
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a: Ta có: \(x\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x^2\left(x+1\right)-x+5\)
\(=x^3+x^2+x-x^3-x^2-x+5\)
=5
b: Ta có: \(x\left(2x+1\right)-x^2\left(x+2\right)+x^3-x+3\)
\(=2x^2+x-x^3-2x^2+x^3-x+3\)
=3
c: Ta có: \(4\left(6-x\right)+x^2\left(3x+2\right)-x\left(5x-4\right)+3x^2\left(1-x\right)\)
\(=24-4x+3x^3+2x^2-5x^2+4x+3x^2-3x^3\)
=24

a, \(A-x^2+5\le5\)Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = 0
b, \(B=-2\left(x-1\right)^2+3\le3\)Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x =1
c, \(C=-\left|3x-2\right|+5\le5\)Dấu ''='' xảy ra khi x = 2/3

a: ĐKXĐ: x>0
Để A là số nguyên thì \(7⋮\sqrt{x}\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}\in\left\{1;7\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{1;49\right\}\)
b: ĐKXĐ: x>1
Để B là số nguyên thì \(3⋮\sqrt{x-1}\)
=>\(\sqrt{x-1}\in\left\{1;3\right\}\)
=>\(x-1\in\left\{1;9\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{2;10\right\}\)
c: ĐKXĐ: x>3
Để C là số nguyên thì \(2⋮\sqrt{x-3}\)
=>\(\sqrt{x-3}\in\left\{1;2\right\}\)
=>\(x-3\in\left\{1;4\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{4;7\right\}\)

a: Để A nguyên thì \(2x-3\in\left\{1;-1;7;-7\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{2;1;5;-2\right\}\)

Bài 1:
a: \(x^2+5x=x\left(x+5\right)\)
Để biểu thức này âm thì \(x\left(x+5\right)< 0\)
hay -5<x<0
b: \(3\left(2x+3\right)\left(3x-5\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{3}{2}< x< \dfrac{5}{3}\)

a: A>0
=>\(x^2-3x>0\)
=>x(x-3)>0
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x-3>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x>3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x>3
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x< 3\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x<0
d: Để D<0 thì \(x^2+\dfrac{5}{2}x< 0\)
=>\(x\left(x+\dfrac{5}{2}\right)< 0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x+\dfrac{5}{2}< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>0\\x< -\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Loại
Th2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x+\dfrac{5}{2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< 0\\x>-\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(-\dfrac{5}{2}< x< 0\)
e: ĐKXĐ: x<>2
Để E<0 thì \(\dfrac{x-3}{x-2}< 0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3>=0\\x-2< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\x< 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Loại
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-3< =0\\x-2>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =3\\x>2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>2<x<=3
g: Để G<0 thì \(\left(2x-1\right)\left(3-2x\right)< 0\)
=>\(\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x-3\right)>0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1>0\\2x-3>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>\dfrac{1}{2}\\x>\dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x>\dfrac{3}{2}\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-1< 0\\2x-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< \dfrac{1}{2}\\x< \dfrac{3}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x< \dfrac{1}{2}\)

a) \(F=\frac{3x-2}{x+3}\)là số nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-2⋮x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x+9-11⋮x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(x+3\right)-11⋮x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow11⋮x+3\)\(\Leftrightarrow x+3\in\left\{-11;-1;1;11\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-14;-4;-2;8\right\}\)
b) \(\frac{x^2-2x+4}{x+1}\)là số nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+4⋮x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x-3x-3+7⋮x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-3\left(x+1\right)+7⋮x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)+7⋮x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7⋮x+1\)\(\Leftrightarrow x+1\in\left\{-7;-1;1;7\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-8;-2;0;6\right\}\)

a) Do \(\left|x\right|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\left|x\right|+5\ge5\)
\(minA=5\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
b) Do \(\left|x-\dfrac{2}{3}\right|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow B=\left|x-\dfrac{2}{3}\right|-4\ge-4\)
\(minB=-4\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
c) Do \(\left|3x-1\right|\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow C=\left|3x-1\right|-\dfrac{1}{2}\ge-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(minC=-\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(A=\left|x\right|+5\ge5\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x=0\)
\(B=\left|x-\dfrac{2}{3}\right|-4\ge-4\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{2}{3}=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(C=\left|3x-1\right|-\dfrac{1}{2}\ge-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow3x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)

