Cho A= 5x - 2 - |2x+ 1|
a) Rút gọn biểu thức A
b) Tìm x để A=2
c) Tìm x để A >0
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a)*TH1: 2x+1>0 .Suy ra: |2x+1|=2x+1. Suy ra A=5x-2-2x-1=5x-2x-2-1=3x-3
*TH2: 2x+1<0. Suy ra: |2x+1|=-2x-1. Suy ra: A= 5x-2+2x+1=5x+2x-2+1=7x-1
b) Ta có: A>0.Suy ra: 5x-2>|2x+1|. Suy ra: 5x-2>0. Suy ra:5x>2. Suy ra x>2/5.
Vậy, nếu x>2/5 thì A>0.

a) A = 5x - 2 - |2x + 1|
A = 5x - 1 - 2x - 1
A = 3x - 3
b) A = 3x - 3 = 2
3x = 2 + 3
3x = 5
x = 5/3
c) 3x > 3
x > 1

a) Ta có: \(A=\left(1+\dfrac{x^2}{x^2+1}\right):\left(\dfrac{1}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{x^3+x-x^2-1}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x^2+1}:\dfrac{x^2+1-2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x^2+1}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x-1}\)
b) Thay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\) vào A, ta được:
\(A=\left(2\cdot\dfrac{1}{4}+1\right):\left(\dfrac{-1}{2}-1\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{2}:\dfrac{-3}{2}=-1\)
c) Để A<1 thì A-1<0
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2+1}{x-1}-1< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2+1-x+1}{x-1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x^2-x+2}{x-1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\)
hay x<1

a: \(A=\left(2x-1\right)\left(4x^2+2x+1\right)-7\left(x^3+1\right)\)
\(=\left(2x\right)^3-1^3-7x^3-7\)
\(=8x^3-1-7x^3-7=x^3-8\)
b: Thay x=-1/2 vào A, ta được:
\(A=\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^3-8=-\dfrac{1}{8}-8=-\dfrac{65}{8}\)

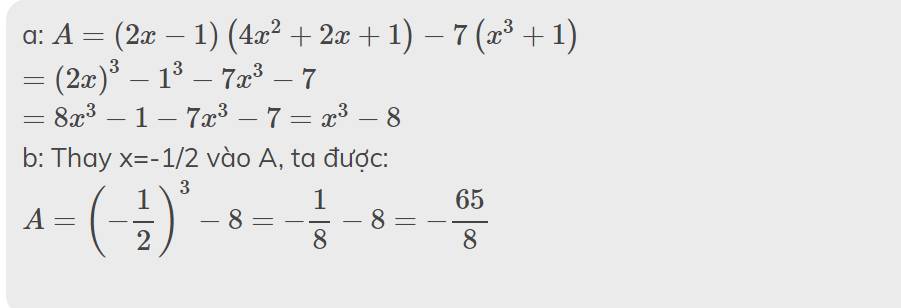
c: \(A=x^3-8=\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+4\right)\)
Để A là số nguyên tố thì x-2=1
=>x=3

a: \(P=\dfrac{x\left(x+2\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}-\dfrac{5x-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50-5x+50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)

Bài 1:
a) Ta có: \(P=1+\dfrac{3}{x^2+5x+6}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^3-8x^2}-\dfrac{3x}{3x^2-12}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{8x^2}{4x^2\left(x-2\right)}-\dfrac{3x}{3\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\left(\dfrac{4}{x-2}-\dfrac{x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{4\left(x+2\right)-x-\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{4x+8-x-x+2}\)
\(=1+3\cdot\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=1+\dfrac{3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)+3\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+10x+6x+30+3x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+19x-6}{\left(x+3\right)\left(2x+10\right)}\)
a.
TH1: 2x+1>=0 => x >=1/2
=>5x-2-(2x+1)
=5x-2-2x-1
=3x-2
TH2:2x+1<0 => x <1/2
=>5x-2- [-(2x-1)]
=5x-2+2x-1
=7x-3
Vậy A=3x-2 khi x>=1/2
A=7x-3 khi x<1/2
b.TH1:x>=1/2
=>A=3x-2
Ta có :
2=3x-2
3x=4
x=4/3 (chọn vì x >= 1/2)
TH2:x <1/2
=>A= 7x-3
Ta có:
2=7x-3
7x=5
=>x=5/7 (loại vì x <1/2)
Vậy x=4/3 thì A=2