Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

| PTHH | Tên gọi sản phẩm |
| \(C+O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}CO_2\) | cacbon đioxit |
| \(4P+5O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}2P_2O_5\) | điphotpho pentaoxit |
| \(2H_2+O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}2H_2O\) | nước |
| \(4Al+3O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}2Al_2O_3\) | nhôm oxit |
| \(2Mg+O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}2MgO\) | magie oxit |
| \(2C_2H_2+5O_2\underrightarrow{t^o}4CO_2+2H_2O\) | cacbon đioxit và nước |

a)
\(C + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2\\ 2Cu + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CuO\\ 3Fe + 2O_2\xrightarrow{t^o} Fe_3O_4\\ S + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} SO_2\\ 4P + 5O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2P_2O_5\\ 2H_2 + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2H_2O\\ 2Zn + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2ZnO\\ 4Na + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2Na_2O\\ \)
b)
\(2CO + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CO_2\\ 2SO_2 + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2SO_3\\ CH_4 + 2O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2 + 2H_2O\\ C_2H_6 + \dfrac{7}{2}O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CO_2 + 3H_2O\)

\(C+O_2\rightarrow^{t^o}CO_2\)
\(2Cu+O_2\rightarrow^{t^o}2CuO\)
\(3Fe+2O_2\rightarrow^{t^o}Fe_3O_4\)
\(S+O_2\rightarrow^{t^o}SO_2\)
\(4P+5O_2\rightarrow^{t^o}2P_2O_5\)
\(H_2O+O_2\rightarrow^{t^o}2H_2O\)
\(a) C + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2\\ 2Cu + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CuO\\ 4Fe + 3O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2Fe_2O_3\\ S + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} SO_2\\ 4P + 5O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2P_2O_5\\ 2H_2 + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2H_2O\\ 2Zn + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2ZnO\\ 4Na + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2Na_2O\\ \)
\(b) 2CO + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CO_2\\ CH_4 + 2O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2 + 2H_2O\\ C_2H_6 + \dfrac{7}{2}O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CO_2 + 3H_2O\)

S + O2 ➝ SO2 ( thuộc loại oxit axit , SO2: lưu huỳnh đioxit)
P + O2 ➝ P2O5 ( thuộc loại oxit axit , P2O5: đi phôtpho pentaoxit)
C + O2➝ CO2 ( thuộc loại oxit axit , CO2 : cacbon đioxit )
Si + O2 ➝ SiO2( thuộc loại oxit axit , SiO2: silic đioxit )
Cu + O2 ➝ Cu2O(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Cu2O: đồng (1) oxit )
Na + O2➝ Na2O( thuộc loại oxit bazo , Na2O: natri oxit)
Fe + O2➝ Fe3O4(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Fe3O4: oxit sắt từ)
Al + O2 ➝ Al2O3(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Al2O3: nhôm oxit)
Mg + O2➝ MgO(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Mg : magie oxit)
CH4 + O2 ➝ CO2 + H2O (thuộc loại oxit axit , CH4: khí metan
H2O: nước
Chúc bạn học tốt

CH4 + 2O2 t0→ CO2 + 2H2O
C2H4 + 3O2 t0→ 2CO2 + 2H2O
C2H2 + 52 O2 t0→ 2CO2 + 2H2O
-Gọi: nCH4:a(mol)
nC2H4:b(mol)
nC2H2:c(mol)
⇒16a+28b+26c=11(1)
BTNT C ⇒a+2b+2c=0,75(2)
-Phân tích (1)và (2) ta được:
{13a+26b+26c=9,75
=>3a+2b=1,25(3)
16a+32b+32c=12
=>4b+6c=1(4)
-Từ (3) ⇒ \(a=\dfrac{1,25-2b}{3}\)
-Từ (4)⇒\(\dfrac{1-4c}{6}\)
-% CH4 =\(\dfrac{16a}{16a+32b+32c}.100\)
-Thay công thức a và c vào (⋅)
⇒%CH4=\(\dfrac{\dfrac{1,25-2b}{3}16}{16\dfrac{1,25-2b}{3}+28b+26.\dfrac{1-4b}{6}}100=12,12\%\)

