Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: \(y'=4\cdot3x^2-3\cdot2x+2=12x^2-6x+2\)
b: \(y'=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)'\left(x-1\right)-\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)'}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{x-1-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{-2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
c: \(y'=-2\cdot\left(\sqrt{x}\cdot x\right)'\)
\(=-2\cdot\left(\dfrac{x+x}{2\sqrt{x}}\right)=-2\cdot\dfrac{2x}{2\sqrt{x}}=-2\sqrt{x}\)
d: \(y'=\left(3sinx+4cosx-tanx\right)\)'
\(=3cosx-4sinx+\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}\)
e: \(y'=\left(4^x+2e^x\right)'\)
\(=4^x\cdot ln4+2\cdot e^x\)
f: \(y'=\left(x\cdot lnx\right)'=lnx+1\)

\(a,y'=8x^3-9x^2+10x\\ \Rightarrow y''=24x^2-18x+10\\ b,y'=\dfrac{2}{\left(3-x\right)^2}\\ \Rightarrow y''=\dfrac{4}{\left(3-x\right)^3}\)
\(c,y'=2cos2xcosx-sin2xsinx\\ \Rightarrow y''=-5sin\left(2x\right)cos\left(x\right)-4cos\left(2x\right)sin\left(x\right)\\ d,y'=-2e^{-2x+3}\\ \Rightarrow y''=4e^{-2x+3}\)

1) \(f\left(x\right)=2x-5\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=2\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(4\right)=2\)
2) \(y=x^2-3\sqrt[]{x}+\dfrac{1}{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=2x-\dfrac{3}{2\sqrt[]{x}}-\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
3) \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+9}{x+3}+4\sqrt[]{x}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1.\left(x+3\right)-1.\left(x+9\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+3-x-9}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{12}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{\sqrt[]{x}}\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(x-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{x}}\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(1\right)=2\left[\dfrac{6}{\left(1-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\sqrt[]{1}}\right]=2\left(\dfrac{3}{2}+1\right)=2.\dfrac{5}{2}=5\)

a) \(y' = 2.3{{\rm{x}}^2} - \frac{1}{2}.2{\rm{x}} + 4.1 - 0 = 6{{\rm{x}}^2} - x + 4\).
b) \(y' = \frac{{{{\left( { - 2{\rm{x}} + 3} \right)}^\prime }.\left( {{\rm{x}} - 4} \right) - \left( { - 2{\rm{x}} + 3} \right).{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 4} \right)}^\prime }}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 4} \right)}^2}}}\)
\( = \frac{{ - 2\left( {{\rm{x}} - 4} \right) - \left( { - 2{\rm{x}} + 3} \right).1}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 4} \right)}^2}}}\)
\( = \frac{{ - 2{\rm{x}} + 8 + 2{\rm{x}} - 3}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 4} \right)}^2}}} = \frac{5}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 4} \right)}^2}}}\)
c) \(y' = \frac{{{{\left( {{x^2} - 2{\rm{x}} + 3} \right)}^\prime }\left( {{\rm{x}} - 1} \right) - \left( {{x^2} - 2{\rm{x}} + 3} \right){{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 1} \right)}^\prime }}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
\( = \frac{{\left( {2{\rm{x}} - 2} \right)\left( {{\rm{x}} - 1} \right) - \left( {{x^2} - 2{\rm{x}} + 3} \right).1}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 1} \right)}^2}}}\) \( = \frac{{2{{\rm{x}}^2} - 2{\rm{x}} - 2{\rm{x}} + 2 - {x^2} + 2{\rm{x}} - 3}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
\( = \frac{{{x^2} - 2{\rm{x}} - 1}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{x}} - 1} \right)}^2}}}\)
d) \(y' = {\left( {\sqrt 5 .\sqrt x } \right)^\prime } = \sqrt 5 .\frac{1}{{2\sqrt x }} = \frac{{\sqrt 5 }}{{2\sqrt x }} = \frac{5}{{2\sqrt {5x} }}\).

