Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
Ta có \(P\) là trung điểm của $AB$, $N$ là trung điểm của $AC$ nên
\(AP=PB,AN=NC\Rightarrow \frac{AP}{PB}=\frac{AN}{NC}\)
Do đó theo định lý Tales suy ra \(PN\parallel BC\), mà \(AH\perp BC\Rightarrow PN\perp AH\) \((1)\)
Xét tam giác vuông tại $H$ là $AHB$ có $P$ là trung điểm của $AB$ nên $PA=PH$ . Tương tự, \(AN=NH\)$(2)$
Từ \((1),(2)\Rightarrow \) $PN$ là đường trung trực của $AH$
b) Do \(HM\parallel PN\Rightarrow HMNP\) là hình thang \((1)\)
Sử dụng tính chất so le trong và đồng vị với các đoạn \(PN\parallel BC, NM\parallel AB\) ta có:
\(\widehat{HPN}=\widehat{PHB}=90^0-\widehat{PHA}=90^0-\widehat{PAH}=\widehat{ABH}=\widehat{ABC}\)
\(\widehat{MNP}=\widehat{NMC}=\widehat{ABC}\)
Do đó \(\widehat{HPN}=\widehat{MNP}\) \((2)\)
Từ \((1),(2)\Rightarrow HMNP\) là hình thang cân.

Bài 1:
Vận tốc cano khi dòng nước lặng là: $25-2=23$ (km/h)
Bài 2:
Đổi 1 giờ 48 phút = 1,8 giờ
Độ dài quãng đường AB: $1,8\times 25=45$ (km)
Vận tốc ngược dòng là: $25-2,5-2,5=20$ (km/h)
Cano ngược dòng từ B về A hết:
$45:20=2,25$ giờ = 2 giờ 15 phút.

\(1.\left(x+4\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=16\Leftrightarrow x^2+8x+16-x^2+1=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow8x=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-\frac{1}{8}\)
\(2.\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(x+3\right)^2+2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+3\right)=4\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1+x+3\right)^2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+2\right)^2=4\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x+2=2\\2x+2=-2\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=0\\x=-2\end{cases}}\)
3.\(\left(x-1\right)^2-x\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left[\left(x-1\right)-x\right]=0\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
\(4.\left(3x-1\right)^2+\left(5x-2\right)^2-2\left(3x-1\right)\left(5x-2\right)=9\Leftrightarrow\left(3x-1-5x+2\right)^2=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)^2=9\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x-1=3\\2x-1=-3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2\\x=-1\end{cases}}\)
5.\(\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)-x\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=5\Leftrightarrow x^3-1-\left(x^3-4x\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{2}\)
6.\(\left(x-1\right)^3-\left(x+3\right)\left(x^2-3x+9\right)+\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^3-3x^2+3x-1-\left(x^3+27\right)+x^2-4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2x^2+3x-34=0\text{ vô nghiệm}\)


Bài 1:
a.
$a^3-a^2c+a^2b-abc=a^2(a-c)+ab(a-c)$
$=(a-c)(a^2+ab)=(a-c)a(a+b)=a(a-c)(a+b)$
b.
$(x^2+1)^2-4x^2=(x^2+1)^2-(2x)^2=(x^2+1-2x)(x^2+1+2x)$
$=(x-1)^2(x+1)^2$
c.
$x^2-10x-9y^2+25=(x^2-10x+25)-9y^2$
$=(x-5)^2-(3y)^2=(x-5-3y)(x-5+3y)$
d.
$4x^2-36x+56=4(x^2-9x+14)=4(x^2-2x-7x+14)$
$=4[x(x-2)-7(x-2)]=4(x-2)(x-7)$
Bài 2:
a. $(3x+4)^2-(3x-1)(3x+1)=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-[(3x)^2-1]=49$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4)^2-(3x)^2=48$
$\Leftrightarrow (3x+4-3x)(3x+4+3x)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 4(6x+4)=48$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x+4=12$
$\Leftrightarrow 6x=8$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{4}{3}$
b. $x^2-4x+4=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)^2=9(x-2)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-2-9)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-2)(x-11)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-2=0$ hoặc $x-11=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=2$ hoặc $x=11$
c.
$x^2-25=3x-15$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5)=3(x-5)$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+5-3)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (x-5)(x+2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-5=0$ hoặc $x+2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=5$ hoặc $x=-2$

\(A=\left(2n-1\right)^3-2n+1\)
\(A=8n^3-6n+6n-1-2n+1\)
\(A=8n^3-2n=2n\left(4n^2-1\right)\)
\(A=2n\left(2n+1\right)\left(2n-1\right)\)
\(A=\left(2n-1\right)2n\left(2n+1\right)⋮6\) ( 3 số tự nhiên liên tiếp)

\(3x^2+7x-20=0\\ < =>3x^2+12x-5x-20=0\\ < =>3x\left(x+4\right)-5\left(x+4\right)=0\\ < =>\left(x+4\right)\left(3x-5\right)=0\\ =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+4=0\\3x-5=0\end{matrix}\right.\\ =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-4\\x=\dfrac{5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Tập nghiệm của phương trình là \(S=\left\{-4;\dfrac{5}{3}\right\}\)
do câu hỏi của lớp 8 nên mình làm ntn nha:
pt <=> \(3x^2+7x=20\)
<=> \(x^2+\dfrac{7}{3}x=\dfrac{20}{3}\)
<=> \(x^2+2.\dfrac{\dfrac{7}{3}}{2}x+\dfrac{49}{36}-\dfrac{49}{36}=\dfrac{20}{3}\) <=> \(\left(x+\dfrac{7}{6}\right)^2=\dfrac{49}{36}+\dfrac{20}{3}\)
<=> \(\left(x+\dfrac{7}{6}\right)^2=\dfrac{289}{36}\)
<=> x+7/6 = \(\pm\sqrt{\dfrac{289}{36}}\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{3}\\x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
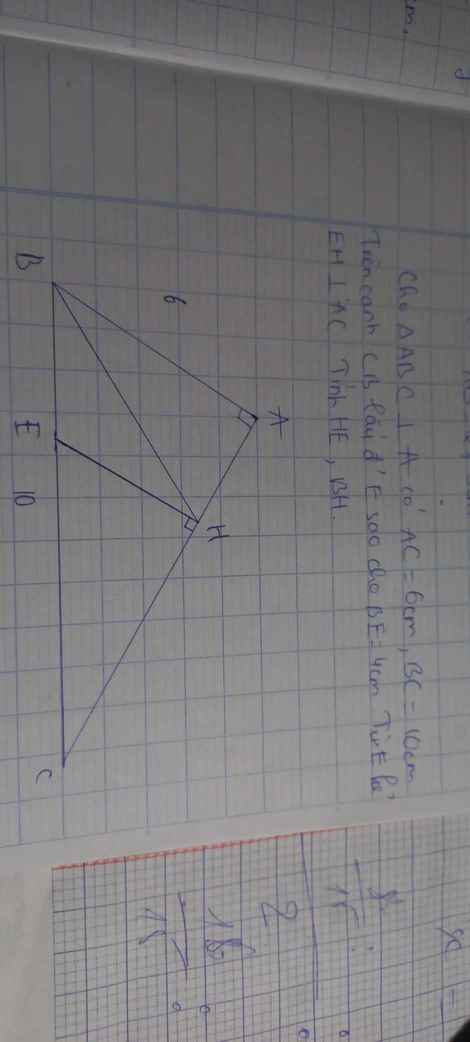


 Mình cần giải bài 6 ạ, giúp mình với huhu ;-;
Mình cần giải bài 6 ạ, giúp mình với huhu ;-;