Câu 1 :
\(n_X=\dfrac{3.36}{22.4}=0.15\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{CO_2}=\dfrac{12.32}{22.4}=0.55\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n_C=0.55\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{H_2O}=\dfrac{10.8}{18}=0.6\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n_H=0.6\cdot2=1.2\left(mol\right)\)
\(m_X=m_C+m_H=0.55\cdot12+1.2=7.8\left(g\right)\)
\(\overline{M}_X=\dfrac{7.8}{0.15}=52\left(\dfrac{g}{mol}\right)\)
\(d_{\dfrac{X}{H_2}}=\dfrac{52}{2}=26\)
Câu 2 :
\(2Al+6HCl\rightarrow2AlCl_3+3H_2\)
\(Fe+2HCl\rightarrow FeCl_2+H_2\)
\(n_{Al}=\dfrac{a}{27}\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{Fe}=\dfrac{a}{56}\left(mol\right)\)
Để cân thăng bằng thì lượng khí H2 thoát ra phải như nhau.
Vì :
\(n_{Fe}=\dfrac{a}{56}< n_{Al}=\dfrac{a}{27}\left(mol\right)\)
và lượng H2 sinh ra ở cả 2 phản ứng trên phụ thuộc vào HCl là như nhau
Để cân thăng bằng thì lượng HCl cho vào không vượt quá lượng tối đa để hòa tan Fe
\(n_{HCl}=2n_{Fe}=\dfrac{2a}{56}\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow b\le\dfrac{2a}{56}\)

