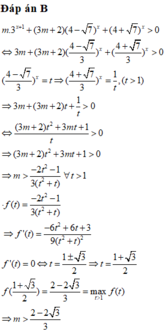Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

ĐKXĐ: \(-x^2+4x+m>0\)
\(log_2\left(-x^2+4x+m\right)-log_2\left(x^2+2\right)< log_23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2\left(\dfrac{-x^2+4x+m}{x^2+2}\right)< log_23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-x^2+4x+m}{x^2+2}< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x^2+4x+m>0\\-x^2+4x+m< 3x^2+6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>x^2-4x\\m< 4x^2-4x+6\end{matrix}\right.\) ; \(\forall x\in\left[1;5\right]\)
Xét hai hàm \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)=x^2-4x\\g\left(x\right)=4x^2-4x+6\end{matrix}\right.\) trên \(\left[1;5\right]\) ta được: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)_{max}=f\left(5\right)=5\\g\left(x\right)_{min}=g\left(1\right)=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow5\le m\le6\)
Có 2 giá trị nguyên của m

a. Vì \(0< 0,1< 1\) nên bất phương trình đã cho
\(\Leftrightarrow0< x^2+x-2< x+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+x-2>0\\x^2-5< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< -2\\x>1\end{matrix}\right.\\-\sqrt{5}< x< \sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\sqrt{5}< x< -2\\1< x< \sqrt{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là \(S=\left\{-\sqrt{5};-2\right\}\) và \(\left\{1;\sqrt{5}\right\}\)
b. Điều kiện \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2-x>0\\x^2-6x+5>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có:
\(log_{\dfrac{1}{3}}\left(x^2-6x+5\right)+2log^3\left(2-x\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_{\dfrac{1}{3}}\left(x^2-6x+5\right)\ge log_{\dfrac{1}{3}}\left(2-x\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+5\le\left(2-x\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-1\ge0\)
Bất phương trình tương đương với:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2-6x+5>0\\2-x>0\\2x-1\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 1\\x>5\end{matrix}\right.\\x< 2\\x\ge\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}\le x< 1\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là: \(\left(\dfrac{1}{2};1\right)\)