Bài 1:
a) \(3x^2\left(2x^3-x+5\right)-6x^5-3x^3+10x^2\)
\(=6x^5-3x^3+10x^2-6x^5-3x^3+10x^2\)
\(=10x^2+10x^2\)
\(=20x^2\)
b) \(-2x\left(x^3-3x^2-x+11\right)-2x^4+3x^3+2x^2-22x\)
\(=-2x^4+6x^3+2x^2-22x-2x^4+3x^3+2x^2-22x\)
\(=-4x^4+9x^3+4x^2-44x\)

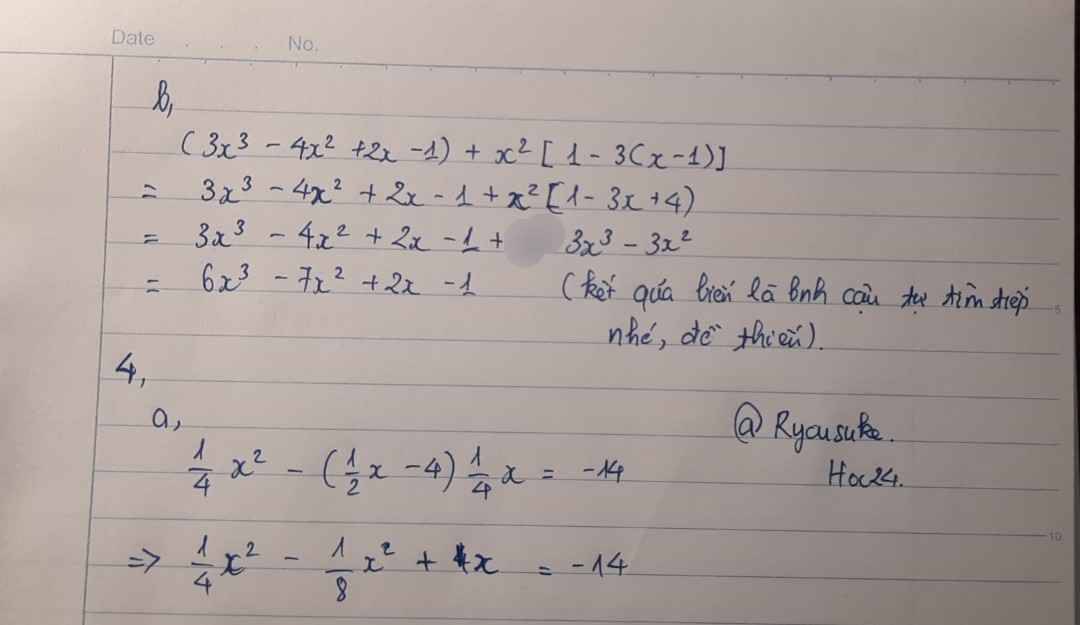

a) Đặt A= x-3/x-5 (đk x khác -5)
<=>A=( x-5)+2/x-5
<=>A= 1+2/x-5
Để A=1+2/x-5 là số nguyên thì 2/x+5 phải là số nguyên
<=> 2 chia hết x-5 hay x-5€ Ư(2)
<=> x-5€ {-2,-1,1,2}
<=> x€ {3,4,6,7}
Mà x€ Z, x khác -5
=> x€{3,4,6,7}
Vậy với x€{3,4,6,7} thì A=x-3/x-5 là số nguyên
b) Đặt B=3x-2/x+3(đk x khác -3) <=> B=3(x+3)-11/x+3
<=> B=3-11/x+3
Để B=3-11/x+3 là số nguyên thì 11/x+3 phải là số nguyên
<=> 11 chia hết cho x+3
<=>x+3€ Ư(11)
<=> x+3€{-11,-1,1,11}
<=> x€{-14,-4,-2,8}
Mà x€Z, x khác -3=> x€{-14,-4,-2,8}
Vậy với x€{-14,-4,-2,8} thì B=3x-2/x+3 là số nguyên