Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

x n y n + 1 : x 2 y 5 = x n : x 2 y n + 1 : y 5 = x n - 2 . y n - 4 là phép chia hết
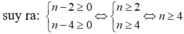

x 4 : x n = x 4 - n là phép chia hết nên 4 – n ≥ 0 ⇒ 0 ≤ n ≤ 4
suy ra: n ∈ {0; 1; 2; 3; 4}

5 x n y 3 : 4 x 2 y 2 = 5/4 x n : x 2 y 3 : y 2 = 5/4 x n - 2 . y là phép chia hết
Suy ra: n – 2 ≥ 0 ⇒ n ≥ 2

Vì đa thức 5 x 3 - 7 x 2 + x chia hết cho 3 x n nên mỗi hạng tử của đa thức chia hết cho x n
=> hạng tử x – có số mũ nhỏ nhất của đa thức chia hết cho 3 x n
Do đó, x : x n ⇒ 0 ≤ x ≤ 1 . Vậy n ∈ {0; 1}

Vì đa thức 13 x 4 y 3 - 5 x 3 y 3 + 6 x 2 y 2 chia hết cho 5 x n y n nên mỗi hạng tử của đa thức trên chia hết cho 5 x n y n Do đó, hạng tử 6 x 2 y 2 chia hết cho 5 x n y n ⇒ 0 ≤ n ≤ 2 . Vậy n ∈ {0;1;2}

Bài 5.5:
\(\left(2x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)+\left(4x^3-6x^2-6x\right):\left(-2x\right)=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x^2+2x-3x-3\right)+2x\cdot\left(2x^2-3x-3\right):\left(-2x\right)=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-x-3-2x^2+3x+3=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{18}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=9\)

\(pkkikkkkkk\min\limits_{kkkkk\max\limits_{ }kkkk\lim\limits_{\rightarrow}kkkk\sqrt{ }kkk\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }k\sqrt{ }k\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }k\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }k\sqrt{ }k\sqrt{ }k\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }k\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }\sqrt{ }}\)
\(x^ny^{n+1}:x^2y^5=x^{n-2}.y^{n-4}\)
Để \(x^ny^{n+1}⋮x^2y^5\) thì \(\hept{\begin{cases}n-2\ge0\\n-4\ge0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow}\hept{\begin{cases}n\ge2\\n\ge4\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow n\ge4.\)