Giúp mk với đang cần gấp , chỉ cần câu2 phần b thoi nhoa
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Cho \(\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x-3=0\\3x-5=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x=3\\3x=5\end{cases}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3}{2}\\x=\frac{5}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(x\in\left\{\frac{3}{2};\frac{5}{3}\right\}\)
\(\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x-5\right)\)
Đa thức có nghiệm : \(\left(2x-3\right)\left(3x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-3=0\\3x-5=0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x=3\\3x=5\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3}{2}\\x=\frac{5}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Kết luận : Vậy nghiệm của đa thức là \(\frac{3}{2}\)và \(\frac{5}{3}\)

1-0 = 1 ; 4-1=3 ; 9-4= 5; ....; 100-81= 19
quy luật là dãy số cách nhau 1 khoảng cách đều là số lẻ
mk nghĩ z
k mk nhé

a. \(y\text{×}\dfrac{1}{5}-\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(y\text{×}\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(y=\dfrac{11}{12}:\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{55}{12}\)
b. \(\dfrac{8}{5}-y:\dfrac{1}{2}=1\)
\(y:\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{8}{5}-1\)
\(y=\dfrac{6}{5}\)
c. \(y\text{×}\dfrac{3}{4}+y\text{×}\dfrac{1}{4}-y=99\)
\(y\text{×}\left(\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}-1\right)=99\)
\(y\text{×}0=99\) (vô lí)
=> Không có giá trị y nào thỏa mãn.
d. \(\dfrac{y}{2}+\dfrac{y}{3}+\dfrac{y}{6}=1\)
\(\dfrac{3\text{×}y+2\text{×}y+y}{6}=\dfrac{6}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow3\text{×}y+2\text{×}y+y=6\)
\(y\text{×}\left(3+2+1\right)=6\) hay \(y\text{×}6=6\)
\(y=1\)
e. \(\dfrac{y}{2}-\dfrac{7}{3}=\dfrac{1}{6}\)
\(\dfrac{y}{2}=\dfrac{1}{6}+\dfrac{7}{3}=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(y=5\)
f. \(\dfrac{15}{y-2}=\dfrac{3}{7}\)
\(\dfrac{15}{y-2}=\dfrac{15}{35}\) \(\Rightarrow y-2=35\)
\(y=37\)
Các bài g, h còn lại bạn làm tương tự như bài f.

☘ Trả lời :
- Từ ngày 13 tháng 3 năm 1954 đến ngày 7 tháng 5 năm 1954 .

a) 1515/3030 = 1/2 × 100% = 50%
b)
*) 2 + 3/4 = 11/4
3 + 4/7 = 25/7
11/4 × 100% : 25/7 = 77%
*) 25/40 = 25 × 100% : 40 = 62,5%
*) 1,6/80 = 1,6 × 100% : 80 = 2%
a, \(\dfrac{1515}{3030}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) = 0,5 = 50%
b, 2 + \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) = \(\dfrac{11}{4}\)
3 + \(\dfrac{4}{7}\) = \(\dfrac{25}{7}\)
Tỉ số phần trăm của 2 + \(\dfrac{3}{4}\) và 3 + \(\dfrac{4}{7}\) là:
\(\dfrac{11}{4}\) : \(\dfrac{25}{7}\) = 0,77
0,77 = 77%
Tỉ số phần trăm của 25 và 40 là:
25: 40 = 0,625
0,625 = 62,5%
Tỉ số phần trăm của 1,6 và 80 là:
1,6 : 80 = 0,02
0,02 = 2%
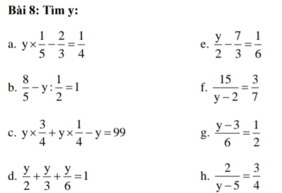

Phương trình có 2 nghiệm dương pb khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m-5\right)>0\\x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)>0\\x_1x_2=2m-5>0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2+6>0\\m>-1\\m>\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow m>\dfrac{5}{2}\)
Khi đó:
\(\left|\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_1}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x_2}}\right|=\sqrt{6}\Rightarrow\left|\dfrac{\sqrt{x_1}-\sqrt{x_2}}{\sqrt{x_1x_2}}\right|=\sqrt{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x_1}-\sqrt{x_2}\right)^2}{x_1x_2}=6\Rightarrow x_1+x_2-2\sqrt{x_1x_2}=6x_1x_2\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(m+1\right)-2\sqrt{2m-5}=6\left(2m-5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(2m-5\right)+2\sqrt{2m-5}-7=0\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2m-5}=t>0\Rightarrow5t^2+2t-7=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=1\\t=-\dfrac{7}{5}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{2m-5}=1\Rightarrow2m-5=1\)
\(\Rightarrow m=3\) (thỏa mãn)