Nếu x+y+z=π/2
Cot x + cot y = 2cot z
Thì cot x . Coty = ?
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a.
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(3x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\ne0\\cos2x\ne0\\sinx\ne-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{18}+\dfrac{k\pi}{3}\\x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{4}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
b.
Do \(5+2cot^2x-sinx=4+2cot^2x+\left(1-sinx\right)>0\) nên hàm xác định khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinx\ne0\\sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}sinx\ne0\\cosx\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow sin2x\ne0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ne\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\)

Chọn A.
Đặt t = cot x, 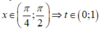
Ta có: ![]()
Để hàm số
c
o
t
x
-
2
c
o
t
x
-
m
nghịch biến trên 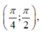 thì hàm số
thì hàm số 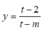 đồng biến trên (0;1)
đồng biến trên (0;1)
Xét hàm số 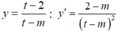
Để hàm số 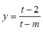 đồng biến trên (0;1) thì
đồng biến trên (0;1) thì 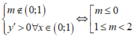

ĐKXĐ:
a. \(cos\left(x-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x-\dfrac{2\pi}{3}\ne\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\Rightarrow x\ne\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
b. \(sin\left(x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\right)\ne0\Rightarrow x+\dfrac{\pi}{6}\ne k\pi\Rightarrow x\ne-\dfrac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\)
c. \(\dfrac{1+x}{2-x}\ge0\Rightarrow-1\le x< 2\)

a, \(\left(1-sin^2x\right)cot^2x+1-cot^2x\)
\(=cot^2x-sin^2x.cot^2x+1-cot^2x\)
\(=1-sin^2x.\frac{\text{cos}^2x}{sin^2x}=1-\text{cos}^2x=sin^2x\)
b,\(\left(tanx+cotx\right)^2-\left(tanx-cotx\right)2\)
\(=tan^2x2.tanx.cotx+cot^2x-tan^2x+2tanx.cotx-cot^2x\)
\(=4tanxcotx=4\)
c,\(\left(xsina-y\text{cos}a\right)^2+\left(x\text{cos}a+ysina\right)^2\)
\(=x^2sin^2a=2xysina\text{cos}a+y^2\text{cos}^2a+2xysina\text{cos}a+y^2sin^2a\)
\(=x^2\left(sin^2a+\text{cos}^2a\right)+y^2\left(sin^2a+\text{cos}^2a\right)\)
\(=x^2+y^2\)

\(\begin{array}{l}f'({x_0}) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{f(x) - f({x_0})}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\cot x - \cot {x_0}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\cot x - \cot {x_0}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\frac{{\cos x}}{{\sin x}} - \frac{{\cos {x_0}}}{{\sin {x_0}}}}}{{x - {x_0}}}\\ = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\frac{{\cos x\sin {x_0} - \cos {x_0}\sin x}}{{\sin x\sin {x_0}}}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} - \frac{1}{{\sin x\sin {x_0}}} = - \frac{1}{{{{\sin }^2}{x_0}}}\\ \Rightarrow f'(x) = (\cot x)' = - \frac{1}{{{{\sin }^2}x}} = \end{array}\)

Đáp án B
+ Xét hàm y = f(x) = cos (x + π)
TXĐ: D = R
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và f(-x) = cos (-x + π) = -cos x = cos (x + π) = f(x)
Do đó y = cos (x + π) là hàm số chẵn .
+ Xét hàm y = g(x) = tan2016x
TXĐ: D = R\{π/2 + kπ, k ∈ Z}
Với mọi x ∈ D, ta có: -x ∈ D và g(-x) = tan2016(-x) = (-tan x)2016 = tan2016x = g(x)
Do đó: y = tan2016x là hàm chẵn trên tập xác định của nó.
+Xét hàm y = cot2x
f(-x) = cot(-2x) = - cot 2x = -f(x) nên đây là hàm số lẻ.
+ Xét hàm số y = 1-sinx
f(-x) = 1- sin(-x) = 1+ sin x
Nên hàm số không chẵn không lẻ
\(x+y+z=\frac{\pi}{2}\Rightarrow x+y=\frac{\pi}{2}-z\)
\(\Rightarrow tan\left(x+y\right)=tan\left(\frac{\pi}{2}-z\right)=cotz\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{tanx+tany}{1-tanx.tany}=cotz\)
Mà \(cotx+coty=2cotz\Rightarrow cotx+coty=\frac{2\left(tanx+tany\right)}{1-tanx.tany}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{tanx}+\frac{1}{tany}=\frac{2\left(tanx+tany\right)}{1-tanx.tany}\Leftrightarrow\frac{tanx+tany}{tanx.tany}=\frac{2\left(tanx+tany\right)}{1-tanx.tany}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{1}{tanx.tany}=\frac{2}{1-tanx.tany}\Leftrightarrow1-tanx.tany=2tanx.tany\)
\(\Rightarrow tanx.tany=\frac{1}{3}\Rightarrow cotx.coty=3\)
Tks !