
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(P=x^4+2x^2+1-x^2=\left(x^2+1\right)^2-x^2\)
\(P=\left(x^2-x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) P luôn có ít nhất 2 ước số là \(x^2-x+1\) và \(x^2+x+1\)
Do \(x^2+x+1\ge x^2-x+1\) nên P là SNT khi và chỉ khi \(x^2-x+1=1\) đồng thời \(x^2+x+1\) là SNT
\(x^2-x+1=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
- Với \(x=0\Rightarrow x^2+x+1=1\) ko phải SNT (loại)
- Với \(x=1\Rightarrow x^2+x+1=3\) là SNT (t/m)
Vậy \(x=1\)

a.
$x^2-y^2-2x+2y=(x^2-y^2)-(2x-2y)=(x-y)(x+y)-2(x-y)=(x-y)(x+y-2)$
b.
$x^2(x-1)+16(1-x)=x^2(x-1)-16(x-1)=(x-1)(x^2-16)=(x-1)(x-4)(x+4)$
c.
$x^2+4x-y^2+4=(x^2+4x+4)-y^2=(x+2)^2-y^2=(x+2-y)(x+2+y)$
d.
$x^3-3x^2-3x+1=(x^3+1)-(3x^2+3x)=(x+1)(x^2-x+1)-3x(x+1)$
$=(x+1)(x^2-4x+1)$
e.
$x^4+4y^4=(x^2)^2+(2y^2)^2+2.x^2.2y^2-4x^2y^2$
$=(x^2+2y^2)^2-(2xy)^2=(x^2+2y^2-2xy)(x^2+2y^2+2xy)$
f.
$x^4-13x^2+36=(x^4-4x^2)-(9x^2-36)$
$=x^2(x^2-4)-9(x^2-4)=(x^2-9)(x^2-4)=(x-3)(x+3)(x-2)(x+2)$
g.
$(x^2+x)^2+4x^2+4x-12=(x^2+x)^2+4(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)^2-2(x^2+x)+6(x^2+x)-12$
$=(x^2+x)(x^2+x-2)+6(x^2+x-2)=(x^2+x-2)(x^2+x+6)$
$=[x(x-1)+2(x-1)](x^2+x+6)=(x-1)(x+2)(x^2+x+6)$
h.
$x^6+2x^5+x^4-2x^3-2x^2+1$
$=(x^6+2x^5+x^4)-(2x^3+2x^2)+1$
$=(x^3+x^2)^2-2(x^3+x^2)+1=(x^3+x^2-1)^2$

\(a,x^4-2x^3+6x^2+x+14\\ =\left(x^4-3x^3+7x^2\right)+\left(x^3-3x^2+7x\right)+\left(2x^2-6x+14\right)\\ =\left(x^2-3x+7\right)\left(x^2+x+2\right):\left(x^2-3x+7\right)=x^2+x+2\)
Ta có \(x^2+x+2=x^2+x+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{7}{4}=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{7}{4}\ge\dfrac{7}{4}>0\)
Vậy ...
\(b,A=x^3+3xy+y^3\\ A=\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2-xy+y^2\right)+3xy\\ A=x^2-xy+y^2+3xy\\ A=x^2+2xy+y^2=\left(x+y\right)^2=1\)

a: Ta có: \(-\left(-3x^2\right)^3+4x-9-27x^6\)
\(=27x^6-27x^6+4x-9\)
=4x-9
=-1

a) \(A=x\left(2x+1\right)-x^2\left(x+2\right)+\left(x^3-x+5\right)\)
\(A=2x^2+x-x^3-2x^2+x^3-x+5\)
\(A=5\)
=> giá trị biểu thức ko phụ thuộc vào biến x
b) \(A=x\left(3x^2-x+5\right)-\left(2x^3+3x-16\right)-x\left(x^2-x+2\right)\)
=> \(A=3x^3-x^2+5x-2x^3-3x+16-x^3+x^2-2x\)
=> \(A=\)16
vậy giá trị của biểu thức A ko phụ thuộc vào biến x

\(f\left(x\right)⋮g\left(x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-3x^3+4x^2-x^2+3x-4+\left(a-3\right)x+\left(b+4\right)⋮x^2-3x+4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a,b\right)=\left(3;-4\right)\)
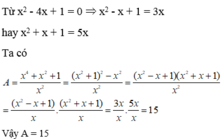
\(x^2=x+1\Rightarrow x^2-x-1=0\)
\(A=x^4-2x^3-3x^2+4x+4\)
\(=x^4-x^3-x^2-x^3+x^2+x-3x^2+3x+3+1\)
\(=x^2\left(x^2-x-1\right)-x\left(x^2-x-1\right)-3\left(x^2-x-1\right)+1=0-0-0+1=1\)