Cho hai đa thức
P ( x ) = - 5 x 3 - 2 x + 4 x 4 + 3 + 3 x 2 - 4 x 4 + 10 x 3 - 8 , Q ( x ) = 6 x 2 + 5 x 3 - 3 x 5 + 4 + 8 x - 4 x 2 + 3 x 5 - 10 x
b. Tính M ( x ) = P ( x ) + Q ( x ) ; N ( x ) = P ( x ) - Q ( x )
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \(M(x) = A(x) + B(x) \\= 4{x^4} + 6{x^2} - 7{x^3} - 5x - 6 - 5{x^2} + 7{x^3} + 5x + 4 - 4{x^4} \\=(4x^4-4x^4)+(-7x^3+7x^3)+(6x^2-5x^2)+(-5x+5x)+(-6+4)\\= {x^2} - 2.\)
b) \(A(x) = B(x) + C(x) \Rightarrow C(x) = A(x) - B(x)\)
\(\begin{array}{l}C(x) = A(x) - B(x)\\ = 4{x^4} + 6{x^2} - 7{x^3} - 5x - 6 - ( - 5{x^2} + 7{x^3} + 5x + 4 - 4{x^4})\\ = 4{x^4} + 6{x^2} - 7{x^3} - 5x - 6 + 5{x^2} - 7{x^3} - 5x - 4 + 4{x^4}\\ =(4x^4+4x^4)+(-7x^3-7x^3)+(6x^2+5x^2)+(-5x-5x)+(-6-4)\\= 8{x^4} - 14{x^3} + 11{x^2} - 10x - 10\end{array}\)

B(3)=2*3^2-4*3+3=18-12+3=9
B(-1/2)=2*1/4-4*(-1/2)+3=1/2+3+2=1/2+5=11/2

a)
\(\begin{array}{l}A(x) = {x^3} + \dfrac{3}{2}x - 7{x^4} + \dfrac{1}{2}x - 4{x^2} + 9\\ = - 7{x^4} + {x^3} - 4{x^2} + \left( {\dfrac{3}{2}x + \dfrac{1}{2}x} \right) + 9\\ = - 7{x^4} + {x^3} - 4{x^2} + 2x + 9\\B(x) = {x^5} - 3{x^2} + 8{x^4} - 5{x^2} - {x^5} + x - 7\\ = \left( {{x^5} - {x^5}} \right) + 8{x^4} + \left( { - 3{x^2} - 5{x^2}} \right) + x - 7\\ = 0 + 8{x^4} + ( - 8{x^2}) + x - 7\\ = 8{x^4} - 8{x^2} + x - 7\end{array}\)
b) * Đa thức A(x):
+ Bậc của đa thức là: 4
+ Hệ số cao nhất là: -7
+ Hệ số tự do là: 9
* Đa thức B(x):
+ Bậc của đa thức là: 4
+ Hệ số cao nhất là: 8
+ Hệ số tự do là: -7

a)
\(\begin{array}{l}P(x) = 5{x^3} + 2{x^4} - {x^2} + 3{x^2} - {x^3} - 2{x^4} - 4{x^3}\\ = \left( {2{x^4} - 2{x^4}} \right) + \left( {5{x^3} - {x^3} - 4{x^3}} \right) + \left( { - {x^2} + 3{x^2}} \right)\\ = 0 + 0 + 2{x^2}\\ = 2{x^2}\\Q(x) = 3x - 4{x^3} + 8{x^2} - 5x + 4{x^3} + 5\\ = \left( { - 4{x^3} + 4{x^3}} \right) + 8{x^2} + \left( {3x - 5x} \right) + 5\\ = 0 + 8{x^2} + ( - 2x) + 5\\ = 8{x^2} - 2x + 5\end{array}\)
b) P(1) = 2.12 = 2
P(0) = 2. 02 = 0
Q(-1) = 8.(-1)2 – 2.(-1) +5 = 8 +2 +5 =15
Q(0) = 8.02 – 2.0 + 5 = 5

