Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

(1); vecto u=2*vecto a-vecto b
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\cdot1-0=2\\y=2\cdot\left(-4\right)-2=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
(2): vecto u=-2*vecto a+vecto b
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-2\cdot\left(-7\right)+4=18\\y=-2\cdot3+1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
(3): vecto a=2*vecto u-5*vecto v
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\cdot\left(-5\right)-5\cdot0=-10\\b=2\cdot4-5\cdot\left(-3\right)=15+8=23\end{matrix}\right.\)
(4): vecto OM=(x;y)
2 vecto OA-5 vecto OB=(-18;37)
=>x=-18; y=37
=>x+y=19

\(m\overrightarrow{a}=m\left(-1;-2\right)=\left(-m;-2m\right)\)
\(n\overrightarrow{b}=n\left(1;-3\right)=\left(n;-3n\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow m\overrightarrow{a}+n\overrightarrow{b}=\left(-m+n;-2m-3n\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-m+n=2\\-2m-3n=-4\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow m-n=-2\) (đảo dấu pt đầu là ra, ko cần giải hẳn ra m; n)

Xét đường thẳng \(\Delta :x + 2y - 5 = 0\)
Vecto \(\overrightarrow n = (1;2)\) là một VTPT của \(\Delta \) => A đúng => Loại A
Vecto \(\overrightarrow u = ( - 2;1)\) là một VTCP của \(\Delta \) => B đúng => Loại B
Đường thẳng \(\Delta \)có hệ số góc \(k = - \frac{a}{b} = - \frac{1}{2}\) => D sai => Chọn D
Chọn D.

\(\overrightarrow{v}=3\overrightarrow{i}-m\overrightarrow{j}\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{v}=\left(3;-m\right)\)
Để \(\overrightarrow{u};\overrightarrow{v}\) cùng phương:
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3}{-2}=\frac{-m}{1}\Rightarrow m=\frac{3}{2}\)

Gọi \(M\left(a;b\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{MB}=\left(2-a;3-b\right)\Rightarrow2\overrightarrow{MB}=\left(4-2a;6-2b\right)\)
\(\overrightarrow{MC}=\left(-1-a;-2-b\right)\Rightarrow3\overrightarrow{MC}=\left(-3-3a;-6-3b\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow2\overrightarrow{MB}+3\overrightarrow{MC}=\left(1-5a;-5b\right)=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1-5a=0\\-5b=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\frac{1}{5}\\b=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow M\left(\frac{1}{5};0\right)\)
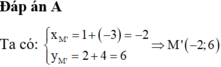
\(\overrightarrow{v}=\left(3;-m\right)\)
Hai vecto đã cho cùng phương khi và chỉ khi:
\(\dfrac{3}{-2}=\dfrac{-m}{1}\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{3}{2}\)