
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


a/Ta có:
\(B\left(-10\right)=\left(-10\right)^2+9\cdot\left(-10\right)-10\)
\(=100-90-10\)
\(=0\)
Do đó -10 là một nghiệm của B(x)
b/\(B\left(x\right)=x^2+9x-10\)
\(=x\left(x+9\right)-10\)
Do đó để B(x) có nghiệm thì \(x\left(x+9\right)-10=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+9\right)=10\)
\(\Rightarrow x=1\)
a)
với `x=-10` thì
`(-10)^2+9*(-10)-10`
`=100-90-10`
`=0`
Vậy -10 là nghiệm của `B(x)`
b)
`x^2+9x-10=0`
`=>x^2+10x-x-10=0`
`=>x(x+10)-(x+10)=0`
`=>(x+10)(x-1)=0`
`=>x+10=0` hoặc `x-1=0`
`=>x=-10` hoặc `x=1`
vậy nghiệm còn lại của đa thức là 1

a) \(f\left(x\right)=x^2+7x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=x^2-x+8x-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(8x-8\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=x\left(x-1\right)+8\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(x\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+8\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1=0\) hoặc \(x+8=0\)
Nếu \(x-1=0\Rightarrow x=1\)
Nếu \(x+8=0\Rightarrow x=-8\)
Vậy đa thức f(x) có nghiệm là 1 và -8
b) \(k\left(x\right)=5x^2+9x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=5x^2+5x+4x+4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=\left(5x^2+5x\right)+\left(4x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=5x\left(x+1\right)+4\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow k\left(x\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(5x+4\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x+1=0\) hoặc \(5x+4=0\)
Nếu \(x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)
Nếu \(5x+4=0\Rightarrow x=-\frac{4}{5}\)
Vậy đa thức k(x) có nghiệm là -1 và -4/5

b: 1/2x-4=0
=>1/2x=4
hay x=8
a: x+7=0
=>x=-7
e: 4x2-81=0
=>(2x-9)(2x+9)=0
=>x=9/2 hoặc x=-9/2
g: x2-9x=0
=>x(x-9)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=9

a: x+7=0
nên x=-7
b: x-4=0
nên x=4
c: -8x+20=0
=>-8x=-20
hay x=5/2
d: x2-100=0
=>(x-10)(x+10)=0
=>x=10 hoặc x=-10

c. Ta có h(x) = 0 ⇒ 5x + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = -1/5
Vậy nghiệm của đa thức h(x) là x = -1/5 (1 điểm)

Để F(x) có nghiệm <=> x^10 - 9x^9 + ... + 9x^2 - 9x +8 = 0
<=> (x^10 - x^9) - (8x^9 - 8x^8) + (x^8 - x^7) - ... + (x^2 - x) - (8x - 8) = 0
<=> x^9(x - 1) - 8x^8(x - 1) + ... + x(x - 1) - 8(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x^9 - 8x^8 + ... + x - 8)(x - 1) = 0
<=> ( (x^9 - 8x^8) + (x^7 - 8x^6) + ... + (x - 8) )(x - 1) = 0
<=> (x^8 + x^6 + ... + 1)(x - 8)(x - 1) = 0
Có nghiệm là 8 và 1

