
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Đáp án C
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
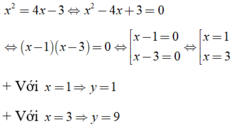
Do đó tọa độ giao điểm là (1; 1), (3; 9)

a:
b: phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
4x+2=2x-2
=>4x-2x=-2-2
=>2x=-4
=>x=-2
Thay x=-2 vào y=4x+2, ta được:
\(y=4\cdot\left(-2\right)+2=-8+2=-6\)
Vậy: M(-2;-6)
c: Tọa độ A là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\4x+2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\4x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ B là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\2x=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: B(1;0); A(-1/2;0)
d: M(-2;-6); B(1;0); A(-1/2;0)
\(MA=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}+2\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=\dfrac{3\sqrt{17}}{2}\)
\(MB=\sqrt{\left(1+2\right)^2+\left(0+6\right)^2}=3\sqrt{5}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}-1\right)^2+\left(0-0\right)^2}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Chu vi tam giác MAB là:
\(C_{MAB}=MA+MB+AB=\dfrac{3}{2}+3\sqrt{5}+\dfrac{3\sqrt{17}}{2}\)
Xét ΔMAB có \(cosAMB=\dfrac{MA^2+MB^2-AB^2}{2\cdot MA\cdot MB}=\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{85}}\)
=>\(sinAMB=\sqrt{1-\left(\dfrac{9}{\sqrt{85}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{85}}\)
Diện tích tam giác MAB là:
\(S_{AMB}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot MA\cdot MB\cdot sinAMB=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot\dfrac{3\sqrt{17}}{2}\cdot3\sqrt{5}\cdot\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{85}}\)
\(=\dfrac{9}{2}\)

a: 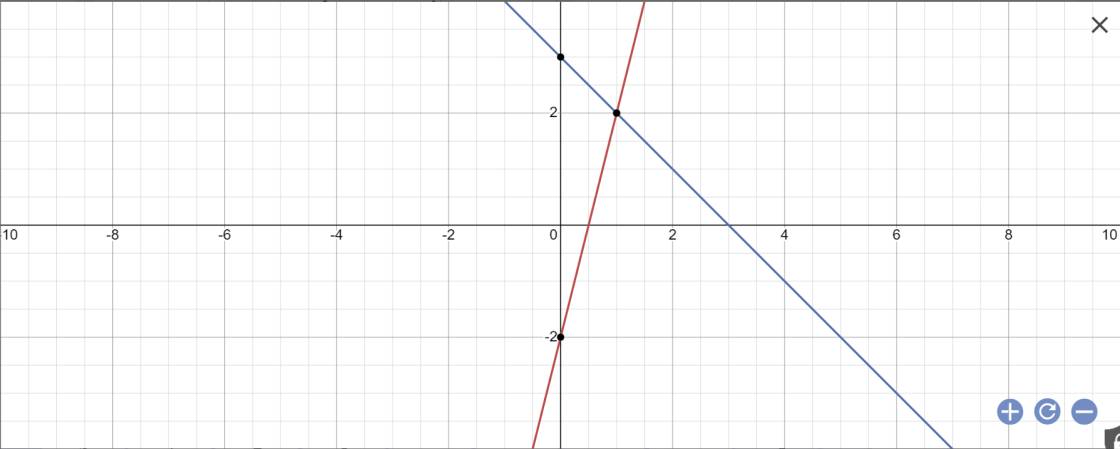
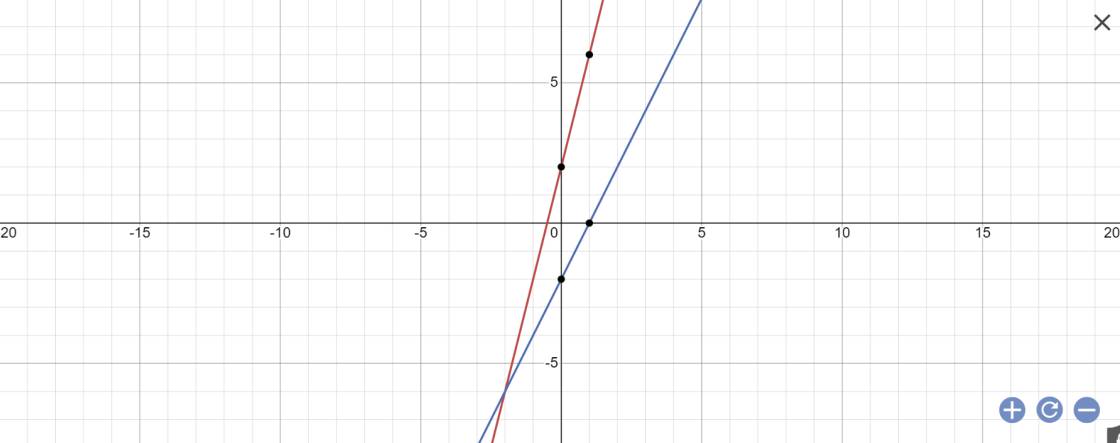
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
4x-2=-x+3
=>4x+x=3+2
=>5x=5
=>x=1
Thay x=1 vào y=-x+3, ta được:
\(y=-1+3=2\)
Vậy: M(1;2)
c: Gọi \(\alpha;\beta\) lần lượt là góc tạo bởi (d1),(d2) với trục Ox
(d1): y=4x-2
=>\(tan\alpha=4\)
=>\(\alpha=76^0\)
(d2): y=-x+3
=>\(tan\beta=-1\)
=>\(\beta=135^0\)
d: Thay y=6 vào (d1), ta được:
4x-2=6
=>4x=8
=>x=2
=>A(2;6)
Thay x=6/2=3 vào (d2), ta được:
\(y=-3+3=0\)
vậy: B(3;0)
Vì (d):y=ax+b đi qua A(2;6) và B(3;0) nên ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b=6\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b-3a-b=6-0\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-a=6\\b=-3a\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-6\\b=-3\cdot\left(-6\right)=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (d): y=-6x+18
e: A(2;6); B(3;0); M(1;2)
\(AM=\sqrt{\left(1-2\right)^2+\left(2-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{17}\)
\(BM=\sqrt{\left(1-3\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(3-2\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{37}\)
Chu vi tam giác AMB là:
\(C_{AMB}=\sqrt{17}+2\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{37}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(cosAMB=\dfrac{MA^2+MB^2-AB^2}{2\cdot MA\cdot MB}=\dfrac{17+8-37}{2\cdot2\sqrt{2}\cdot\sqrt{17}}=\dfrac{-3}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(\widehat{AMB}\simeq121^0\) và \(sinAMB=\sqrt{1-\left(-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{34}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(\dfrac{AB}{sinAMB}=\dfrac{AM}{sinABM}=\dfrac{BM}{sinBAM}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{sinABM}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{sinBAM}=\sqrt{37}:\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(sinABM\simeq0,58;\widehat{BAM}\simeq0,4\)
=>\(\widehat{ABM}\simeq35^0;\widehat{BAM}\simeq24^0\)

