\(\dfrac{2x+19}{21}-\dfrac{2x+17}{23}=\dfrac{2x+7}{33}-\dfrac{2x+5}{35}\) tìm x
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


`@` `\text {Ans}`
`\downarrow`
\(\dfrac{x-3}{3}=\dfrac{2x+1}{5}\)
`=> (x-3)5 = (2x+1)3`
`=> 5x-15 = 6x+3`
`=> 5x-6x = 15+3`
`=> -x=18`
`=> x=-18`
\(\dfrac{x+1}{22}=\dfrac{6}{x}\)
`=> (x+1)x = 22*6`
`=> (x+1)x = 132`
`=> x^2 + x = 132`
`=> x^2+x-132=0`
`=> (x-11)(x+12)=0`
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-11=0\\x+12=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=11\\x=-12\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{2x-1}{2}=\dfrac{5}{x}\)
`=> (2x-1)x = 2*5`
`=> 2x^2 - x =10`
`=> 2x^2 - x - 10 =0`
`=> 2x^2 + 4x - 5x - 10 =0`
`=> (2x^2 + 4x) - (5x+10)=0`
`=> 2x(x+2) - 5(x+2)=0`
`=> (2x-5)(x+2)=0`
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-5=0\\x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=5\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{2x-1}{21}=\dfrac{3}{2x+1}\)
`=> (2x-1)(2x+1)=21*3`
`=> 4x^2 + 2x - 2x - 1 = 63`
`=> 4x^2 - 1=63`
`=> 4x^2 - 1 - 63=0`
`=> 4x^2 - 64 = 0`
`=> 4(x^2 - 16)=0`
`=> 4(x^2 + 4x - 4x - 16)=0`
`=> 4[(x^2+4x)-(4x+16)]=0`
`=> 4[x(x+4)-4(x+4)]=0`
`=> 4(x-4)(x+4)=0`
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\x+4=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{2x+1}{9}=\dfrac{5}{x+1}\)
`=> (2x+1)(x+1) = 9*5`
`=> (2x+1)(x+1)=45`
`=> 2x^2 + 2x + x + 1 = 45`
`=> 2x^2 + 3x + 1 =45`
`=> 2x^2 + 3x + 1 - 45 =0`
`=> 2x^2+3x-44=0`
`=> 2x^2 + 11x - 8x - 44=0`
`=> (2x^2 +11x) - (8x+44)=0`
`=> x(2x+11) - 4(2x+11)=0`
`=> (x-4)(2x+11)=0`
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-4=0\\2x+11=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\2x=-11\end{matrix}\right.\)
`=>`\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{11}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{x-3}{3}=\dfrac{2x+1}{5}\\ \left(x-3\right)\cdot5=\left(2x+1\right)\cdot3\\ x5-15=6x+3\\ x5-6x=3+15\\ -x=18\\ \Rightarrow x=-18\)
\(\dfrac{x+1}{22}=\dfrac{6}{x}\\ \left(x+1\right)\cdot x=6\cdot22\\ \left(x+1\right)\cdot x=2\cdot3\cdot2\cdot11\\ \left(x+1\right)\cdot x=12\cdot11\\ \Rightarrow x=11\)
\(\dfrac{2x-1}{21}=\dfrac{3}{2x+1}\\ \left(2x-1\right)\cdot\left(2x+1\right)=21\cdot3\\ \left(2x-1\right)\cdot\left(2x+1\right)=7\cdot3\cdot3\\ \left(2x-1\right)\cdot\left(2x+1\right)=7\cdot9\\ \Rightarrow2x+1=9\\ 2x=8\\ x=4\)

