Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Ta có : 1/x - 1/(x+1) = 1/x(x+1)
<=> pcm \(\frac{x+1}{x\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
<=> pcm \(\frac{x+1-x}{x\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}\)
<=> pcm 1/x(x+1) = 1/x(x+1)
Đây là điều luôn đúng nên ta có điều phải chứng minh
Chú ý : Chữ pcm là phải chứng minh
Ta có : \(\frac{1}{x^2+x}+\frac{1}{x^2+3x+2}+\frac{1}{x^2+5x+6}+\frac{1}{x^2+7x+12}+\frac{1}{x^2+9x+20}+\frac{1}{x+5}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{x^2+x+2x+2}+\frac{1}{x^2+2x+3x+6}+\frac{1}{x^2+3x+4x+12}+\frac{1}{x^2+4x+5x+20}+\frac{1}{x+5}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{x\left(x+2\right)+3\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{1}{x\left(x+3\right)+4\left(x+3\right)}\)
\(+\frac{1}{x\left(x+4\right)+5\left(x+4\right)}+\frac{1}{x+5}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{1}{x+5}\)
Áp dụng chứng minh trên ta có :
\(=\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x+1}+\frac{1}{x+1}-\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{1}{x+3}+\frac{1}{x+3}-\frac{1}{x+4}+\frac{1}{x+4}-\frac{1}{x+5}+\frac{1}{x+5}\)
=1/x

Lời giải:
a. $x^3-4x^2+x+6=(x^3-2x^2)-(2x^2-4x)-(3x-6)$
$=x^2(x-2)-2x(x-2)-3(x-2)=(x-2)(x^2-2x-3)$
$=(x-2)[(x^2+x)-(3x+3)]=(x-2)[x(x+1)-3(x+1)]$
$=(x-2)(x+1)(x-3)$
-------------------
b.
$x^3+7x^2+14x+8=(x^3+x^2)+(6x^2+6x)+(8x+8)$
$=x^2(x+1)+6x(x+1)+8(x+1)=(x+1)(x^2+6x+8)$
$=(x+1)[(x^2+2x)+(4x+8)]=(x+1)[x(x+2)+4(x+2)]$
$=(x+1)(x+2)(x+4)$

Câu a bạn xem lại đề bài nhé. Đa thức đề cho thậm chí còn không có nghiệm hữu tỉ luôn cơ.
b) Lập sơ đồ Horner:
| 1 | 7 | 14 | 8 | |
| \(x=-1\) | 1 | 6 | 8 | 0 |
\(\Rightarrow x^3+7x^2+14x+8=\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+6x+8\right)\)
Ta thấy đa thức \(g\left(x\right)=x^2+6x+8\), dự đoán được 1 nghiệm \(x=-2\). Ta lại lập sơ đồ Horner:
| 1 | 6 | 8 | |
| \(x=-2\) | 1 | 4 | 0 |
\(\Rightarrow g\left(x\right)=\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\)
Vậy đa thức đã cho có thể được phân tích thành \(\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)\left(x+4\right)\)

quá dễ tách ra thành 1\x-1\x+1+1\x+1-1\x+2+1\x+2-1\x+3+1\x+3-1\x+4+...+1\x+5-1\x+6
=1\x-1\x+6
=6\x(x+6)
\(\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x+4\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}\)\(=\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x+1}+\frac{1}{x+1}-\frac{1}{x+2}+\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{1}{x+3}+\frac{1}{x+3}-\frac{1}{x+4}+\frac{1}{x+4}-\frac{1}{x+5}+\frac{1}{x+5}-\frac{1}{x+6}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x+6}\)\(=\frac{6}{x\left(x+6\right)}\)

\(P=\left(x-y\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)\left(x^4+y^4\right)-x^8+y^8+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)\left(x^4+y^4\right)-x^8+y^8+1\) (Vì: \(x-y=1\))
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\left(x^2-y^2\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)\left(x^4+y^4\right)-x^8+y^8+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=\left(x^4-y^4\right)\left(x^4+y^4\right)-x^8+y^8+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=x^8-y^8-x^8+y^8+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow P=1\)

\(\left(5-x^2\right)\left(5+x^2\right)-x^2\left(2-x^2\right)\)
\(=25-x^4-2x^2+x^4\)
\(=25-2x^2\)
Câu này áp dụng hằng đẳng thức quái gì, sửa lại
\(\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-3x+9\right)-x\left(x-1\right)\left(1+x\right)\)
\(=x^3+27-x\left(x^2-1\right)\)
\(=x^3+27-x^3+x=27+x\)
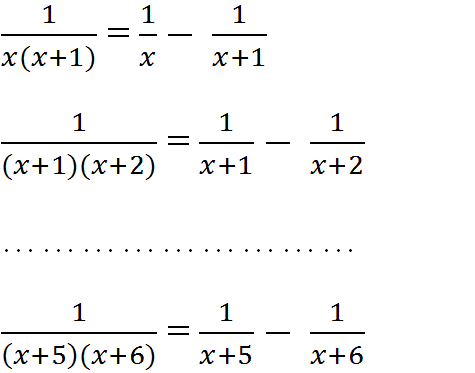
\(P=\frac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}+...+\frac{1}{\left(x+5\right)\left(x+6\right)}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x+1}+\frac{1}{x+1}-\frac{1}{x+2}+...+\frac{1}{x+5}-\frac{1}{x+6}\)
\(=\frac{1}{x}-\frac{1}{x+6}\)