Giải phương trình trùng phương: 5 x 4 + 2 x 2 - 16 = 10 - x 2
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,\dfrac{x-3}{x}=\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}\)\(\left(đk:x\ne0,-3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-3}{x}-\dfrac{x-3}{x+3}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)-x\left(x-3\right)}{x\left(x+3\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9-x^2+3x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=3\left(n\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{3\right\}\)
\(b,\dfrac{4x-3}{4}>\dfrac{3x-5}{3}-\dfrac{2x-7}{12}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x-3}{4}-\dfrac{3x-5}{3}+\dfrac{2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3\left(4x-3\right)-4\left(3x-5\right)+2x-7}{12}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x-9-12x+20+2x-7>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+4>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x>-4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)

a) \(3x-2\sqrt{x-1}=4\) (ĐK: x ≥ 1)
\(\Rightarrow3x-2\sqrt{x-1}-4=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-6-2\sqrt{x-1}+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(x-2\right)-2\left(\sqrt{x-1}-1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(x-2\right)-2.\dfrac{x-2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left[3-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}\right]=0\)
*TH1: x = 2 (t/m)
*TH2: \(3-\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x-1}+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{x-1}+3=2\)
\(\Rightarrow3\sqrt{x-1}=-1\) (vô lí)
Vậy S = {2}
b) \(\sqrt{4x+1}-\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{3-x}\) (ĐK: \(-\dfrac{1}{4}\le x\le3\) )
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{4x+1}-3-\sqrt{x+2}+2-\sqrt{3-x}+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{4x-8}{\sqrt{4x+1}+3}-\dfrac{x-2}{\sqrt{x+2}+2}+\dfrac{x-2}{\sqrt{3-x}+1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(\dfrac{4}{\sqrt{4x+1}+3}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+2}+2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3-x}+1}\right)=0\)
=> x = 2
\(a,3x-2\sqrt{x-1}=4\left(x\ge1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{x-1}=4-3x\\ \Leftrightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=16-24x+9x^2\\ \Leftrightarrow9x^2-28x+20=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(9x-10\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{10}{9}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,\sqrt{4x+1}-\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{3-x}\left(-\dfrac{1}{4}\le x\le3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow4x+1+x+2-2\sqrt{\left(4x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=3-x\\ \Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{\left(4x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=2-6x\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{4x^2+9x+2}=3x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow4x^2+9x+2=9x^2-6x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow5x^2-15x-1=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\Delta=225+20=245\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{15-\sqrt{245}}{10}=\dfrac{15-7\sqrt{5}}{10}\left(ktm\right)\\x=\dfrac{15+\sqrt{245}}{10}=\dfrac{15+7\sqrt{5}}{10}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{15+7\sqrt{5}}{10}\)

a) 16 - 3x = 4
<=> 3x = 12
<=> x = 4
Vậy x = 4 là nghiệm phương trình
b) (x2 - 4x + 5)2 - (x - 1)(x - 3) = 4
<=> (x2 - 4x + 5)2 - 4 - (x - 1)(x - 3) = 0
<=> (x2 - 4x + 5 - 2)(x2 - 4x + 5 + 2) - (x - 1)(x - 3) = 0
<=> (x2 - 4x + 3)(x2 - 4x + 7) - (x - 1)(x - 3) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x - 3)(x2 - 4x + 7) - (x - 1)(x - 3) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x - 3)(x2 - 4x + 6) = 0
<=> (x - 1)(x - 3) = 0 (Vì x2 - 4x + 6 > 0 \(\forall x\))
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x-3=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=3\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x \(\in\left\{1;3\right\}\)là nghiệm phương trình
a)16-3x=4
3x=16-4
3x=12
x=4
Vậy x=4
b)(x2-4x+5)2-(x-1).(x-3)=4
[(x-2)2+1]2-[(x-2)+1].[(x-2)-1]=4
=>(x-2)2+2.(x-2).1+1-(x-2)2-12=4
2(x-2)=4
=>x-2=2
=>x=4
Vậy ....................
Chú bn học tốt

a) \(x^2-4x+4=25\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=25\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=-5\\x-2=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\\x=7\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(\left(5-2x\right)^2-16=0\\ \Rightarrow\left(5-2x\right)^2=16\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5-2x=-4\\5-2x=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4,5\\0,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
c) \(\left(x-3\right)^3-\left(x-3\right)\left(x^2+3x+9\right)+9\left(x+1\right)^2=15\\ \Rightarrow\left(x-3\right)^3-\left(x-3\right)^3+9\left(x+1\right)^2=15\\ \Rightarrow9\left(x+1\right)^2=15\\ \Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2=\dfrac{5}{3}\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x+1=-\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{3}}\\x+1=\sqrt{\dfrac{5}{3}}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{3+\sqrt{15}}{3}\\x=\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{15}}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
a)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x^2-4x-21=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x^2-7x+3x-21=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x(x-7)+3(x-7)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\((x-7)(x+3)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[\begin{array}{} x=7\\ x=-3 \end{array} \right.\)
b)\(\Leftrightarrow\)\((5-2x)^2-4^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\((5-2x-4)(5-2x+4)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\((-2x+1)(-2x+9)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(\left[\begin{array}{} x=\dfrac{1}{2}\\ x=\dfrac{9}{2} \end{array} \right.\)