a. \(\dfrac{5x+2}{6}-\dfrac{8x-1}{3}=\dfrac{4x+2}{5}-5\)
<=> \(5\left(5x+2\right)-10\left(8x-1\right)=6\left(4x+2\right)-6\cdot5\)
<=> \(25x+10-80x+10=24x+12-30\)
<=> \(25x-80x-24x=12-30-10-10\)
<=> \(-79x=-38\)
<=> \(x=\dfrac{-38}{-79}\)
\(x=\dfrac{38}{79}\)
b. \(x-\dfrac{2x-5}{5}+\dfrac{x+8}{6}=7+\dfrac{x-1}{3}\)
<=> \(30\cdot x-6\left(2x-5\right)+5\left(x+8\right)=30\cdot7+10\left(x-1\right)\)
<=> \(30x-12x+30+5x+40=210+10x-10\)
<=> \(30x-12x+5x-10x=210-10-30-40\)
<=> \(13x=130\)
<=> \(x=\dfrac{130}{13}\)
\(x=10\)
c. \(\dfrac{x+1}{15}+\dfrac{x+2}{7}+\dfrac{x+4}{4}+6=0\)
<=> \(28\left(x+1\right)+60\left(x+2\right)+105\left(x+4\right)+420\cdot6=0\)
<=> \(28x+28+60x+120+105x+420+2520=0\)
<=> \(28x+60x+105x=-28-120-420-2520\)
<=> \(193x=-3088\)
<=> \(x=\dfrac{-3088}{193}\)
\(x=-16\)
d. \(\dfrac{x-342}{15}+\dfrac{x-323}{17}+\dfrac{x-300}{19}+\dfrac{x-273}{21}=10\)
<=> \(6783\left(x-342\right)+5985\left(x-323\right)+5355\left(x-300\right)+4845\left(x-273\right)=101745\cdot10\)
<=> \(6783x-2319786+5985x-1933155+5355x-1606500+4845x-1322685=1017450\)
<=> \(6783x+5985x+5355x+4845x=1017450+2319786+1933155+1606500+1322685\)
<=> \(22968x=8199576\)
<=> \(x=\dfrac{8199576}{22968}\)
\(x=357\)

a) \(2x^2+20x+52=0\Rightarrow x^2+10x+26=0\Rightarrow\left(x+5\right)^2+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) vô nghiệm
b) ĐK: \(x\ne1;-1\)
\(\dfrac{2x-19}{5x^2-5}-\dfrac{17}{x-1}=\dfrac{8}{1-x}\Rightarrow\dfrac{2x-19}{5\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{17}{x-1}+\dfrac{8}{x-1}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{2x-19}{5\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{9}{x-1}=0\Rightarrow\dfrac{2x-19-45\left(x+1\right)}{5\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-43x-64=0\Rightarrow x=-\dfrac{64}{43}\)
a) Ta có: \(\Delta'=100-104=-4< 0\)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm.
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne1;x\ne-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-19}{5\left(x^2-1\right)}=\dfrac{17}{x-1}-\dfrac{8}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-19}{5\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{9}{x-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-19}{5\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{45\left(x+1\right)}{5\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-19=45x+45\)
\(\Leftrightarrow43x=-64\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{64}{43}\)(TM)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là: \(x=-\dfrac{64}{43}\)

a: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2\left(2x+3\right)}{4x-6}-\dfrac{3}{4x-6}=\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5\left(4x+6-3\right)}{5\left(4x-6\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(4x-6\right)}{5\left(4x-6\right)}\)
=>5(4x+3)=2(4x-6)
=>20x+15=8x-12
=>12x=-27
hay x=-9/4
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+29}{31}+1-\dfrac{x+27}{33}-1=\dfrac{x+17}{43}+1-\dfrac{x+15}{45}-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+60\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{31}-\dfrac{1}{33}-\dfrac{1}{43}+\dfrac{1}{45}\right)=0\)
=>x+60=0
hay x=-60

a: \(\Leftrightarrow7\left(7-3x\right)+12\left(5x+2\right)=84\left(x+13\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow49-21x+60x+24=84x+1092\)
\(\Leftrightarrow39x-84x=1092-73\)
=>-45x=1019
hay x=-1019/45
b: \(\Leftrightarrow21\left(x+3\right)-14=4\left(5x+9\right)-7\left(7x-9\right)\)
=>21x+63-14=20x+36-49x+63
=>21x+49=-29x+99
=>50x=50
hay x=1
c: \(\Leftrightarrow7\left(2x+1\right)-3\left(5x+2\right)=21x+63\)
=>14x+7-15x-6-21x-63=0
=>-22x-64=0
hay x=-32/11
d: \(\Leftrightarrow35\left(2x-3\right)-15\left(2x+3\right)=21\left(4x+3\right)-17\cdot105\)
=>70x-105-30x-45=84x+63-1785
=>40x-150-84x+1722=0
=>-44x+1572=0
hay x=393/11

