Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) ĐK: \(\cos x\ne0\)( vì tan x = sinx/cosx nên cos x khác 0)
<=> \(x\ne\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\); k thuộc Z
TXĐ: \(ℝ\backslash\left\{\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\right\}\); k thuộc Z
b) ĐK: \(1+\cos2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow\cos2x\ne-1\Leftrightarrow2x\ne\pi+k2\pi\Leftrightarrow x\ne\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\); k thuộc Z
=> TXĐ: \(ℝ\backslash\left\{\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\right\}\); k thuộc Z
c) ĐK: \(\hept{\begin{cases}\cot x-\sqrt{3}\ne0\\\sin x\ne0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne\frac{\pi}{6}+k\pi\text{}\text{}\\x\ne l\pi\end{cases}}\); k,l thuộc Z
=>TXĐ: ....
d) ĐK: \(1-2\sin^2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow\cos2x\ne0\Leftrightarrow2x\ne\frac{\pi}{2}+k\pi\Leftrightarrow x\ne\frac{\pi}{4}+\frac{k\pi}{2}\)
=> TXĐ:...

a) \(\sin \left( {x + h} \right) - \sin x = 2\cos \frac{{2x + h}}{2}.\sin \frac{h}{2}\)
b) Với \({x_0}\) bất kì, ta có:
\(\begin{array}{l}f'\left( {{x_0}} \right) = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{f\left( x \right) - f\left( {{x_0}} \right)}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\sin x - \sin {x_0}}}{{x - {x_0}}}\\ = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{2\cos \frac{{x + {x_0}}}{2}.\sin \frac{{x - {x_0}}}{2}}}{{x - {x_0}}} = \mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \frac{{\sin \frac{{x - {x_0}}}{2}}}{{\frac{{x - {x_0}}}{2}}}.\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {x_0}} \cos \frac{{x + {x_0}}}{2} = \cos {x_0}\end{array}\)
Vậy hàm số y = sin x có đạo hàm là hàm số \(y' = \cos x\)

Tham khảo:
a) Ta có: \(M = {a^{{{\log }_a}M}},N = {a^{{{\log }_a}N}} \Rightarrow MN = {a^{{{\log }_a}M}}.{a^{{{\log }_a}N}} = {a^{{{\log }_a}M + {{\log }_a}N}}\)
Mặt khác: \(MN = {a^{{{\log }_a}\left( {MN} \right)}}\)
Vậy \({a^{{{\log }_a}M + {{\log }_a}N}} = {a^{{{\log }_a}\left( {MN} \right)}} \Leftrightarrow {\log _a}M + {\log _a}N = {\log _a}\left( {MN} \right)\)
b)
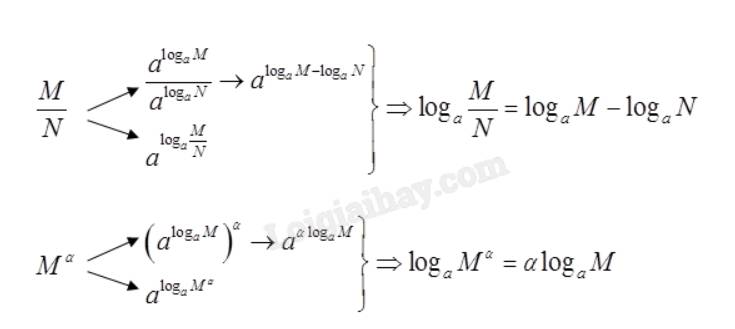
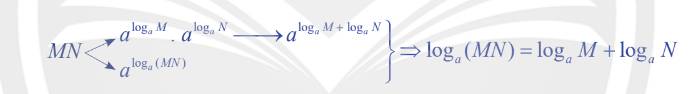
Thay vì băn khoăn với việc tách biểu thức, sao bạn không sử dụng phương pháp cơ bản nhất là đạo hàm của một thương? Hoàn toàn ko chậm hơn:
\(y=\frac{f\left(x\right)}{g\left(x\right)}\Rightarrow y'=\frac{f'\left(x\right).g\left(x\right)-f\left(x\right).g'\left(x\right)}{g^2\left(x\right)}\)
Ví dụ: \(y=\frac{1-2x}{2x-4}\Rightarrow y'=\frac{-2\left(2x-4\right)-2\left(1-2x\right)}{\left(2x-4\right)^2}=\frac{6}{\left(2x-4\right)^2}\)
Mất ko đến 20s
Trong khi tách thì mất thời gian hơn nhiều với 2 bước: tách, đạo hàm
\(y=\frac{-2x+4-3}{2x-4}=\frac{-\left(2x-4\right)}{2x-4}-\frac{3}{2x-4}=-1-\frac{3}{2x-4}\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=-\frac{\left(-3\right)\left(2x-4\right)'}{\left(2x-4\right)^2}=\frac{6}{\left(2x-4\right)^2}\)
Mất ít nhất 1-2ph
Vừa phức tạp hơn, vừa tốn thời gian hơn, chẳng ai sử dụng phương pháp tách này bao giờ