Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a. Đặt CT muối: \(RCO_3\)
\(RCO_3\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)RO+CO_2\) (1)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=\dfrac{200.17,1}{171.100}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=\dfrac{29,55}{197}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
`@` TH1: Chỉ tạo ra kết tủa
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,15 0,15 0,15 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=n_{CO_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{21}{0,15}=140\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=80\) ( loại )
`@` TH2: Ba(OH)2 hết
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,2 ( mol )
0,15 0,15 0,15 ( mol )
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
0,05 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=n_{CO_2}=0,15+0,1=0,25\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{21}{0,25}=84\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=24\) `->` R là Mg
\(n_{MgO}=0,25.\left(24+16\right)=10\left(g\right)\)
b.\(n_{MgCO_3}=\dfrac{4,2}{84}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{HCl}=0,05.3=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(m_{HCl}=50.1,15=57,5\left(g\right)\)
\(MgCO_3+2HCl\rightarrow MgCl_2+CO_2+H_2O\)
0,05 < 0,15 ( mol )
0,05 0,1 0,05 0,05 ( mol )
\(m_{ddspứ}=4,2+57,5-0,05.44=59,5\left(g\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\%m_{MgCl_2}=\dfrac{0,05.95}{59,5}.100=7,98\%\\\%m_{HCl\left(dư\right)}=\dfrac{\left(0,15-0,1\right).36,5}{59,5}.100=3,06\%\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(MCO_3-^{t^o}\rightarrow MO+CO_2\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=0,1\left(mol\right);n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn nguyên tố Ba => \(n_{Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn nguyên tố C =>\(n_{CO_2}=n_{BaCO_3}+n_{Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
Bảo toàn khối lượng => \(m_B=m_{muối}-m_{CO_2}=20-0,2.44=11,2\left(g\right)\)
Theo PT ta có : \(n_{MCO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(M_{MCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,2}=100\)
=> M + 60 =100
=> M=40 (Ca)
=> CT muối : CaCO3

Đặt CT muối \(RCO_3\)
\(RCO_3\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)RO+CO_2\) (1)
\(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=15.0,01=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{BaCO_3}=\dfrac{19,7}{197}=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
`@`TH1: Chỉ tạo ra kết tủa
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,1 0,1 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1) \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{CO_2}=0,1\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,1}=200\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=140\) \((g/mol)\) (loại )
`@`TH2: Tạo ra 2 muối
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+CO_2\rightarrow BaCO_3\downarrow+H_2O\)
0,15 ( mol )
0,1 0,1 0,1 ( mol )
\(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+2CO_2\rightarrow Ba\left(HCO_3\right)_2\)
0,05 0,1 ( mol )
Theo ptr (1): \(n_{RCO_3}=n_{RO}=0,1+0,1=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(M_{RCO_3}=\dfrac{20}{0,2}=100\) \((g/mol)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow R=40\) \((g/mol)\) `->` R là Canxi ( Ca )
\(m_{CaO}=0,2\left(40+16\right)=11,2\left(g\right)\)

nMg= 0.09 mol
nNO= 0.04 mol
Mg----> Mg2+ + 2e
0.09 ----------------------------0.18
N+5 + 3e-----------.> N+2
0.12<--------0.04
vi số mol e nhận < số mol e nhường----> sản phâm muối còn có NH4NO3
gọi x là số mol của NH4NO3
N+5 +8e-----------> N-3
8x<------------x
Theo bao toàn e ta có: 8x + 0.12= 0.18 +> x= 0.0075
==> m NH4No3 = 0.0075 x 80=.........
m Mg(NO3)2= 0.09 x 148=......
khối luọng muói tạo thành = m Mg(NO3)2 + m NH4No3 =......
n NaOH = 0,03 mol
1)
Trong Z chứa: NaAlO2 + NaOH dư có tổng số mol = 0,03 mol
Z tác dụng vs HCl đến khi xuất hiện kết tủa thì ngừng => phản ứng hết NaOH dư => nNaOH dư = n HCl = 0,01 mol
=> n NaAlO2 = 0,03 -0,01 = 0,02 mol => nAl2O3 = 0,01 mol
2)
+) Phần 1 của Y
nH2SO4 = 0,03 mol = nCuO + nFeO
+) Phần 2 của Y
Hỗn hợp khí thoát ra là CO2 và CO dư
Theo sơ đồ chéo tính được n CO2 = 2nCO và tổng số mol khí = 0,03
=> nCO2 = 0,02 mol
=> m Hỗn hợp oxit ban đầu = 2+ 0,02.16 = 2,32 g
Ta có hệ phương trình:
x+y = 0,03
72x + 80y= 2,32
=> x = 0,01 y =0,02
=> trong hỗn hợp ban đầu: n FeO = 0,02 mol. nCuO = 0,04 mol

a. PTHH:
Cu + HCl ---x--->
Fe + 2HCl ---> FeCl2 + H2
Vậy chất rắn A là Cu.
b. Ta có: \(n_{H_2}=\dfrac{6,72}{22,4}=0,3\left(mol\right)\)
Theo PT: \(n_{Fe}=n_{H_2}=0,3\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(m_{Fe}=0,3.56=16,8\left(g\right)\)
=> \(\%_{m_{Fe}}=\dfrac{16,8}{30}.100\%=56\%\)
\(\%_{m_{Cu}}=100\%-56\%=44\%\%\)
c.
Theo PT: \(n_{FeCl_2}=n_{Fe}=0,3\left(mol\right)\)
=> \(m_{FeCl_2}=0,3.127=38,1\left(g\right)\)
d.
Ta có: \(m_{dd_{FeCl_2}}=100+16,8=116,8\left(g\right)\)
=> \(C_{\%_{FeCl_2}}=\dfrac{38,1}{116,8}.100\%=32,62\%\)
ta có Cu ko phản ứng với HCl
-> V khí là do Fe phản ứng hết tạo ra
Fe + 2HCl -> FeCl2 + H2
0,3 .............................0,3
n H2 = 6,72 : 22,4=0,3 mol
m Fe = 0,3.56 =16,8 g
% Fe = 16,8 : 30 .100 = 56 %
% Cu = 100% - 56% = 44%

a) MX = 146g/mol
VCO2 : VH2O = 6 : 5
=> nC : nH = 3 : 5
=> CTĐGN: (C3H5Oa)n
→ (41 + 16a).n = 146 → (a; n) = (4; 2) → X: C6H10O4
b) C6H10O4 + 6,5O2 → 6CO2 + 5H2O
0,05 0,325
=> p = 7,3g
c)
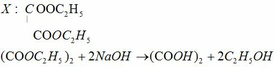

a)
2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2↑
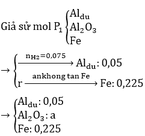
Pt: 2Al + 6H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3SO2↑ + 6H2O
2Fe + 6H2SO4 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 3SO2↑ + 6H2O
Al2O3 + 3H2SO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + 3H2O
Giả sử P2 = kP1
=> a=0.1
=> m = 128,8g
b)
2yAl + 3FexOy → yAl2O3 + 3xFe
0,1 0,225
=> 0,225y = 0,3x => 3y = 4x
=> Fe3O4
