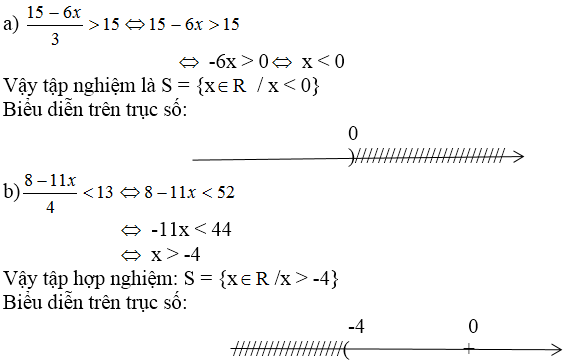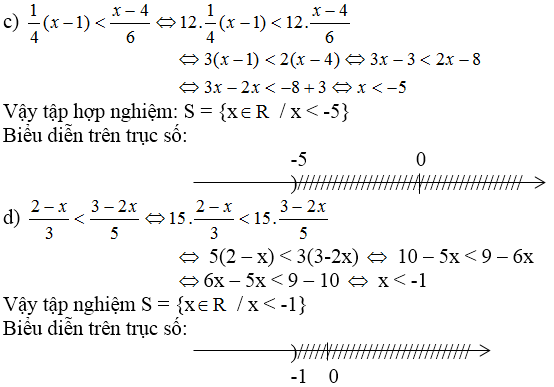Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{a-1}{4}=\dfrac{b-2}{3}=\dfrac{c-3}{2}=\dfrac{d-4}{1}=\dfrac{a+b+c+d-1-2-3-4}{4+3+2+1}=\dfrac{350}{10}=35\)
Do đó: a-1=140; b-2=105; c-3=70; d-4=35
=>a=141; b=107; c=73; d=39

a: =>3x-1>8
=>3x>9
hay x>3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow2x+4< 9\)
=>2x<5
hay x<5/2
c: \(\Leftrightarrow1-2x>12\)
=>-2x>11
hay x<-11/2
d: \(\Leftrightarrow6-4x< 5\)
=>-4x<-1
hay x>1/4

Áp dụng tính chất của dãy tỉ số bằng nhau, ta được:
\(\dfrac{a-1}{4}=\dfrac{b-2}{3}=\dfrac{c-3}{2}=\dfrac{d-4}{1}=\dfrac{a+b+c+d-1-2-3-4}{4+3+2+1}=\dfrac{360-10}{10}=35\)
Do đó: a-1=140; b-2=105; c-3=70; d-4=35
=>a=141; b=107; c=73; d=39

a: \(B=\left(\dfrac{21}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\right):\dfrac{x+3-1}{x+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{21+x^2-x-12-x^2+4x-3}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}:\dfrac{x+2}{x+3}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+6}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+3}{x+2}=\dfrac{3}{x-3}\)
b: Ta có: |2x+1|=5
=>2x+1=5 hoặc 2x+1=-5
=>2x=4 hoặc 2x=-6
=>x=2
Thay x=2 vào B, ta được:
\(B=\dfrac{3}{2-3}=\dfrac{3}{-1}=-3\)
d: Để B<0 thì x-3<0
hay x<3

a: \(x< -9:\dfrac{3}{2}=-9\cdot\dfrac{2}{3}=-6\)
b: 2/3x>-2
hay x>-2:2/3=-3
c: \(2x>\dfrac{9}{5}-\dfrac{4}{5}=1\)
hay x>1/2
d: \(\Leftrightarrow x\cdot\dfrac{3}{5}>6-4=2\)
hay x>2:3/5=2x5/3=10/3

a: \(A=x^2-4x+4-3=\left(x-2\right)^2-3>=-3\)
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=2
b: \(x^2+4x-10=x^2+4x+4-14=\left(x+2\right)^2-14>=-14\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{x^2+4x-10}< =-\dfrac{4}{14}\)
=>B>=2/7
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=-2
c: \(x^2-x+1=\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{3}{4}>=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
=>2/x^2-x+1<=2:3/4=8/3
=>C>=-8/3
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=1/2
d: x^2-6x+12=(x-3)^2+3>=3
=>6/x^2-6x+12<=2
=>D>=-2
Dấu = xảy ra khi x=3