1) \(C+O2-->CO2\)==>Pư hóa hợp
\(2Mg+O2-->2MgO\)==>Pư hóa hợp
\(4Al+3O2-->2Al2O3\)==>Pư hóa hợp
\(C2H6+\frac{7}{2}O2-->2CO2+3H2O\)
\(C2H2+\frac{5}{2}O2-->2CO2+H2O\)
2)
\(3Fe+2O2-->Fe3O4\)
\(S+O2-->SO2\)
\(CH4+2O2-->CO2+2H2O\)
\(2Cu+O2-->2CuO\)
\(4P+5O2-->2P2O5\)
\(C3H8O+\frac{9}{2}O2-->3CO2+4H2O\)
\(C4H10+\frac{13}{2}O2-->4CO2+5H2O\)
\(C7H16+11O2-->7CO2+8H2O\)
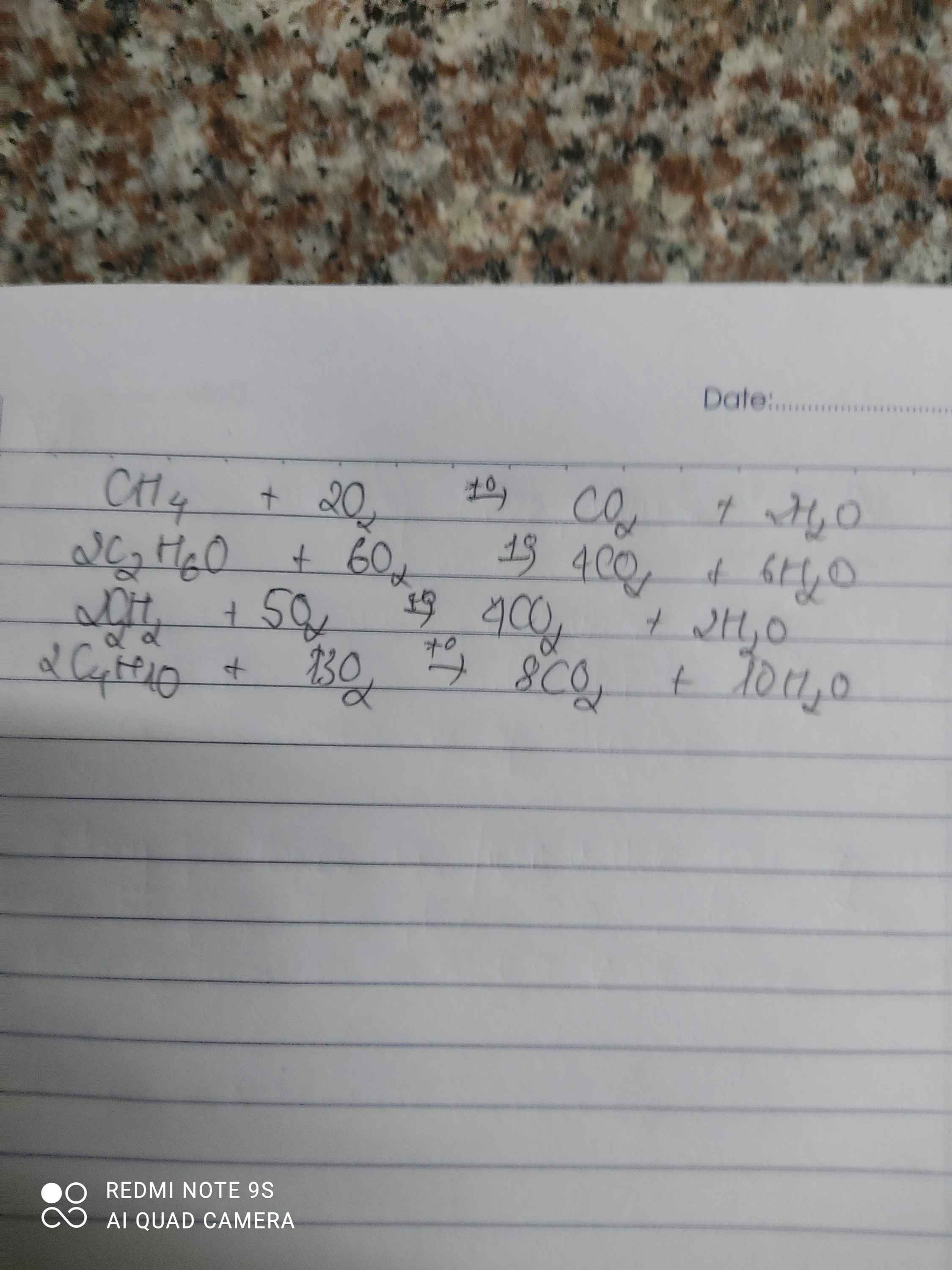
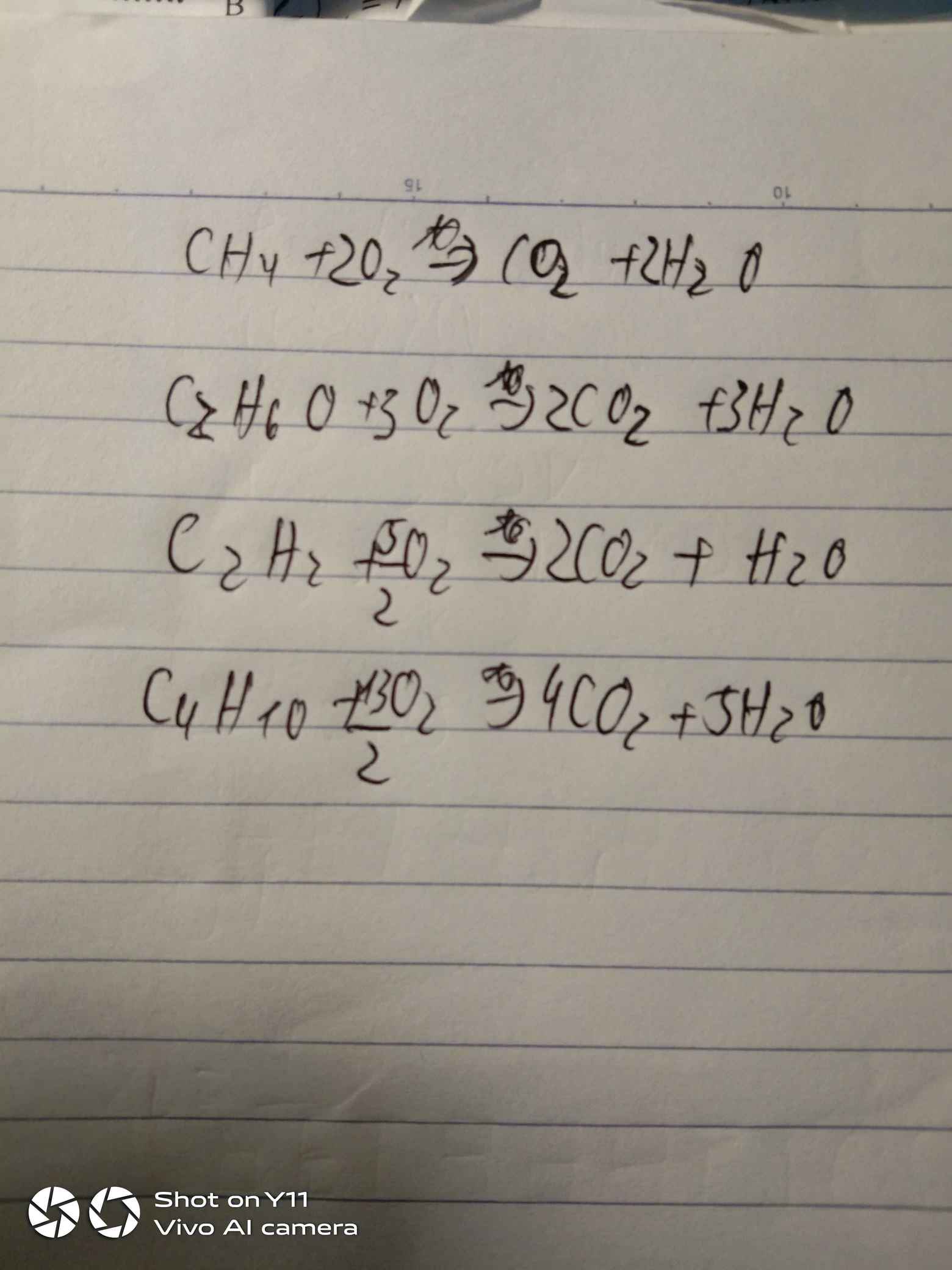
C.ơn