1. \(\dfrac{x}{19}=\dfrac{y}{21};2x-y=34\)
Có: \(\dfrac{x}{19}=\dfrac{y}{21}\)
=> \(\dfrac{2x}{38}=\dfrac{y}{21}\)
Theo tính chất dãy tỉ số bằng nhau ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{38}=\dfrac{y}{21}=\dfrac{2x-y}{38-21}=\dfrac{34}{17}=2\)
=> \(\dfrac{x}{19}=2=>x=2.19=38\)
=> \(\dfrac{y}{21}=2=>y=2.21=42\)
Vậy x= 38 ; y= 42
2. \(\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}\);\(2x+3y-z=186\)
Có: \(\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}\)
=> \(\dfrac{2x}{30}=\dfrac{3y}{60}=\dfrac{z}{28}=\dfrac{2x+3y-z}{30+60-28}=\dfrac{186}{62}=3\)
=> \(\dfrac{x}{15}=3=>x=3.15=45\)
=>\(\dfrac{y}{20}=3=>y=3.20=60\)
=> \(\dfrac{z}{28}=3=>z=3.28=84\)
Vậy x=45;y=60;z=84
1) \(\dfrac{x}{19}=\dfrac{y}{21}\) và 2x -y =34
Từ \(\dfrac{x}{19}=\dfrac{y}{21}=>\dfrac{2x}{38}=\dfrac{y}{21}\)
Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau,ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{38}=\dfrac{y}{21}=\dfrac{2x-y}{38-21}=\dfrac{34}{17}=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{38}=2=>2x=2.38=>2x=76=>x=76:2=>x=38\)
=>\(\dfrac{y}{21}=2=>y=2.21=>y=42\)
Vậy x=38; y=42
2)\(\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}\)và 2x+3y-z=186
Từ \(\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}=>\dfrac{2x}{30}=\dfrac{3y}{60}=\dfrac{z}{28}\)
Áp dụng t/c của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau,ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{30}=\dfrac{3y}{60}=\dfrac{z}{28}=\dfrac{2x+3y-z}{30+60-28}=\dfrac{186}{62}=3\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{30}=3=>2x=3.30=>2x=90=>x=90:2=>x=45\)
=>\(\dfrac{3y}{60}=3=>3y=3.60=>3y=180=>y=180:3=>y=60\)
=>\(\dfrac{z}{28}=3=>z=3.28=>z=84\)
Vậy x=45; y=60; z=84
3)\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{4}\) và\(\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{z}{7}\)và 2x+3y-z=372
Từ\(\dfrac{x}{3}=\dfrac{y}{4}=>\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}\)
\(\dfrac{y}{5}=\dfrac{z}{7}=>\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}\)
=>\(\dfrac{x}{15}=\dfrac{y}{20}=\dfrac{z}{28}=>\dfrac{2x}{30}=\dfrac{3y}{60}=\dfrac{z}{28}\)
Áp dụng t/c của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau,ta có:
\(\dfrac{2x}{30}=\dfrac{3y}{60}=\dfrac{z}{28}=\dfrac{2x+3y-z}{30+60-28}=\dfrac{372}{62}=6\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x}{30}=6=>2x=6.30=>2x=180=>x=180:2=>x=90\)
=>\(\dfrac{3y}{60}=6=>3y=6.60=>3y=360=>y=360:3=>y=120\)
=>\(\dfrac{z}{28}=6=>z=6.28=>z=148\)
Vậy x=90; y=120; z=148

