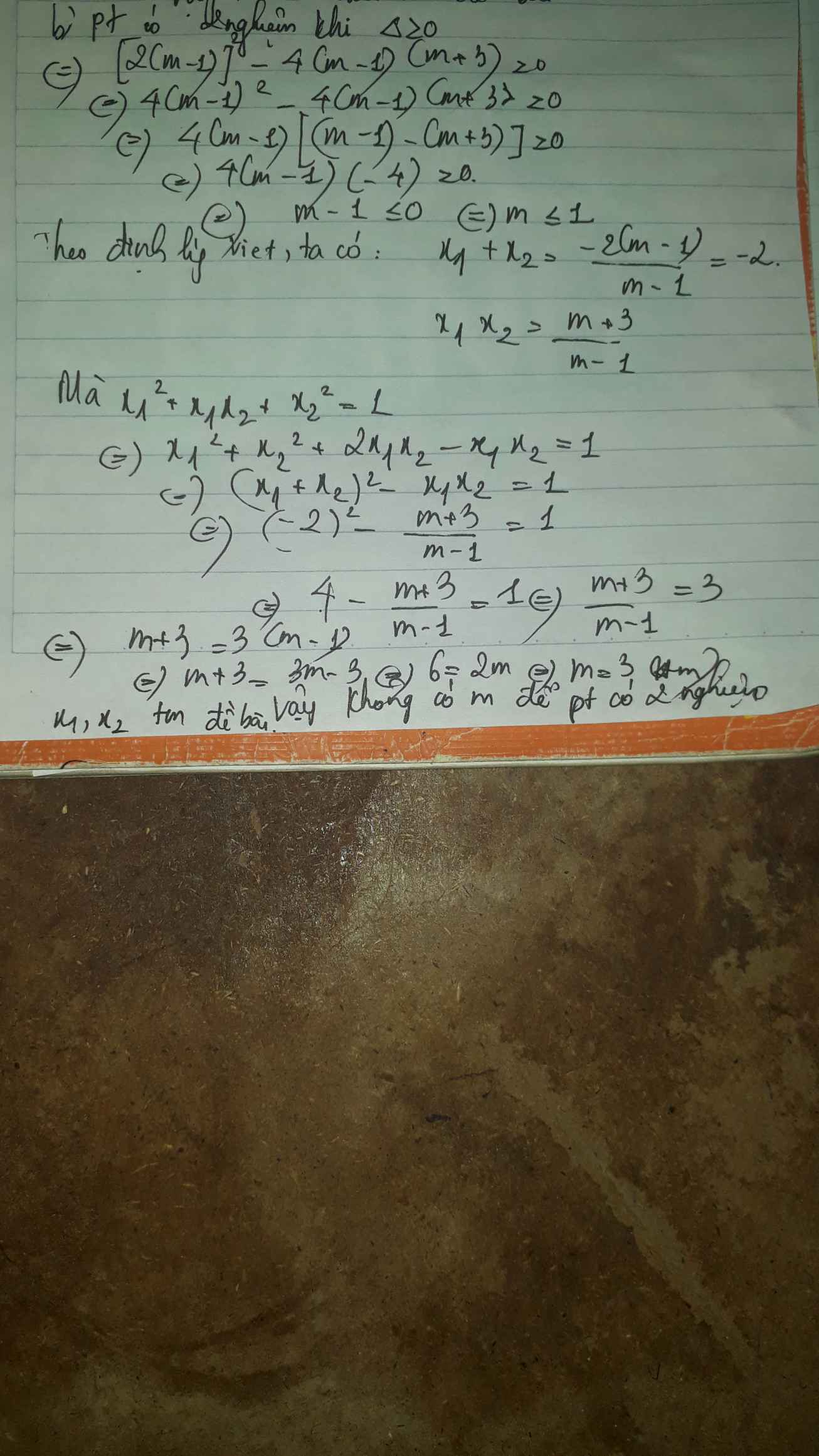Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a, với =-3
\(=>x^2-6x+6=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-6\right)^2-4.6=12>0\)
=>pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x3,x4
\(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}x3=\dfrac{6+\sqrt{12}}{2}=3+\sqrt{3}\\x4=\dfrac{6-\sqrt{12}}{2}=3-\sqrt{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b, \(\Delta=\left(2m\right)^2-4\left(m^2+m\right)=4m^2-4m^2-4m=-4m\)
pt đã cho đề bài có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x1,x2 khi
\(-4m>0< =>m< 0\)
theo vi ét \(=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x1+x2=-2m\\x1x2=m^2+m\end{matrix}\right.\)
có \(\left(x1-x2\right)\left(x1^2-x2^2\right)=32\)
\(< =>\left(x1-x2\right)^2\left(x1+x2\right)=32\)
\(< =>\left[x1^2-2x1x2+x2^2\right]\left(-2m\right)=32\)
\(< =>\left[\left(x1+x2\right)^2-4x1x2\right]\left(-2m\right)=32\)
\(< =>\left[\left(-2m\right)^2-4\left(m^2+m\right)\right]\left(-2m\right)=32< =>m=2\)(loại)
Vậy \(m\in\varnothing\)
Lời giải:
a. Với $m=-3$ thì pt trở thành:
$x^2-6x+6=0\Leftrightarrow x=3\pm \sqrt{3}$
b. Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì: $\Delta'=m^2-(m^2+m)=-m\geq 0$
$\Leftrightarrow m\leq 0$
Áp dụng định lý Viet: $x_1+x_2=-2m; x_1x_2=m^2+m$
Khi đó:
$(x_1-x_2)(x_1^2-x_2^2)=32$
$\Leftrightarrow (x_1-x_2)^2(x_1+x_2)=32$
$\Leftrightarrow [(x_1+x_2)^2-4x_1x_2](x_1+x_2)=32$
$\Leftrightarrow [(-2m)^2-4(m^2+m)](-2m)=32$
$\Leftrightarrow 8m^2=32$
$\Leftrightarrow m^2=4$
$\Rightarrow m=-2$ (do $m\leq 0$)
Vây.........

