4 )
= ( x2 + x - 2 )( x2 + x + 5 )
= ( x2 - x + 2x - 2 )( x2 + x + 5 )
= [ x( x - 1 ) + 2( x - 1 ) ]( x2 + x + 5 )
= ( x - 1 )( x + 2 )( x2 + x + 5 )
Bài làm
b) 10n2 + n - 10
= 10n2 - 10n + 9n - 9 - 1
= ( 10n2 - 10n ) + ( 9n - 9 ) - 1
= 10n( n - 1 ) + 9( n - 1 ) - 1
= ( n - 1 )( 10n + 9 ) - 1
Ta có ( n - 1 )( 10n + 9 ) chia hết ( n - 1 )
=> Để ( 10n2 + n - 10 ) chia hết ( n - 1 )
thì -1 chia hết ( n - 1 )
hay ( n - 1 ) ∈ Ư(-1) = { ±1 }
=> n ∈ { 2 ; 0 }