
Giúp em câu b với. Chi tiết giúp ạ.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 1:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y-2x< =2\\2y-x>=4\\x+y< =5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y< =2x+2\\2y>=x+4\\y< =-x+5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y< =2x+2\\y< =-x+5\\y>=\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
y<=2x+2
=>y-2x-2<=0
Vẽ đường thẳng y=2x+2
Khi x=0 và y=0 thì \(y-2x-2=0-0-2=-2< =0\)(đúng)
=>Miền nghiệm của BPT y<=2x+2 là nửa mặt phẳng vừa chứa biên vừa chứa điểm O(0;0)
y<=-x+5
=>x+y-5<=0
Khi x=0 và y=0 thì \(x+y-5=0+0-5< =0\)(đúng)
=>Miền nghiệm của BPT y<=-x+5 là nửa mặt phẳng vừa chứa biên vừa chứa điểm O(0;0)
y>=1/2x+2
=>\(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+y-2>=0\)
Khi x=0 và y=0 thì \(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+y-2=-\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot0+0-2=-2< 0\)
=>O(0;0) không thỏa mãn BPT \(-\dfrac{1}{2}x+y-2>=0\)
=>Miền nghiệm của BPT \(y>=\dfrac{1}{2}x+2\) là nửa mặt phẳng chứa biên nhưng không chứa điểm O(0;0)
Vẽ đồ thị:
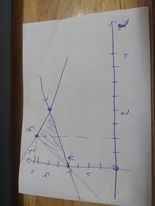
Theo hình vẽ, ta có: Miền nghiệm của hệ BPT sẽ là ΔABC, với A(0;2); B(1;4); C(2;3)
Khi x=0 và y=2 thì F=2-0=2
Khi x=1 và y=4 thì F=4-1=3
Khi x=2 và y=3 thì F=3-2=1
=>Chọn A

a, \(u_n=u_1.q^{n-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow192=u_1.2^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_1=\dfrac{192}{2^n}\)
\(S_n=\dfrac{u_1\left(1-q^n\right)}{1-q}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow189=\dfrac{\dfrac{192}{2^n}\left(1-2^n\right)}{1-2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow189=192-\dfrac{192}{2^n}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{192}{2^n}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2^n=2^6\)
\(\Rightarrow n=6\)


\(b,B=\dfrac{x-4+2\sqrt{x}+6-3\sqrt{x}-4}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\\ B=\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\\ c,M=B:A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}+3}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+3}{x-\sqrt{x}+2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{x-\sqrt{x}+2}\\ M=\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}+2-x+2\sqrt{x}-1}{x-\sqrt{x}+2}\\ M=1-\dfrac{x-2\sqrt{x}+1}{x-\sqrt{x}+2}=1-\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{x-\sqrt{x}+2}\)
Ta có \(\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2\ge0;x-\sqrt{x}+2=\left(\sqrt{x}-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}>0\)
Do đó \(\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{x-\sqrt{x}+2}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M=1-\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{x-\sqrt{x}+2}\le1-0=1\)
Vậy \(M_{max}=1\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x}=1\Leftrightarrow x=1\left(tm\right)\)
a: Thay \(x=3+2\sqrt{2}\) vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{3+2\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2}-1+2}{\sqrt{2}+1+3}=\dfrac{4+\sqrt{2}}{4+\sqrt{2}}=1\)


24.
Đường thẳng có 1 vtcp là \(\overrightarrow{u}=\left(2;-5\right)\)
25.
\(a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc.cosA\)
26.
A là mệnh đề sai, công thức đúng: \(S=\dfrac{1}{2}ab.sinC\)
27.
\(BC=\sqrt{AB^2+AC^2-2AB.AC.cosA}=\sqrt{3^2+4^2-2.3.4.cos60^0}=\sqrt{13}\)
28.
\(\widehat{A}=180^0-\left(35^030'+45^0\right)=99^030'\)
Áp dụng định lý hàm sin:
\(\dfrac{a}{sinA}=\dfrac{b}{sinB}\Rightarrow b=\dfrac{a.sinB}{sinA}=\dfrac{12,5.sin\left(35^030'\right)}{sin\left(99^030'\right)}=7,36\left(m\right)\)