a: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
3x-4=4x-6
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-4x=-6+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-2\)
hay x=2
Thay x=2 vào \(\left(d1\right)\), ta được:
\(y=3\cdot2-4=2\)
b: Thay y=0 vào \(\left(d1\right)\), ta được:
\(3x-4=0\)
hay \(x=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Thay x=0 vào \(\left(d1\right)\), ta được:
\(y=3\cdot0-4=-4\)
Vậy: \(A\left(\dfrac{4}{3};0\right);B\left(0;-4\right)\)

Lời giải:
a.
Đồ thị xanh lá: $y=2x+1$
Đồ thị xanh dương: $y=x-3$
b.
PT hoành độ giao điểm:
$y=2x+1=x-3$
$\Leftrightarrow x=-4$
$y=x-3=(-4)-3=-7$
Vậy tọa độ điểm $M$ là $(-4;-7)$


Xét d cắt với Ox khi đó \(y=0\Rightarrow-4x+3=0\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{4}\) Vậy giao với Ox tại điểm \(\left(\frac{3}{4};0\right)\)
d cắt với Oy khi đó : \(x=0\Rightarrow y=-4.0+3=3\) vậy giao với Oy tại điểm \(\left(0,3\right)\)

làm bài này đâu nhất thiết phải dùng cách nào đâu bạn, vận dụng cách khoa học nhất là đc rồi nhé
a, bạn tự vẽ
b, Theo bài ra ta có hệ
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2+4x+2=0\\y=2x^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2+4x+2=0\\y=2x^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+1\right)^2=0\\y=2x^2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy (P) cắt (d) tại A(-1;2)
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của hai đồ thị :
\(4x^2=4x+3\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-4x+1=3+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2=4\Leftrightarrow|2x-1|=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-1=2\\2x-1=-2\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{3}{2}\\x=-\frac{1}{2}\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm là :\(\left(\frac{3}{2};9\right)\) và \(\left(-\frac{1}{2};1\right)\)