Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1: Sửa đề: 3x-5
\(=\dfrac{-x^2\left(3x-5\right)-3\left(3x-5\right)}{3x-5}=-x^2-3\)
2: \(=\dfrac{5x^4-5x^3+14x^3-14x^2+12x^2-12x+8x-8}{x-1}\)
=5x^2+14x^2+12x+8
3: \(=\dfrac{5x^3+10x^2+4x^2+8x+4x+8}{x+2}=5x^2+4x+4\)
4: \(=\dfrac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)-2x\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^2-1}=x^2+1-2x\)
5: \(=\dfrac{x^2\left(5-3x\right)+3\left(5-3x\right)}{5-3x}=x^2+3\)

a) Sắp xếp đa thức - 3 x 3 + 5 x 2 – 9x + 15 và -3x + 5.
Thực hiện phép chia thu được đa thức thương x 2 + 3.
b) Sắp xếp đa thức x 3 – 4 x 2 + 5x – 20.
Thực hiện phép chia thu được đa thức thương x 2 + 5.

c) Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x^4+9x^3-2x^2-4x-8}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x^4-5x^3+14x^3-14x^2+12x^2-12x+8x-8}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x^3\left(x-1\right)+14x^2\left(x-1\right)+12x\left(x-1\right)+8\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}\)
\(=5x^3+14x^2+12x+8\)
d) Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x^3+14x^2+12x+8}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x^3+10x^2+4x^2+8x+4x+8}{x+2}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x^2\left(x+2\right)+4x\left(x+2\right)+4\left(x+2\right)}{x+2}\)
\(=5x^2+4x+4\)

c) Ta có: \(\dfrac{5x^4+9x^3-2x^2-4x-8}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x^4-5x^3+14x^3-14x^2+12x^2-12x+8x-8}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x^3\left(x-1\right)+14x^2\left(x-1\right)+12x\left(x-1\right)+8\left(x-1\right)}{x-1}\)
\(=5x^3+14x^2+12x+8\)

b: \(\dfrac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)-2x\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^2-1}\)
\(=x^2-2x+1\)
\(=\left(x-1\right)^2\)
c: \(=\dfrac{5x^4-5x^3+14x^3-14x^2+12x^2-12x+8x-8}{x-1}\)
\(=5x^3+14x^2+12x+8\)

Lời giải
Ta có
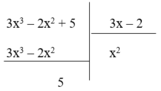
Vì phần dư R = 5 ≠ 0 nên phép chia đa thức 3 x 3 – 2 x 2 + 5 cho đa thức 3x – 2 là phép chia có dư. Do đó (I) sai
Lại có
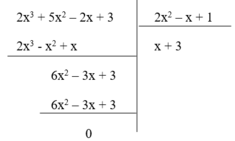
Nhận thấy phần dư R = 0 nên phép chia đa thức ( 2 x 3 + 5 x 2 – 2x + 3) cho đa thức (2 x 2 – x + 1) là phép chia hết. Do đó (II) đúng
Đáp án cần chọn là: D


a: \(5x^2\left(3x^3-2x^2+x+2\right)\)
\(=15x^5-10x^4+5x^3+10x^2\)
b: \(3x^4\left(-2x^3+5x^2-\dfrac{2}{3}x+\dfrac{1}{3}\right)\)
\(=-6x^7+15x^6-2x^5+x^4\)

Bài 13:
1: \(A=-x^2+4x+3\)
\(=-\left(x^2-4x-3\right)=-\left(x^2-4x+4-7\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-2\right)^2+7\le7\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=2
2: \(B=-\left(x^2-6x+11\right)\)
\(=-\left(x-3\right)^2-2\le-2\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=3
a) Ta có: \(\frac{15+5x^2-3x^3-9x}{5-3x}\)
\(=\frac{-3x^3+5x^2-9x+15}{5-3x}\)
\(=\frac{3x^3-5x^2+9x-15}{3x-5}\)
\(=\frac{x^2\left(3x-5\right)+3\left(3x-5\right)}{3x-5}\)
\(=\frac{\left(3x-5\right)\left(x^2+3\right)}{3x-5}\)
\(=x^2+3\)
b) Ta có: \(\frac{x^4-2x^3-1+2x}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\frac{x^4-2x^3-1+2x}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)-2x\left(x^2-1\right)}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1-2x\right)}{x^2-1}\)
\(=x^2-2x+1=\left(x-1\right)^2\)