23.
Ta sẽ tìm điểm \(I\left(a;b;c\right)\) sao cho \(\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{IC}+\overrightarrow{ID}=\overrightarrow{0}\) (1)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{IA}=\left(-2-a;2-b;6-c\right)\\\overrightarrow{IB}=\left(-3-a;1-b;8-c\right)\\\overrightarrow{IC}=\left(-1-a;-b;7-c\right)\\\overrightarrow{ID}=\left(1-a;2-b;3-c\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{IC}+\overrightarrow{ID}=\left(-5-4a;5-4b;24-4c\right)\)
(1) thỏa mãn khi: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-5-4a=0\\5-4b=0\\24-4c=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-\dfrac{5}{4}\\b=\dfrac{5}{4}\\c=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I\left(-\dfrac{5}{4};\dfrac{5}{4};6\right)\)
Khi đó:
\(T=MA^2+MB^2+MC^2+MD^2=\left(\overrightarrow{MI}+\overrightarrow{IA}\right)^2+\left(\overrightarrow{MI}+\overrightarrow{IB}\right)^2+\left(\overrightarrow{MI}+\overrightarrow{IC}\right)^2+\left(\overrightarrow{MI}+\overrightarrow{ID}\right)^2\)
\(=4MI^2+IA^2+IB^2+IC^2+ID^2+2\overrightarrow{MI}\left(\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{IC}+\overrightarrow{ID}\right)\)
\(=4MI^2+IA^2+IB^2+IC^2+ID^2\) (do \(\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{IC}+\overrightarrow{ID}=\overrightarrow{0}\))
\(IA^2+IB^2+IC^2+ID^2\) cố định nên \(T_{min}\) khi \(MI_{min}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow M\) trùng I
\(\Rightarrow M\left(-\dfrac{5}{4};\dfrac{5}{4};6\right)\Rightarrow x+y+z=-\dfrac{5}{4}+\dfrac{5}{4}+6=6\)
24.
\(a+b=4\Rightarrow b=4-a\)
ABCD là hình chữ nhật \(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AB}=\overrightarrow{DC}\)
\(\Rightarrow C\left(a;a;0\right)\)
Tương tự ta có: \(C'\left(a;a;b\right)\)
M là trung điểm CC' \(\Rightarrow M\left(a;a;\dfrac{b}{2}\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{A'B}=\left(a;0;-b\right)=\left(a;0;a-4\right)\\\overrightarrow{A'D}=\left(0;a;-b\right)=\left(0;a;a-4\right)\\\overrightarrow{A'M}=\left(a;a;-\dfrac{b}{2}\right)=\left(a;a;\dfrac{a-4}{2}\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo công thức tích có hướng:
\(\left[\overrightarrow{A'B};\overrightarrow{A'D}\right]=\left(-a^2+4a;-a^2+4a;a^2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow V=\dfrac{1}{6}\left|\left[\overrightarrow{A'B};\overrightarrow{A'D}\right].\overrightarrow{A'M}\right|=\dfrac{1}{6}\left|a\left(-a^2+4a\right)+a\left(-a^2+4a\right)+\dfrac{a^2\left(a-4\right)}{2}\right|\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left|a^3-4a^2\right|=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(4a^2-a^3\right)\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(a\right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(4a^2-a^3\right)\) trên \(\left(0;4\right)\)
\(f'\left(a\right)=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(8a-3a^2\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}a=0\left(loại\right)\\a=\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)_{max}=f\left(\dfrac{8}{3}\right)=\dfrac{64}{27}\)

11.
Đường tròn (C) tâm \(I\left(4;3\right)\) bán kính \(R=\sqrt{2}\)
\(d\left(I;\Delta\right)=\dfrac{\left|4+3-11\right|}{\sqrt{1^2+1^2}}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow d\left(M;\Delta\right)_{max}=R+d\left(I;\Delta\right)=\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{2}=3\sqrt{2}\)