Ta có \(x^2-7x+8=0\Leftrightarrow x^2-\dfrac{2.7}{2}x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-7x+\dfrac{49}{4}-\dfrac{49}{4}+8=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{7}{2}\right)^2-\dfrac{17}{4}=0\)
\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\dfrac{7}{2}=\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x-\dfrac{7}{2}=-\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\sqrt{17}+7}{2}\\x=\dfrac{-\sqrt{17}+7}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đặt \(x^2-7x+8=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-7\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot8=17>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{7-\sqrt{17}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{7+\sqrt{17}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
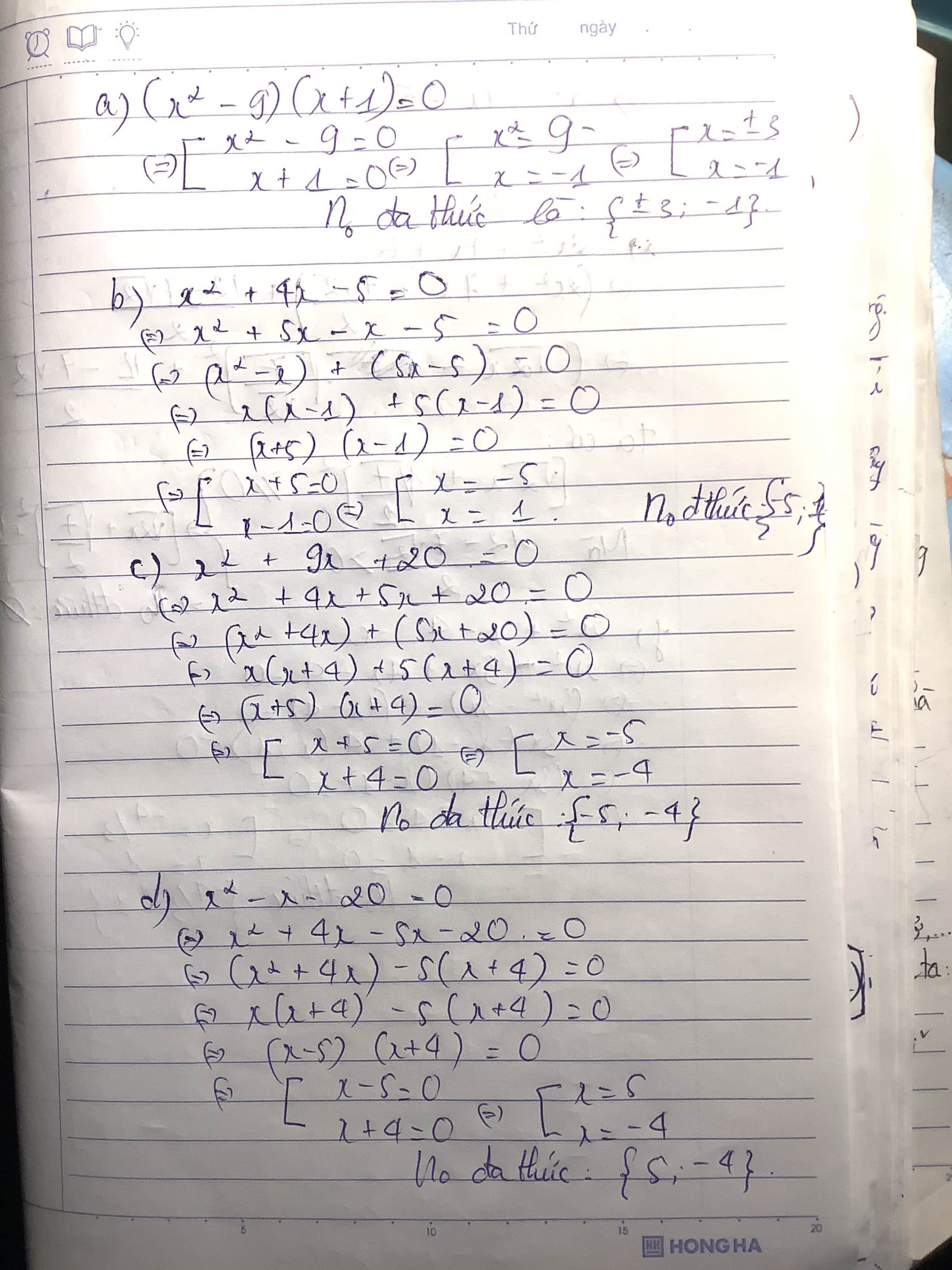

-1
v
à
-8
n
h
a
b
ạ
n
\(x^2+9x+8=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+x+8x+8=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\left(x+1\right)+8\left(x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)\left(x+8\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\x+8=0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\\x=-8\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là -1 và -8