b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)

\(x^2-2\left(m+4\right)x+m^2+8m-9=0\left(1\right)\)
Ta giải \(\Delta=[-2\left(m+4\right)]^2-4\left(m^2+8m-9\right)=100>0\forall m\)
suy ra pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1,x_2\forall m\).
Ta có: \(x_1=m-1\), \(x_2=m+1\) (thay \(\Delta\) vào công thức tìm nghiệm phân biệt).
Gọi \(A=\dfrac{x_1^2+x_2^2-48}{x_1^2+x_2^2}\).
\(\Rightarrow A=1-\dfrac{48}{x_1^2+x_2^2}=1-\dfrac{48}{\left(m-1\right)^2+\left(m+1\right)^2}=1-\dfrac{24}{m^2+1}\).
Để biểu thức A nguyên thì \(\dfrac{24}{m^2+1}\) nguyên, suy ra \(m^2+1\inƯ\left(24\right)\).
\(\Rightarrow m^2+1\in\left\{1;2;4;6;8;12;24\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\left\{0;\pm1\right\}\) (vì m nhận giá trị nguyên)
Vậy \(m\in\left\{0;\pm1\right\}\) là giá trị cần tìm.
Mình chỉnh sửa lại một chút nhé.
\(A=1-\dfrac{24}{m^2+2}\)
\(\Rightarrow...\)\(\Rightarrow\)\(m^2+2\in\left\{1;2;3;4;6;8;12;24\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\in\left\{0;\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
Vậy...

Cách ngắn ngọn nhất:
x2−2(m+1)x+4m=0(1)�2−2(�+1)�+4�=0(1)
⇔x2−2x−2mx+4m=0⇔�2−2�−2��+4�=0
⇔x(x−2)−2m(x−2)=0⇔�(�−2)−2�(�−2)=0
⇔(x−2)(x−2m)=0⇔(�−2)(�−2�)=0
⇔[x=2x=2m⇔[�=2�=2�
Phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm là x=2;x=2m�=2;�=2�. Mặt khác phương trình (1) cũng có 2 nghiệm là x1, x2 nên ta chia làm 2 trường hợp:
TH1: x1=2;x2=2m�1=2;�2=2�.
Có 2x1−x2=−2⇒2.2−2m=−2⇔m=32�1−�2=−2⇒2.2−2�=−2⇔�=3
TH2: x1=2m;x2=2�1=2�;�2=2
Có 2x1−x2=−2⇒2.(2m)−2=−2⇔m=02�1−�2=−2⇒2.(2�)−2=−2⇔�=0
Vậy m=0 hay m=3

