Giải hệ phương trình sau
3 x + y = 5 3 − x = y
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\left(x+y\right)+3\left(x-y\right)=4\\2\left(x+y\right)+4\left(x-y\right)=10\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=6\\2\left(x+y\right)+24=10\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=6\\x+y=-7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\y=-\dfrac{13}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{x+y}{5}=\dfrac{x-y}{3}\\\dfrac{x}{4}=\dfrac{y}{2}+1\end{matrix}\right.\)<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+3y=5x-5y\\x=2y+4\end{matrix}\right.\)<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-8y=0\\x-2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-4y=0\\x-2y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)<=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\x=8\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-5\right)\left(y-2\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(y-1\right)\\\left(x-4\right)\left(y+7\right)=\left(x-3\right)\left(y+4\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}xy-2x-5y+10=xy-x+2y-2\\xy+7x-4y-28=xy+4x-3y-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+7y=12\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x+21y=36\\3x-y=16\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}22y=20\\x+7y=12\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{62}{11}\\y=\dfrac{10}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

x+y+xy=5
<=> x+1+y+xy=6
<=>(x+1)+y(x+1)=6
<=>(x+1)(y+1)=6
Đật X+1 =a và y+1=b ta được:
a+b=6 và a3+b3=35
<=>a3b3=216 và a3+b3=35
Theo hệ thức Vi-ét ta có a, b là nghiệm của phương trình:
X2-35X+216=0
<=> X=27 hoặc X=8
=> a3=27;b3=8 hoặc a3=8;b3=27
<=>a=3; b=2 hoặc a=2;b=3
TH1: a=3;b=2
=> x+1=3 và y+1=2
<=>x=2 và y=1
TH2:a=2 và b=2
=>x+1=2 và y+1=3
<=>x=1 và y=2
Vậy,hpt đã cho có 2 cặp nghiệm (x,y) là (2;1) ; (1;2)

Lấy phương trình (2) trừ phương trình (1), vế trừ vế ta được:
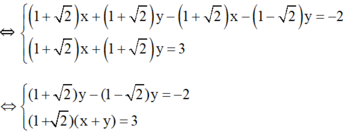
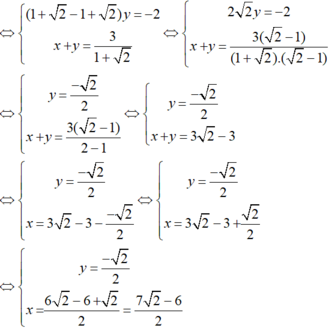
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất 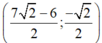
Lưu ý:
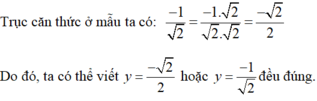
Kiến thức áp dụng
Giải hệ phương trình bằng phương pháp cộng đại số
1) Nhân hai vế của phương trình với mỗi hệ số thích hợp (nếu cần) sao cho hệ số của một trong hai ẩn bằng nhau hoặc đối nhau.
2) Áp dụng quy tắc cộng đại số để được hệ phương trình mới, trong đó có một phương trình mà hệ số của một trong hai ẩn bằng 0 (tức là phương trình một ẩn).
3) Giải phương trình một ẩn vừa thu được rồi suy ra nghiệm của hệ đã cho và kết luận.

Đặt \(x+\dfrac{1}{x}=a;y+\dfrac{1}{y}=b\left(\left|a\right|\ge2;\left|b\right|\ge2\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}+y+\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\x^3+y^3+\dfrac{1}{x^3}+\dfrac{1}{y^3}=15m-25\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}+y+\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\\left(x^3+\dfrac{1}{x^3}\right)+\left(y^3+\dfrac{1}{y^3}\right)=15m-25\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}+y+\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)^3-3\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)+\left(y+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)^3-3\left(y+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)=15m-25\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}+y+\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)^3+\left(y+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)^3-3\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}+y+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)=15m-25\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}+y+\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)^3+\left(y+\dfrac{1}{y}\right)^3=15m-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=5\\a^3+b^3=15m-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=5\\\left(a+b\right)^3-3ab\left(a+b\right)=15m-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=5\\125-15ab=15m-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=5\\ab=9-m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow a,b\) là nghiệm của phương trình \(t^2-5t+9-m=0\left(1\right)\)
a, Nếu \(m=3\), phương trình \(\left(1\right)\) trở thành
\(t^2-5t+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=2\\t=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b=3\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=3\\b=2\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}=2\\y+\dfrac{1}{y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x-1\right)^2=0\\y^2-3y+1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=\dfrac{3\pm\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}=3\\y+\dfrac{1}{y}=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3\pm\sqrt{5}}{2}\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...
b, \(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow t=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{4m-11}}{2}\left(m\ge\dfrac{11}{4}\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{4m-11}}{2}\\b=\dfrac{5\mp\sqrt{4m-11}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{4m-11}}{2}\\y+\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{5\mp\sqrt{4m-11}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2-\left(5\pm\sqrt{4m-11}\right)+2=0\left(2\right)\\2y^2-\left(5\mp\sqrt{4m-11}\right)+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Yêu cầu bài toán thỏa mãn khi phương trình \(\left(2\right)\) có nghiệm dương
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta=\left(5\pm\sqrt{4m-11}\right)^2-16\ge0\\\dfrac{5\pm\sqrt{4m-11}}{2}>0\\1>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow...\)

\(ĐK:x,y\ne0\\ HPT\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{2}{y}=4\\\dfrac{2}{x}+\dfrac{3}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}+1=2\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\left(tm\right)\)


Từ phương trình (2) thay y= 3-x vào phương trình (1) ta được: 3 x + 3 − x = 5 ⇔ x = 1 .
Với x = 1 ⇒ y = 2 .Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm: x = 1 y = 2