Đáp án B
Đặt 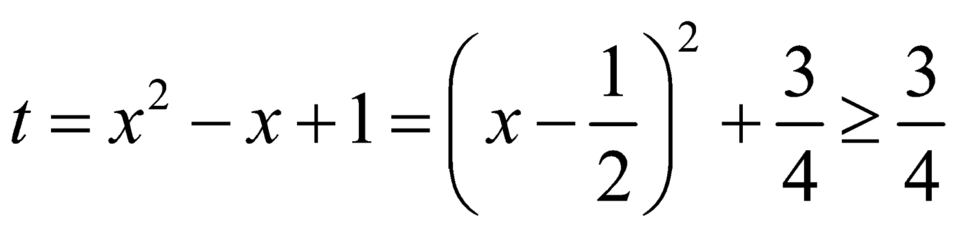
Ta có:
![]()
![]()
Đặt ![]() .
.
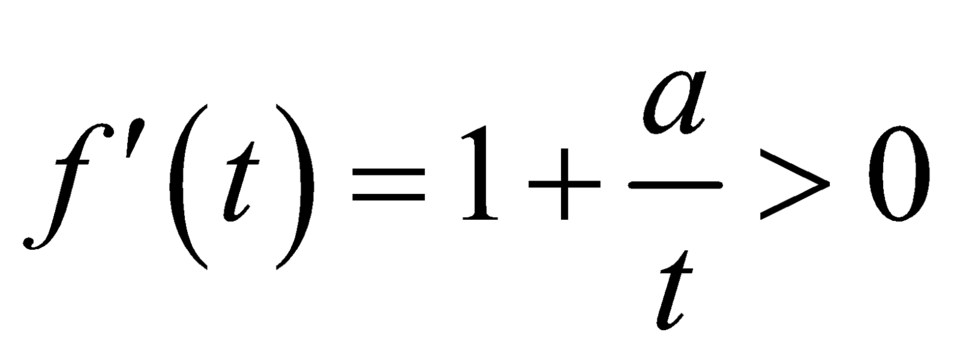
![]() là hàm số đồng biến trên
là hàm số đồng biến trên 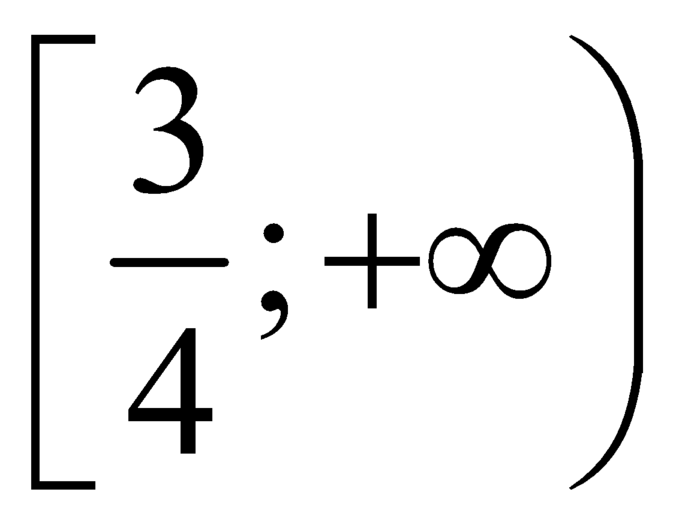 .
.
Khi đó 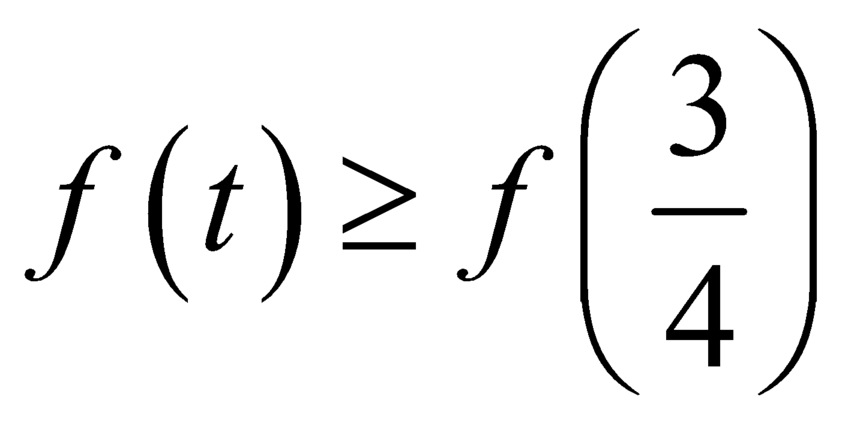
![]()
![]()
![]()

a.
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3+3x^2+x+1\ge mx\) ; \(\forall x\ge0\) (1)
- Với \(x=0\) thỏa mãn
- Với \(x>0\)
(1) \(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x+1+\dfrac{1}{x}\ge m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le\min\limits_{x>0}\left(x^2+3x+1+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)\)
Xét \(f\left(x\right)=x^2+3x+1+\dfrac{1}{x}\) với \(x>0\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=2x+3-\dfrac{1}{x^2}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)^2}{x^2}=0\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Từ BBT ta thấy \(f\left(x\right)_{min}=f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{19}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\le\dfrac{19}{4}\)

\(f\left(1-x\right)+f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{9^{1-x}}{9^{1-x}+3}+\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}=\dfrac{9}{9+3.9^x}+\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}=\dfrac{3}{9^x+3}+\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}=1\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=1-f\left(1-x\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(cos^2x\right)=1-f\left(sin^2x\right)\)
Do đó:
\(f\left(3m+\dfrac{1}{4}sinx\right)+f\left(cos^2x\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(3m+\dfrac{1}{4}sinx\right)=f\left(sin^2x\right)\) (1)
Hàm \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{9^x}{9^x+3}\) có \(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{3.9^x.ln9}{\left(9^x+3\right)^2}>0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến trên R
\(\Rightarrow\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow3m+\dfrac{1}{4}sinx=sin^2x\)
Đến đây chắc dễ rồi, biện luận để pt \(sin^2x-\dfrac{1}{4}sinx=3m\) có 8 nghiệm trên khoảng đã cho