Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow{MN}=\overrightarrow{MA}+\overrightarrow{MB}+4\overrightarrow{MC}\)
\(=6\overrightarrow{MI}+\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+4\overrightarrow{IC}\)
\(=6\overrightarrow{MI}+4\overrightarrow{IG}+4\overrightarrow{IC}\)
\(=6\overrightarrow{MI}\)
\(\Rightarrow M,I,N\) thẳng hàng

Do M là trung điểm BC nên: \(\overrightarrow{AM}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AC}\)
Tương tự: \(\overrightarrow{BN}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{BA}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{BC}\) ; \(\overrightarrow{CP}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
Cộng vế:
\(\overrightarrow{AM}+\overrightarrow{BN}+\overrightarrow{CP}=\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AC}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{BA}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{BC}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{CA}+\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BA}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{AC}+\overrightarrow{CA}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\overrightarrow{BC}+\overrightarrow{CB}\right)=\overrightarrow{0}\)
b. Từ câu a ta có:
\(\overrightarrow{AM}+\overrightarrow{BN}+\overrightarrow{CP}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{AO}+\overrightarrow{OM}+\overrightarrow{BO}+\overrightarrow{ON}+\overrightarrow{CO}+\overrightarrow{OP}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\overrightarrow{OA}+\overrightarrow{OM}-\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{ON}-\overrightarrow{OC}+\overrightarrow{OP}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{OA}+\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}=\overrightarrow{OM}+\overrightarrow{ON}+\overrightarrow{OP}\) (đpcm)

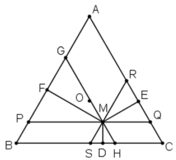
Ta có:
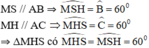
⇒ ΔMHS đều.
MD ⊥ SH nên MD là đường cao đồng thời là trung tuyến của ΔMHS.
⇒ D là trung điểm của HS
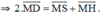
Chứng minh tương tự ta có:
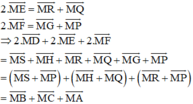
(Vì các tứ giác BSMP, HMQC, MRAG là hình bình hành)
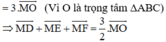

Ta có: \(\overrightarrow {OA} = \overrightarrow {OG} + \overrightarrow {GA} \); \(\overrightarrow {OB} = \overrightarrow {OG} + \overrightarrow {GB} \); \(\overrightarrow {OC} = \overrightarrow {OG} + \overrightarrow {GC} \)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {OB} + \overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OC} = \overrightarrow {OG} + \overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {OG} + \overrightarrow {GB} + \overrightarrow {OG} + \overrightarrow {GC} \\ \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {OB} + \overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OC} = 3\overrightarrow {OG} + \left( {\overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {GB} + \overrightarrow {GC} } \right)\end{array}\)
Do G là trọng tâm của tam giác ABC nên \(\overrightarrow {GB} + \overrightarrow {GA} + \overrightarrow {GC} = \overrightarrow 0 \)
\(\begin{array}{l} \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {OB} + \overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OC} = 3\overrightarrow {OG} + \overrightarrow 0 \\ \Leftrightarrow \overrightarrow {OB} + \overrightarrow {OA} + \overrightarrow {OC} = 3\overrightarrow {OG} \end{array}\)

Tọa độ G là;
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{4+2+0}{3}=2\\y=\dfrac{0-4-2}{3}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Tọa độ M là:
x=(2+0)/2=1 và y=(-4-2)/2=-3
Tọa độ N là:
x=(4+0)/2=2 và y=(0-2)/2=-1
Tọa độ P là;
x=(4+2)/2=3 và y=(0-4)/2=-2
Tọa độ trọng tâm của tam giác MNP là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1+2+3}{3}=2\\y=\dfrac{-3-1-2}{3}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>Tam giác ABC và tam giác MNP có chung trọng tâm

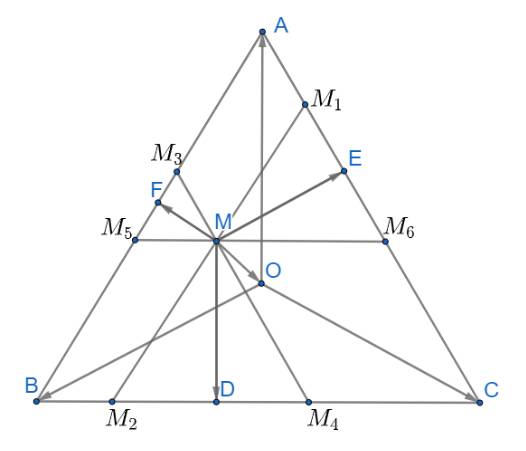
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OD} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OE} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OF} } \right)\)
Qua M kẻ các đường thẳng \({M_1}{M_2}//AB;{M_3}{M_4}//AC;{M_5}{M_6}//BC\)
Từ đó ta có: \(\widehat {M{M_1}{M_6}} = \widehat {M{M_6}{M_1}} = \widehat {M{M_4}{M_2}} = \widehat {M{M_2}{M_4}} = \widehat {M{M_3}{M_5}} = \widehat {M{M_5}{M_3}} = 60^\circ \)
Suy ra các tam giác \(\Delta M{M_3}{M_5},\Delta M{M_1}{M_6},\Delta M{M_2}{M_4}\) đều
Áp dụng tính chất trung tuyến \(\overrightarrow {AM} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} } \right)\)(với M là trung điểm của BC) ta có:
\(\overrightarrow {ME} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MD} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right);\overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( \Rightarrow \overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
Ta có: các tứ giác \(A{M_3}M{M_1};C{M_4}M{M_6};B{M_2}M{M_5}\) là hình bình hành
Áp dụng quy tắc hình bình hành ta có
\(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_4}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_3}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_1}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_3}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_2}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_5}} } \right) + \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {M{M_4}} + \overrightarrow {M{M_6}} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MA} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MB} + \frac{1}{2}\overrightarrow {MC} = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {\left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OA} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OB} } \right) + \left( {\overrightarrow {MO} + \overrightarrow {OC} } \right)} \right)\)
\( = \frac{1}{2}\left( {3\overrightarrow {MO} + \left( {\overrightarrow {MA} + \overrightarrow {MB} + \overrightarrow {MC} } \right)} \right) = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \) (đpcm)
Vậy \(\overrightarrow {MD} + \overrightarrow {ME} + \overrightarrow {MF} = \frac{3}{2}\overrightarrow {MO} \)
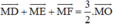
Do G là trọng tâm tam giác \(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{GA}+\overrightarrow{GB}+\overrightarrow{GC}=\overrightarrow{0}\)
Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow{GM}-\overrightarrow{NG}+\overrightarrow{GP}=\left(\overrightarrow{GA}+\overrightarrow{AM}\right)-\left(\overrightarrow{NB}+\overrightarrow{BG}\right)+\left(\overrightarrow{GC}+\overrightarrow{CP}\right)\)
\(=\overrightarrow{GA}-\overrightarrow{BG}+\overrightarrow{GC}+\overrightarrow{AM}-\overrightarrow{BG}+\overrightarrow{CP}\)
\(=\overrightarrow{GA}+\overrightarrow{GB}+\overrightarrow{GC}+\overrightarrow{AM}-\overrightarrow{BG}+\overrightarrow{CP}\)
\(=\overrightarrow{AM}-\overrightarrow{BG}+\overrightarrow{CP}\)