1. Ta có \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+6\right)\left(x+8\right)+16=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(\left[\left(x+2\right)\left(x+8\right)\right].\left[\left(x+4\right)\left(x+6\right)\right]+16=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2+10x+16\right)\left(x^2+10x+24\right)+16=0\)
Đặt \(x^2+10x=t\)
Pt \(\Leftrightarrow\left(t+16\right)\left(t+24\right)+16=0\Leftrightarrow t^2+40t+400=0\Leftrightarrow t=-20\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+10x+20=0\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-5+\sqrt{5}\\x=-5-\sqrt{5}\end{cases}}\)
2. Ta có \(\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)-24=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[\left(x+2\right)\left(x+5\right)\right].\left[\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)\right]-24=0\)\(\Rightarrow\left(x^2+7x+10\right)\left(x^2+7x+12\right)-24=0\)
Đặt \(x^2+7x=t\Rightarrow\left(t+10\right)\left(t+12\right)-24=0\Rightarrow t^2+22t+96=0\)\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=-6\\t=-16\end{cases}}\)
Với \(t=-6\Rightarrow x^2+7x+6=0\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-6\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
Với \(t=-16\Rightarrow x^2+7x+16=0\left(l\right)\)
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm là \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-6\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
Quản lí Hoàng Thị Lan Hương giúp em giải bài toán vừa đăng lên đc ko ạ.??? ^^
Giải phương trình: \(\frac{x^2}{9}+\frac{16}{x^2}=\frac{10}{3}\left(\frac{x}{3}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\)

Điều kiện:\(x\ne0\)
Đặt \(\frac{x}{3}-\frac{4}{x}=t\).Ta có:\(t^2=\left(\frac{x}{3}-\frac{4}{x}\right)^2=\frac{x^2}{9}-2.\frac{x}{3}.\frac{4}{x}+\frac{16}{x^2}=\frac{x^2}{9}+\frac{16}{x^2}-\frac{8}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x^2}{9}+\frac{16}{x^2}=t^2+\frac{8}{3}\).Thay vào pt ta có:\(t^2+\frac{8}{3}=\frac{10}{3}.t\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3t^2-10t+8=0\)\(\Leftrightarrow3t^2-4t-6t+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t\left(3t-4\right)-2\left(3t-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(t-2\right)\left(3t-4\right)=0\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=2\\t=\frac{4}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Với \(t=2\) thì \(\frac{x^2-12}{3x}=2\Leftrightarrow x^2-12-6x=0\)\(\Rightarrow x^2-6x+9-21=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2=21\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-3=\sqrt{21}\\x-3=-\sqrt{21}\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{21}+3\\x=3-\sqrt{21}\end{cases}}\)
Với \(t=\frac{4}{3}\) thì \(\frac{x^2-12}{3x}=\frac{4}{3}\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x-12=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)\left(x-6\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-2\\x=6\end{cases}}\)
Tập nghiệm của pt S=\(\left\{\sqrt{21}+3;3-\sqrt{21};-2;6\right\}\)

\(\frac{x^2}{9}+\frac{16}{x^2}=\frac{10}{3}\left(\frac{x}{3}-\frac{4}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^2}{9}-\frac{10x}{9}+\frac{40}{3x}+\frac{16}{x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{x^4-10x^3+120x+144}{9x^2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-10x^3+120x+144=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-6x^3-12x^2-4x^3+24x^2+48x-12x^2+72x+144=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2-6x-12\right)-4x\left(x^2-6x-12\right)-12\left(x^2-6x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-4x-12\right)\left(x^2-6x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2x-6x-12\right)\left(x^2-6x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[x\left(x+2\right)-6\left(x+2\right)\right]\left(x^2-6x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-6\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-6x-12\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x-6=0\\x+2=0\\x^2-6x-12=0\left(1\right)\end{array}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\begin{array}{nghiempt}x=6\\x=-2\end{array}\right.\)(tm)
\(\Delta_{\left(1\right)}=\left(-6\right)^2-\left(-4\left(1.12\right)\right)=84\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(x_{1,2}=\frac{6\pm\sqrt{84}}{2}\) (tm)
Vậy pt có nghiệm là \(x=-2;x=6\)và \(x=\frac{6\pm\sqrt{84}}{2}\)
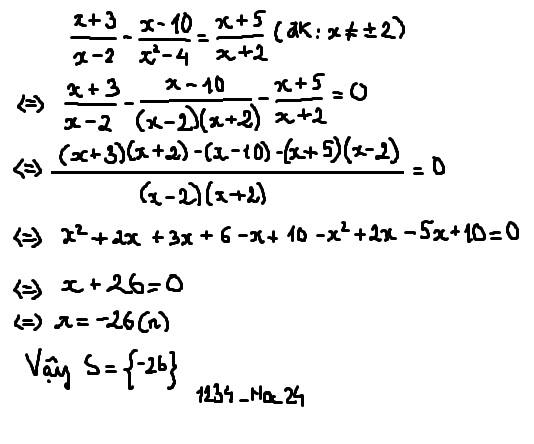
5x4 + 2x2 – 16 = 10 – x2
⇔ 5x4 + 2x2 – 16 – 10 + x2 = 0
⇔ 5x4 + 3x2 – 26 = 0 (1)
Đặt x2 = t, điều kiện t ≥ 0.
Khi đó (1) trở thành : 5t2 + 3t – 26 = 0 (2)
Giải (2) :
Có a = 5 ; b = 3 ; c = -26
⇒ Δ = 32 – 4.5.(-26) = 529 > 0
⇒ Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Đối chiếu điều kiện chỉ có t1 = 2 thỏa mãn
+ Với t = 2 ⇒ x2 = 2 ⇒ x = √2 hoặc x = -√2.
Vậy phương trình (1) có tập nghiệm S = {-√2; √2}