Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, Cho pt đt (d) có dạng y = ax + b
(d) đi qua N(2;3) => 3 = 2a + b
(d) // y = 2x - 5 <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2\\b\ne-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay a = 2 ta được : 3 = 4 + b => b = -1 (tmđk )
Vậy ptđt (d) có dạng y = 2x - 1
b, Hoành độ giao điểm tm pt
\(x^2-2x-3=0\)ta có : a - b + c = 0
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm \(x_1=-1;x_2=3\)
Với x = -1 => y = 1
Với x = 3 => y = 9
Vậy A(-1;1) ; B(3;9)
c, Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\\x_1x_2=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có : \(A=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-3x_1x_2\)
Thay vào ta được :
\(A=4-3\left(-5\right)=19\)

a: tọa độ giao điểm M là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=-x+2\\y=2x-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(\dfrac{-1}{2}x^2-4x+16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+4x-16=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x-32=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+4\right)^2=48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\sqrt{3}-4\\x=-4\sqrt{3}-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi \(x=4\sqrt{3}-4\) thì \(y=\dfrac{-1}{2}\cdot\left(4\sqrt{3}-4\right)^2=-32+16\sqrt{3}\)
Khi \(x=-4\sqrt{3}-4\) thì \(y=\dfrac{-1}{2}\left(-4\sqrt{3}-4\right)^2=-32-16\sqrt{3}\)
b: Để hai đường song song thì
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-1=-1\\m+3< >1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow m=0\)

a: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3=-3x-2\\y=2x+3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=5\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a,\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }2x+3=-3x-2\Leftrightarrow x=-1\Leftrightarrow y=1\Leftrightarrow A\left(-1;1\right)\\ b,\text{Gọi đt đó là }y=ax+b\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-a+b=1\\a=-1;b\ne5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-1\\b=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow y=-x\\ d,\text{Gọi đt cần tìm là }y=ax+b\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-a+b=1\\b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-2\\b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow y=-2x-1\)

a: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+3=-3x-2\\y=2x+3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

a: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(3x-2=-\dfrac{2}{3}x\)
=>\(3x+\dfrac{2}{3}x=2\)
=>\(\dfrac{11}{3}x=2\)
=>\(x=2:\dfrac{11}{3}=\dfrac{6}{11}\)
Khi x=6/11 thì \(y=-\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot\dfrac{6}{11}=-\dfrac{4}{11}\)
Vậy: \(A\left(\dfrac{6}{11};-\dfrac{4}{11}\right)\)
b: Đặt (d): y=ax+b
Vì (d)//(d3) nên a=1 và b<>-1
=>(d): y=x+b
Thay x=6/11 và y=-4/11 vào (d), ta được:
\(b+\dfrac{6}{11}=-\dfrac{4}{11}\)
=>\(b=-\dfrac{4}{11}-\dfrac{6}{11}=-\dfrac{10}{11}\)
Vậy: (d): \(y=x-\dfrac{10}{11}\)
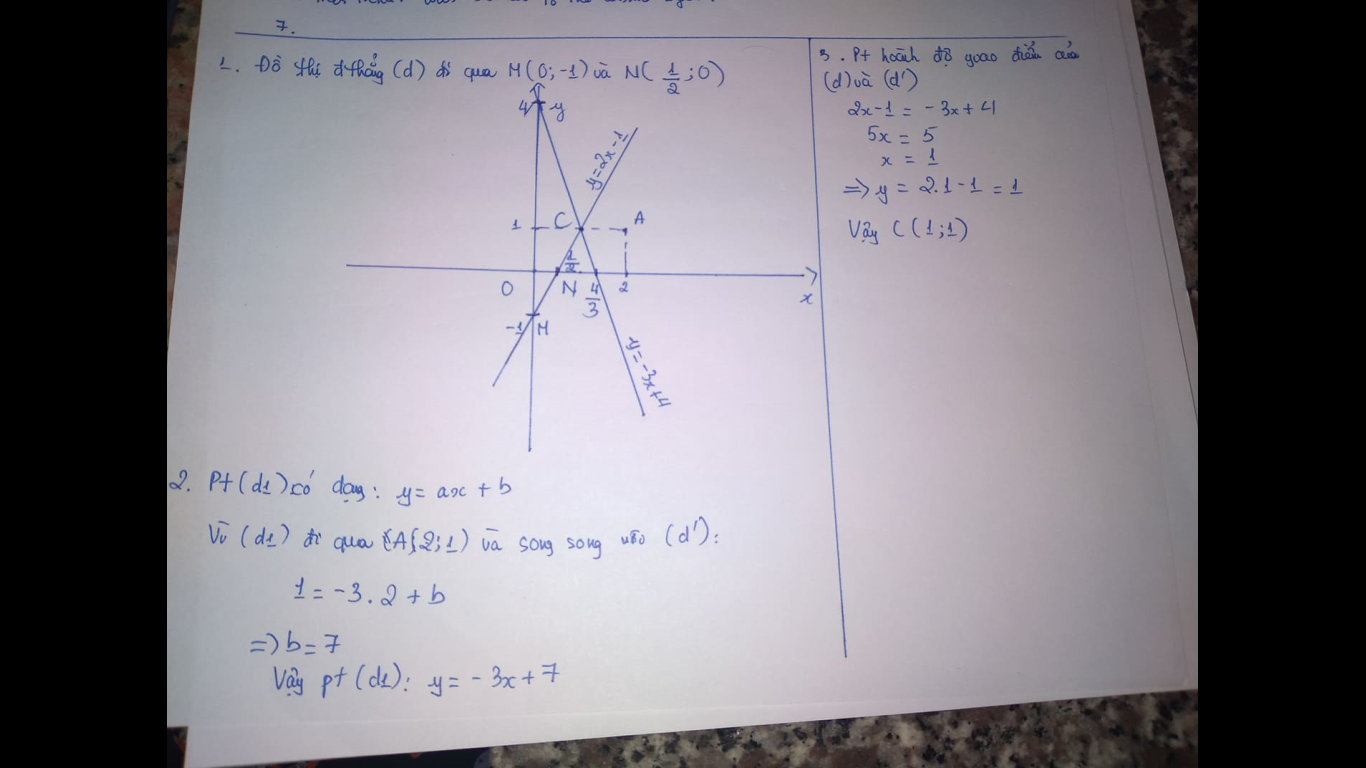
b: Vì (d)//y=3x+2 nên a=3
Vậy: (d): y=3x+b
Thay x=1 và y=2 vào (d), ta được:
b+3=2
hay b=-1
a: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+2x-3=0\\y=-2x+3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\in\left\{-3;1\right\}\\y\in\left\{9;1\right\}\end{matrix}\right.\)