100ml dung dịch H2SO4 0,1M tác dụng với 100ml KOH 0,1M COI H2SO4 phân li hoàn toàn 2 nấc. tính pH thu được sau phản ứng
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Chọn B
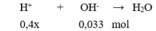
Dung dịch sau phản ứng có pH = 2 < 7 nên dung dịch sau phản ứng có H + dư
→ 0,4x – 0,033 = 10 - 2 .0,3 → x = 0,09

Bài 1.
\(n_{H^+}=2n_{H_2SO_4}=2.10^{-2}.0,1=0,002\) mol
\(n_{OH^-}=n_{NaOH}=0,01.0,1=0,001\) mol
\(H^++OH^-\rightarrow H_2O\)
0,001<-0,001
\(\Rightarrow n_{H^+}\text{còn}=0,002-0,001=0,001\) mol
\(\Rightarrow\left[H^+\right]=\dfrac{0,001}{0,2}=0,005\) mol/lít
\(\Rightarrow pH=-lg\left[H^+\right]=-lg\left(\dfrac{0,001}{0,2}\right)=2,3\)
\(H_2SO_4+2NaOH\rightarrow Na_2SO_4+2H_2O\)
0,0005<--0,001------> 0,001
\(Na_2SO_4\rightarrow2Na^++SO_4^{2-}\)
0,001 ------>0,002-->0,001
\(H_2SO_4\rightarrow2H^++SO_4^{2-}\)
0,0005--->0,001-->0,0005
\(\Rightarrow\left[Na^+\right]=\dfrac{0,002}{0,2}=0,01\) mol/lít; \(\left[SO_4^{2-}\right]=\dfrac{0,001+0,0005}{0,2}=0,0075\) mol/lít
\(\left[H^+\right]=0,005\) mol/lít
Bài 2.
200 ml dung dịch H2SO4 có pH = 1 nên \(\left[H^+\right]=0,1\)M
\(\Rightarrow n_{H^+}=2n_{H_2SO_4}=2.0,1.0,2=0,04\) mol
\(n_{OH^-}=n_{NaOH}=\dfrac{0,88}{40}=0,022\) mol
\(H^++OH^-\rightarrow H_2O\)
0,022<-0,022
\(\Rightarrow n_{H^+}\text{còn}=0,04-0,022=0,018\) mol
\(\Rightarrow pH=-lg\left[H^+\right]=-lg\left(\dfrac{0,018}{0,2}\right)=1,046\)

Đáp án : A
dd X : nH+ = 2nH2SO4 + nHCl = 0,02 mol
dd Y : nOH = nNaOH + 2nBa(OH)2 = 0,04 mol
=> Trong Y : nOH – nH+ = 0,02 mol = nOH- => COH = 0,1M => pH = 13

$n_{Ba^{2+}} = 0,1.0,5 = 0,05 < n_{SO_4^{2-}} = 0,1$ nên $SO_4^{2-}$ dư
$n_{BaSO_4} = n_{Ba^{2+}} = 0,05(mol)$
$m_{BaSO_4} = 0,05.233 = 11,65(gam)$
$n_{OH^-} = 0,1.0,5.2 + 0,1.0,5 = 0,15(mol)$
$n_{H^+} = 0,1.2 = 0,2(mol)$
$H^+ + OH^- \to H_2O$
$n_{H^+\ dư} = 0,2 - 0,15 = 0,05(mol)$
$V_{dd} = 0,1 + 0,1 + 0,1 = 0,3(lít)$
$[H^+] = \dfrac{0,05}{0,3} = \dfrac{1}{6}M$
$pH = -log( \dfrac{1}{6} ) = 0,778$
\(n_{Ba^{2+}}=0.1\cdot0.5=0.05\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{OH^-}=0.1\cdot0.5\cdot2+0.1\cdot0.5=0.15\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{H^+}=2\cdot0.1\cdot1=0.2\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{SO_4^{2-}}=0.1\left(mol\right)\)
\(Ba^{2+}+SO_4^{2-}\rightarrow BaSO_4\)
\(0.05.........0.05.............0.05\)
\(SO_4^{2-}dư\)
\(m_{\downarrow}=0.05\cdot233=11.65\left(g\right)\)
\(H^++OH^-\rightarrow H_2O\)
\(0.15.......0.15\)
\(n_{H^+\left(dư\right)}=0.2-0.15=0.05\left(mol\right)\)
\(\left[H^+\right]=\dfrac{0.05}{0.1+0.1+0.1}=\dfrac{1}{6}\)
\(pH=-log\left(\dfrac{1}{6}\right)=0.77\)

Đáp án C
nH+ = 0,02 mol; nOH-= 0,04 mol
H+ + OH- → H2O
0,02 0,04
nOH- dư = 0,02 mol; [OH-] dư = 0,02/0,2 = 0,1M suy ra [H+] = 10-13 M suy ra pH = 13

Đáp án B
nH+ = 0,05 mol; nOH- = 0,07 mol
H+ + OH- → H2O
Ta thấy H+ hết, OH- dư nên nhúng quỳ tím vào Y thì quỳ tím chuyển thành màu xanh.

Đáp án B
nOH-= 0,03 mol; nBa2+ = 0,01 mol
nH+ = 0,035 mol; nSO4(2-) = 0,015 mol
H+ + OH- → H2O
0,035 0,03
nH+ dư = 5.10-3 mol; [H+] dư = 5.10-3/0,5 = 0,01 suy ra pH = 2
Số mol H+ = 0,1. 0,1 . 2 = 0,02 mol. Số mol OH- = 0,1. 0,1 = 0,01 mol => H+ dư = 0,02 - 0,01 = 0,01 mol. Mà thể tích dung dịch sau pứ = 200 ml = 0,2 l => Nồng độ H+ dư = 0,01: 0,2 = 0,05 mol => pH = -lg0,05 = 1,3