a) (2x - 3)(6 - 2x) = 0
=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=0\\6-2x=0\end{matrix}\right.=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x=3\\2x=6\end{matrix}\right.=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{2}\\x=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) \(5\dfrac{4}{7}:x=13=>\dfrac{39}{7}:x=13=>x=\dfrac{39}{7}:13=>x=\dfrac{3}{7}\)
c) \(2x-\dfrac{3}{7}=6\dfrac{2}{7}=>2x-\dfrac{3}{7}=\dfrac{44}{7}=>2x=\dfrac{47}{7}=>x=\dfrac{47}{14}\)
d) \(\dfrac{x}{5}+\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{6}{10}=>\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{6}{10}-\dfrac{1}{2}=>\dfrac{x}{5}=\dfrac{1}{10}=>x.10=5=>x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
e) \(\dfrac{x+3}{15}=\dfrac{1}{3}=>\left(x+3\right).3=15=>x+3=5=>x=2\)
giải phương trình sau
\(\dfrac{\text{x+1}}{11}-\dfrac{2x-5}{15}=\dfrac{3x-47}{17}-\dfrac{4x-59}{19}\)

Lời giải:
PT \(\Leftrightarrow (\frac{x+1}{11}-1)-(\frac{2x-5}{15}-1)=(\frac{3x-47}{17}+1)-(\frac{4x-59}{19}+1)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{x-10}{11}-\frac{2(x-10)}{15}=\frac{3(x-10)}{17}-\frac{4(x-10)}{19}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow (x-10)(\frac{1}{11}+\frac{4}{19}-\frac{2}{15}-\frac{3}{17})=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-10=0\Leftrightarrow x=10\)
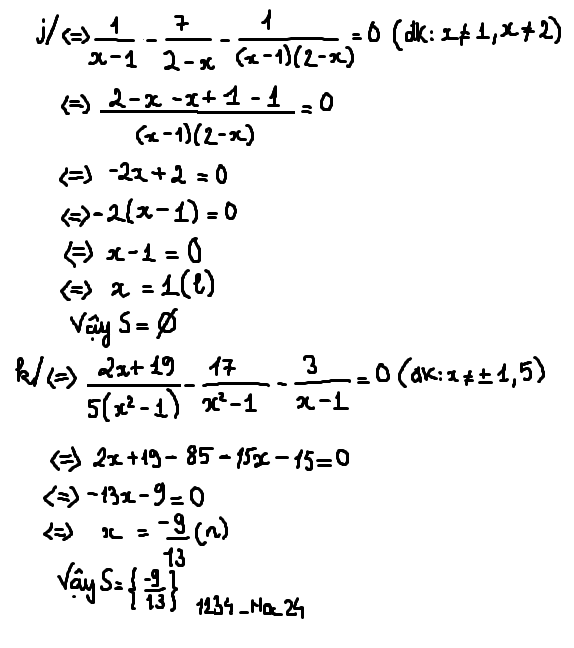
\(\dfrac{2x+19}{21}-\dfrac{2x+17}{23}=\dfrac{2x+7}{33}-\dfrac{2x+5}{35}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{2x+19}{21}-\dfrac{2x+17}{23}-\dfrac{2x+7}{33}+\dfrac{2x+5}{35}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(\dfrac{2x+19}{21}+1\right)-\left(\dfrac{2x+17}{23}+1\right)-\left(\dfrac{2x+7}{33}+1\right)+\left(\dfrac{2x+5}{35}+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{2x+40}{21}-\dfrac{2x+40}{23}-\dfrac{2x+40}{33}+\dfrac{2x+40}{35}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2x+40\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{21}-\dfrac{1}{23}-\dfrac{1}{33}+\dfrac{1}{35}\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow2x+40=0\Rightarrow x=-20\)( do \(\dfrac{1}{21}-\dfrac{1}{23}-\dfrac{1}{33}+\dfrac{1}{35}>0\))
Ta có: \(\dfrac{2x+19}{21}-\dfrac{2x+17}{23}=\dfrac{2x+7}{33}-\dfrac{2x+5}{35}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+40\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{21}-\dfrac{1}{23}-\dfrac{1}{33}+\dfrac{1}{35}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+40=0\)
hay x=-20