\(\begin{array}{l}A + B = (6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3}) + ( - 3{x^4} - 2{x^3} - 5{x^2} + x + \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3} - 3{x^4} - 2{x^3} - 5{x^2} + x + \dfrac{2}{3}\\ = (6{x^4} - 3{x^4}) + ( - 4{x^3} - 2{x^3}) - 5{x^2} + (x + x) + ( - \dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 3{x^4} - 6{x^3} - 5{x^2} + 2x + \dfrac{1}{3}\\A - B = (6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3}) - ( - 3{x^4} - 2{x^3} - 5{x^2} + x + \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3} + 3{x^4} + 2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - \dfrac{2}{3}\\ = (6{x^4} + 3{x^4}) + ( - 4{x^3} + 2{x^3}) + 5{x^2} + (x - x) + ( - \dfrac{1}{3} - \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 9{x^4} - 2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - 1\end{array}\)\(\begin{array}{l}A + B = (6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3}) + ( - 3{x^4} - 2{x^3} - 5{x^2} + x + \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3} - 3{x^4} - 2{x^3} - 5{x^2} + x + \dfrac{2}{3}\\ = (6{x^4} - 3{x^4}) + ( - 4{x^3} - 2{x^3}) - 5{x^2} + (x + x) + ( - \dfrac{1}{3} + \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 3{x^4} - 6{x^3} - 5{x^2} + 2x + \dfrac{1}{3}\\A - B = (6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3}) - ( - 3{x^4} - 2{x^3} - 5{x^2} + x + \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 6{x^4} - 4{x^3} + x - \dfrac{1}{3} + 3{x^4} + 2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - x - \dfrac{2}{3}\\ = (6{x^4} + 3{x^4}) + ( - 4{x^3} + 2{x^3}) + 5{x^2} + (x - x) + ( - \dfrac{1}{3} - \dfrac{2}{3})\\ = 9{x^4} - 2{x^3} + 5{x^2} - 1\end{array}\)

a. \(x^4-5x^3+4x-5-x^4+3x^2+2x+1\)
\(=-5x^3+3x^2+6x-4\)
b. \(R\left(x\right)=x^4-5x^3+4x-5-\left(-x^4+3x^2+2x+1\right)\)
\(=x^4-5x^3+4x-5+x^4-3x^2-2x-1\)
\(=2x^4-5x^3-3x^2+2x-6\)
a) �(�)+�(�)P(x)+Q(x)
=(�4−5�3+4�−5)+(−�4+3�2+2�+1)=(x4−5x3+4x−5)+(−x4+3x2+2x+1)
=�4−5�3+4�−5−�4+3�2+2�+1=x4−5x3+4x−5−x4+3x2+2x+1
=(�4−�4)−5�3+3�2+(4�+2�)+(1−5)=(x4−x4)−5x3+3x2+(4x+2x)+(1−5)
=−5�3+3�2+6�−4=−5x3+3x2+6x−4
b) �(�)=�(�)−�(�)R(x)=P(x)−Q(x)
=(�4−5�3+4�−5)−(−�4+3�2+2�+1)=(x4−5x3+4x−5)−(−x4+3x2+2x+1)
=�4−5�3+4�−5+�4−3�2−2�−1=x4−5x3+4x−5+x4−3x2−2x−1
=(�4+�4)−5�3−3�2+(4�−2�)+(−1−5)=(x4+x4)−5x3−3x2+(4x−2x)+(−1−5)
=2�4−5�3−3�2+2�−6=2x4−5x3−3x2+2x−6

Tham khảo:
Cách 1 :
Ta có P(x) - Q(x)
= 2x3 – 9x2 + 5 – (2x2 + 4x3 – 7x)
= 2x3 – 9x2 + 5 – 2x2 – 4x3 + 7x
= (2x3 – 4x3) + (-9x2 – 2x2) + 7x + 5
= -2x3 – 11x2 + 7x + 5
Cách 2 :
P(x) = 2x3 – 9x2 + 5
Q(x) = 4x3 + 2x2 – 7x
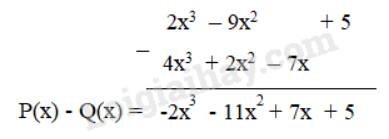

Để thu gọn và sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức, ta cần thực hiện các bước sau:
Đối với đa thức P(x): P(x) = (4x + 1 - x^2 + 2x^3) - (x^4 + 3x - x^3 - 2x^2 - 5) = 4x + 1 - x^2 + 2x^3 - x^4 - 3x + x^3 + 2x^2 + 5 = -x^4 + 3x^3 + x^2 + x + 6
Đối với đa thức Q(x): Q(x) = 3x^4 + 2x^5 - 3x - 5x^4 - x^5 + x + 2x^5 - 1 = 2x^5 - x^5 + 3x^4 - 5x^4 + x - 3x - 1 = x^5 - 2x^4 - 2x - 1
Sau khi thu gọn và sắp xếp các hạng tử, ta có: P(x) = -x^4 + 3x^3 + x^2 + x + 6 Q(x) = x^5 - 2x^4 - 2x - 1
a: \(P\left(x\right)=\left(4x+1-x^2+2x^3\right)-\left(x^4+3x-x^3-2x^2-5\right)\)
\(=4x+1-x^2+2x^3-x^4-3x+x^3+2x^2+5\)
\(=-x^4+3x^3+x^2+x+6\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=3x^4+2x^5-3x-5x^4-x^5+x+2x^5-1\)
\(=\left(2x^5-x^5+2x^5\right)+\left(3x^4-5x^4\right)+\left(-3x+x\right)-1\)
\(=-x^5-2x^4-2x-1\)
b: Bạn ghi lại đề đi bạn
b. M(x) = P(x) + Q(x) = 10x3 + 5x2 - 4x - 1 (0.5 điểm)
N(x) = P(x) - Q(x) = x2 - 9 (0.5 điểm)