
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(PT\Leftrightarrow-5x^2-24x+60=\left(x^2+5x-10\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow-5x^2-24x+60=x^4+10x^3+5x^2-100x+100\\ \Leftrightarrow x^4+10x^3+10x^2-76x+40=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^4+4x^3-10x^2+6x^3+24x^2-60x-4x^2-16x+40=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+4x-10\right)\left(x^2+6x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x^2+4x-10=0\\x^2+6x-4=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-2+\sqrt{14}\\x=-2-\sqrt{14}\\x=-3+\sqrt{13}\\x=-3-\sqrt{13}\end{matrix}\right.\)

5 x 2 + 4 x − x 2 − 3 x − 18 = 5 x 1
ĐK: 5 x 2 + 4 x ≥ 0 x 2 − 3 x − 18 ≥ 0 x ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 0 , x ≤ − 4 5 x ≥ 6 , x ≤ − 3 x ≥ 0 ⇔ x ≥ 6
Khi đó 1 ⇔ 5 x 2 + 4 x = 5 x + x 2 − 3 x − 18
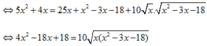
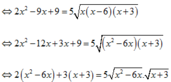
Dễ thấy x = 6 không là nghiệm phương trình nên với x > 6 ta chia cả hai vế cho x 2 − 6 x > 0 ta được:
2 + 3. x + 3 x 2 − 6 x = 5. x + 3 x 2 − 6 x 2
Đặt x + 3 x 2 − 6 x = t > 0 thì (2) trở thành 3 t 2 − 5 t + 2 = 0 ⇔ t = 1 ( T M ) t = 2 3 ( T M )
+ Nếu t = 1 thì x + 3 = x 2 − 6 x
⇔ x + 3 = x 2 − 6 x ⇔ x 2 − 7 x − 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 7 + 61 2 ( T M ) x = 7 − 61 2 ( L )
+ Nếu t = 2 3 thì x + 3 = 2 3 x 2 − 6 x ⇔ x + 3 = 4 9 ( x 2 − 6 x )
⇔ 4 x 2 − 33 x − 27 = 0 ⇔ x = 9 ( T M ) x = − 3 4 ( L )
Vậy phương trình đã cho có tập nghiệm s = 7 + 61 2 ; 9 hay S có 2 phần tử.
Đáp án cần chọn là: D

Bài 1:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+6< =0\)
=>(x-2)(x-3)<=0
=>2<=x<=3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)^2< =0\)
=>x=6
c: \(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1>=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2>=0\)
hay \(x\in R\)

b: \(\Delta=2^2-4\cdot1\cdot1=0\)
Do đó: Tam thức này dương khi x khác -1; bằng 0 khi x=-1
a: \(\Delta=3^2-4\cdot\left(-5\right)\cdot\left(-1\right)=9-20=-11< 0\)
Do đó: Tam thức này luôn âm với mọi x
c: \(\Delta=1^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-2\right)=9\)
Do đó: Tam thức này âm khi -2<x<1
Bằng 0 khi x=-2 hoặc x=1
Dương khi x<-2 hoặc x>1

\(a,A=\left\{0;1;2;3;4\right\}\\ b,B=\left\{-16;-13;-10;-7;-4;-1;2;5;8\right\}\\ c,C=\left\{-9;-8;-7;...;7;8;9\right\}\\ d,x^2-3x+1=0\\ \Delta=9-4=5\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\\x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow D=\left\{\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2};\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\right\}\)
\(e,2x^3-5x^2+2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow E=\left\{0;2\right\}\\ f,F=\left\{0;3;6;9;12;15;18\right\}\)

Điều kiện xác định x 2 + 5 x + 10 ≥ 0 ⇔ x ∈ R
Khi đó phương trình ⇔ x 2 + 5 x + 10 + 2 x 2 + 5 x + 10 − 8 = 0
⇔ ( x 2 + 5 x + 10 − 2 ) ( x 2 + 5 x + 10 + 4 ) = 0
⇔ x 2 + 5 x + 10 = 2 x 2 + 5 x + 10 = − 4 ⇔ x 2 + 5 x + 10 = 2 ⇔ x 2 + 5 x + 6 = 0 ⇔ x = − 3 x = − 2
Vậy x 1 2 + x 2 2 = 2 2 + 3 3 = 13
Đáp án cần chọn là: B

Đáp án: D
(x2 - 4) (x2 - 1) = 0 ⇔ x = ±2; x = ±1 nên A = {-2; -1; 1; 2}
(x2 - 4) (x2 + 1) = 0 ⇔ x2 - 4 = 0 ⇔ x = ±2 nên B = {-2; 2}
x4 - 5x2 + 4)/x = 0 ⇔ x4 - 5x2 + 4 = 0 ⇔ x = ±2; x = ±1 nên D = {-2; -1; 1; 2}
=> A = D
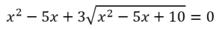
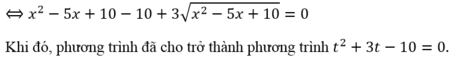
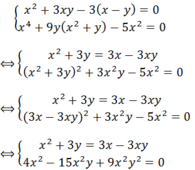
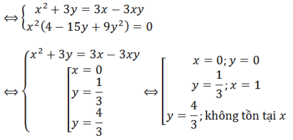
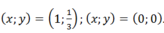
x=-căn bậc hai(13)-3, x=căn bậc hai(14)-2