ài 11: Cho biểu thức .A=x+15/x^2-9 + 2/x+3
a, Rút gọn .A
b, Tìm x để A có giá trị bằng .-1/2
c, Tìm số tự nhiên x để A có giá trị nguyên.
giúp mình với
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

`B17:`
`a)` Với `x \ne +-3` có:
`A=[x+15]/[x^2-9]+2/[x+3]`
`A=[x+15+2(x-3)]/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`A=[x+15+2x-6]/[(x-3)(x+3)]`
`A=[3x+9]/[(x-3)(x+3)]=3/[x-3]`
`b)A=[-1]/2<=>3/[x-3]=-1/2<=>-x+3=6<=>x=-3` (ko t/m)
`=>` Ko có gtr nào của `x` t/m
`c)A in ZZ<=>3/[x-3] in ZZ`
`=>x-3 in Ư_3`
Mà `Ư_3={+-1;+-3}`
`@x-3=1=>x=4`
`@x-3=-1=>x=2`
`@x-3=3=>x=6`
`@x-3=-3=>x=0`
________________________________
`B18:`
`a)M=1/3` `ĐK: x \ne +-4`
`<=>(4/[x-4]-4/[x+4]).[x^2+8x+16]/32=1/3`
`<=>[4(x+4)-4(x-4)]/[(x-4)(x+4)].[(x+4)^2]/32=1/3`
`<=>32/[x-4].[x+4]/32=1/3`
`<=>3x+12=x-4`
`<=>x=-8` (t/m)

a) Ta có: \(A=\left(1+\dfrac{x^2}{x^2+1}\right):\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{x^3+x-x^2-1}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x^2+1}:\dfrac{x^2+1-2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x^2+1}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x-1}\)
b) Thay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\) vào A, ta được:
\(A=\left(2\cdot\dfrac{1}{4}+1\right):\left(\dfrac{-1}{2}-1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2}:\dfrac{-3}{2}=-1\)
c) Để A<1 thì A-1<0
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x-1}-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2+1-x+1}{x-1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2-x+2}{x-1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\)
hay x<1

a: DKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-3\right\}\)
b: \(A=\left(\dfrac{x}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{-1}{x-3}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x+3}{3}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-x-3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+3}{3}=\dfrac{-1}{x-3}\)
c: Thay x=5 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\dfrac{-1}{5-3}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
d: Để A là số nguyên thì \(x-3\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{4;2\right\}\)
ab, đk x khác 3 ; -3
\(A=\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-9}-\dfrac{1}{x-3}\right):\dfrac{3}{x+3}\Leftrightarrow=\left(\dfrac{x-x-3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\right):\dfrac{3}{x+3}=-\dfrac{1}{x-3}\)
c, x^2 - 8x + 15 = 0 <=> (x-3)(x-5) = 0 <=> x = 3 (ktm) ; x= 5
Thay x = 5 vào A ta được : A =-1/2
d, \(\Rightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(-1\right)=\left\{\pm1\right\}\)
TH1 : x - 3 = 1 <=> x = 4
TH2 : x - 3 = -1 <=> x = 2

a: \(A=\left(2x-1\right)\left(4x^2+2x+1\right)-7\left(x^3+1\right)\)
\(=\left(2x\right)^3-1^3-7x^3-7\)
\(=8x^3-1-7x^3-7=x^3-8\)
b: Thay x=-1/2 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3-8=-\dfrac{1}{8}-8=-\dfrac{65}{8}\)

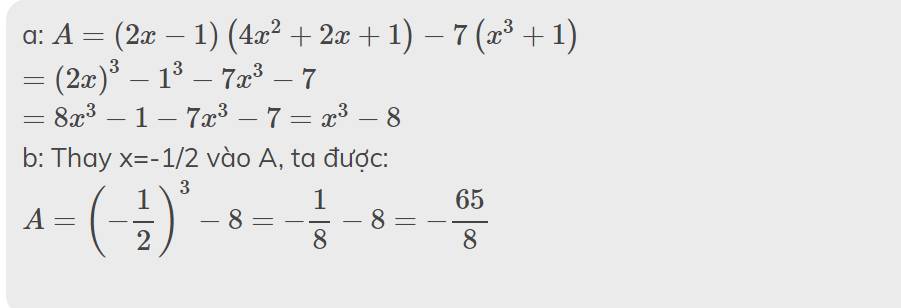
c: \(A=x^3-8=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)\)
Để A là số nguyên tố thì x-2=1
=>x=3

a: \(P=\dfrac{x^2+x-x^2+x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)

Lời giải:
a. Để A là số nguyên tố thì 1 trong 2 thừa số $x-2, x+4$ có giá trị bằng 1 và số còn lại là số nguyên tố.
Mà $x-2< x+4$ nên $x-2=1$
$\Rightarrow x=3$
Thay vào $A$ thì $A=7$ là snt (thỏa mãn)
b. Để $A<0\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x+4)<0$
Điều này xảy ra khi $x-2,x+4$ trái dấu. Mà $x-2< x+4$ nên:
$x-2<0< x+4$
$\Rightarrow -4< x< 2$
$x$ nguyên nên $x=-3,-2,-1,0,1$
a: \(A=\dfrac{x+15+2x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{3x+9}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{3}{x-3}\)