a: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-9}=+\infty\) vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}x+3=3+3=6\\\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}x^2-9=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=3 là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-9}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-3}\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-9}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-3}\dfrac{1}{x-3}=\dfrac{1}{-3-3}=-\dfrac{1}{6}\)
=>x=-3 không là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x+3}{x^2-9}\)
b: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow5}\dfrac{x-5}{x^2-25}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow5}\dfrac{1}{x+5}=\dfrac{1}{5+5}=\dfrac{1}{10}\)
=>x=5 không là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x-5}{x^2-25}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-5}\dfrac{x-5}{x^2-25}=-\infty\) vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-5}x-5=-5-5=-10< 0\\\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-5}x^2-25=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=-5 là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x-5}{x^2-25}\)
c: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{x^2-1}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1}\dfrac{x-3}{x+1}=\dfrac{1-3}{1+1}=\dfrac{-2}{2}=-1\)
=>x=1 không là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{x^2-1}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{x^2-1}=+\infty\) vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}x^2-4x+3=\left(-1\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)+3=8>0\\\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}x^2-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=-1 là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{x^2-1}\)
d: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}\dfrac{x^2-3x-4}{x^2-2x-3}=-\infty\) vì \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}x^2-3x-4=3^2-3\cdot3-4=-4< 0\\\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow3}x^2-2x-3=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x=3 là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x^2-3x-4}{x^2-2x-3}\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\dfrac{x^2-3x-4}{x^2-2x-3}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1}\dfrac{x-4}{x-3}=\dfrac{-1-4}{-1-3}=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
=>x=-1 không là tiệm cận đứng của đồ thị hàm số \(y=\dfrac{x^2-3x-4}{x^2-2x-3}\)

b) \(3\left(1-2x\right)^{20}\left(3x-2\right)^{10}\left(-14\left(3x-2\right)+11\left(1-2x\right)\right)\)
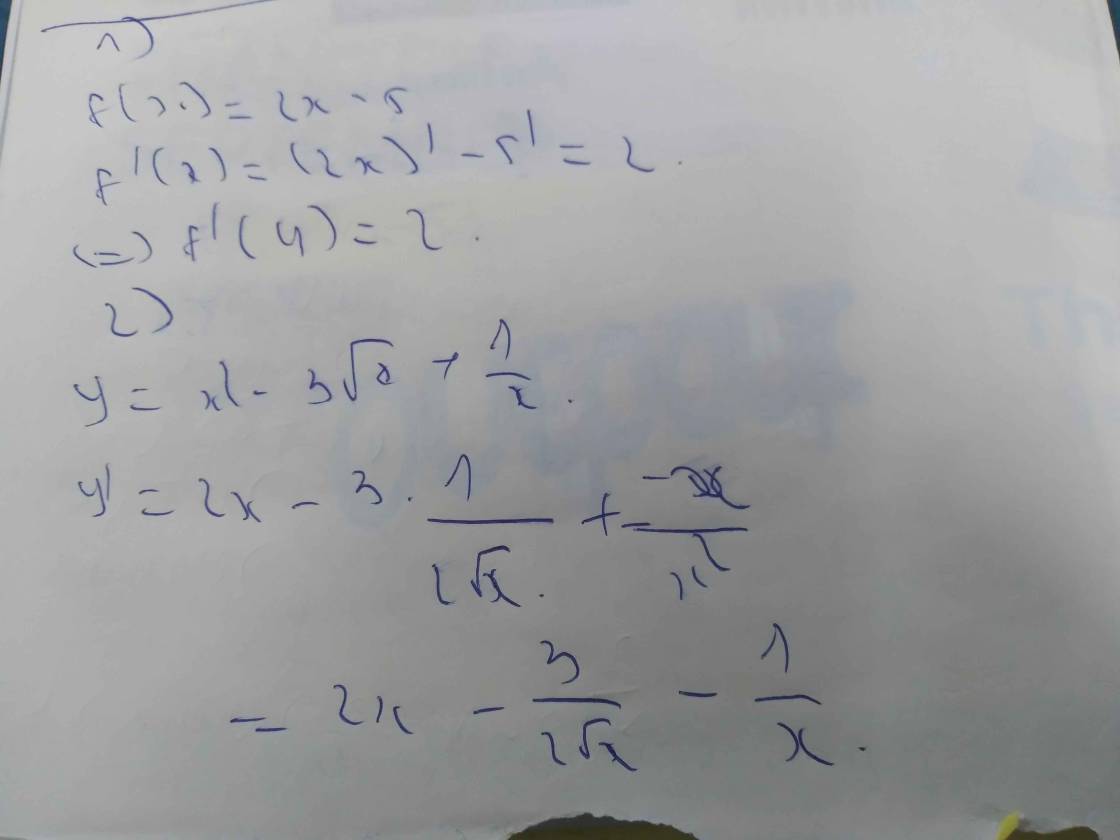

Ta có:
Chọn C.