a: Thay m=-5 vào (1), ta được:
\(x^2+2\left(-5+1\right)x-5-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-8x-9=0\)
=>(x-9)(x+1)=0
=>x=9 hoặc x=-1
b: \(\text{Δ}=\left(2m+2\right)^2-4\left(m-4\right)=4m^2+8m+4-4m+16=4m^2+4m+20>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
\(\dfrac{x_1}{x_2}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1}=-3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2=-3x_1x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2+x_1x_2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m+2\right)^2+m-4=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+9m=0\)
=>m(4m+9)=0
=>m=0 hoặc m=-9/4

\(x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+3\left(m+1\right)-3=0\)
\(x^2-2nx+3n+3=\left(x-n\right)^2-\left(n^2-3n+3\right)=0\)\(\left(x-n\right)^2=\left(n-\frac{3}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}=\frac{\left(2n-3\right)^2+3}{4}>0\forall n\) vậy luôn tồn tại hai nghiệm
\(\orbr{\begin{cases}x_1=\frac{n-\sqrt{\left(2n-3\right)^2+3}}{2}\\x_2=\frac{n+\sqrt{\left(2n-3\right)^2+3}}{2}\end{cases}}\)
a) \(\frac{x_1}{x_2}=\frac{4x_1-x_2}{x_1}\Leftrightarrow\frac{x_1^2-4x_1x_2+x_2^2}{x_1x_2}=0\)
\(x_1x_2=n^2-\frac{\left(2n-3\right)^2+3}{4}=\frac{4n^2-4n^2+12n-9-3}{4}=3n-3\)
với n=1 hay m=0 : Biểu thức cần C/m không tồn tại => xem lại đề

Phương trình có : \(\Delta=b^2-4ac=\left[-\left(m+1\right)\right]^2-4.1.\left(-2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta=\left(m+1\right)^2+8>0\)
Suy ra phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt với mọi \(m\).
Theo định lí Vi-ét : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m+1\\x_1x_2=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo đề bài : \(\left(1-\dfrac{2}{x_1+1}\right)^2+\left(1-\dfrac{2}{x_2+1}\right)^2=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x_1-1\right)^2}{\left(x_1+1\right)^2}+\dfrac{\left(x_2-1\right)^2}{\left(x_2+1\right)^2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left[\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2+1\right)\right]^2+\left[\left(x_2-1\right)\left(x_1+1\right)\right]^2}{\left[\left(x_1+1\right)\left(x_2+1\right)\right]^2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2+1\right)\right]^2+\left[\left(x_2-1\right)\left(x_1+1\right)\right]^2-2\left[\left(x_1+1\right)\left(x_2+1\right)\right]^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_2+1\right)^2\left[\left(x_1-1\right)^2-\left(x_1+1\right)^2\right]+\left(x_1+1\right)^2\left[\left(x_2-1\right)^2-\left(x_2+1\right)^2\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4x_1\left(x_2+1\right)^2-4x_2\left(x_1+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2^2+2x_1x_2+x_1+x_1^2x_2+2x_1x_2+x_2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+4x_1x_2+\left(x_1+x_2\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow-2\left(m+1\right)+4\cdot\left(-2\right)+m+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=-9\)
Vậy : \(m=-9.\)

\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m-3\right)=m^2+4>0,\forall m\inℝ\)
nên phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1+x_2\).
Theo định lí Viete:
\(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=2m+2\\x_1x_2=2m-3\end{cases}}\)
\(P=\left|\frac{x_1+x_2}{x_1-x_2}\right|=\frac{\left|x_1+x_2\right|}{\left|x_1-x_2\right|}=\frac{\left|x_1+x_2\right|}{\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}}\)
\(=\frac{\left|2m+2\right|}{\sqrt{\left(2m+2\right)^2-4\left(2m-3\right)}}=\frac{\left|2m+2\right|}{\sqrt{4m^2+16}}=\frac{\left|m+1\right|}{\sqrt{m^2+4}}\ge0\)
Dấu \(=\)xảy ra khi \(m=-1\).