
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Câu 1:
1: \(\overrightarrow{OM}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{OA}+\overrightarrow{OD}}{2}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{BO}+\overrightarrow{OA}}{2}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{BA}}{2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\overrightarrow{BD}=2\cdot\overrightarrow{BO}=-2\cdot\overrightarrow{OB}\)
nên y=-2
2: \(2\cdot\overrightarrow{ON}=\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}=\overrightarrow{DO}+\overrightarrow{OC}=\overrightarrow{DC}=\overrightarrow{AB}\)
Vậy: Các vecto u thỏa mãn là vecto DC và vecto AB

Câu 5:
\(\overrightarrow{AM}=\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BM}\)
\(=\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{BC}\)
\(=\overrightarrow{AB}-\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}\)
\(c5\) \(\overrightarrow{AM}=\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{BM}=\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{BC}\)
\(=\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{2}{3}\left(\overrightarrow{BA}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right)=\overrightarrow{AB}-\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{3}\overrightarrow{AB}+\dfrac{2}{3}\overrightarrow{AC}\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(c4:\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{GA}+\overrightarrow{GB}+\overrightarrow{GC}=\overrightarrow{GG'}\)
\(\overrightarrow{G'A'}+\overrightarrow{G'B'}+\overrightarrow{G'C'}=\overrightarrow{GG'}\)\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{G'A}+\overrightarrow{AA'}+\overrightarrow{G'B}+\overrightarrow{B'B}+\overrightarrow{G'C}+\overrightarrow{CC'}=\overrightarrow{GG'}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{AA'}+\overrightarrow{BB'}+\overrightarrow{CC'}=3\overrightarrow{GG'}\)\(\left(dpcm\right)\)
\(c3:a,\) \(2\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{IC}=2\overrightarrow{IA}+2\overrightarrow{IM}=2\overrightarrow{MI}+2\left(\overrightarrow{IM}+\overrightarrow{MI}\right)=2.\overrightarrow{0}=\overrightarrow{0}\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(b,2\overrightarrow{OA}+\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}\)
\(=2\left(\overrightarrow{OI}+\overrightarrow{IA}\right)+\overrightarrow{OI}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{OI}+\overrightarrow{IC}\)
\(=4\overrightarrow{OI}+2\overrightarrow{IA}+\overrightarrow{IB}+\overrightarrow{IC}\)\(=4\overrightarrow{OI}+\overrightarrow{0}=4\overrightarrow{OI}\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(c2:\) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3AH=2AB\\3AK=AC\\4BM=3MC\\\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\overrightarrow{AB}=\dfrac{3}{2}\overrightarrow{AH}\\\overrightarrow{AC}=3\overrightarrow{AK}\\\overrightarrow{BM}=\dfrac{3}{7}\overrightarrow{BC}\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{BC}=\dfrac{7}{3}\overrightarrow{BM}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{BC}=\overrightarrow{AC}-\overrightarrow{AB}=3\overrightarrow{AK}-\dfrac{3}{2}\overrightarrow{AH}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{7}{3}\overrightarrow{BM}=3\overrightarrow{AK}-\dfrac{3}{2}\overrightarrow{AH}\Leftrightarrow\overrightarrow{BM}=\dfrac{9}{7}\overrightarrow{AK}-\dfrac{9}{14}\overrightarrow{AH}\)

a) Bảng phân bố tần số (về tuổi thọ bóng đèn điện) có thể viết dưới dạng như sau:

Số trung bình về tuổi thọ của bóng đèn trong bảng phân bố trên là:
.(3x1150 + 6x1160 + 12x1170 + 6x1180 + 3x1190)
= 1170.
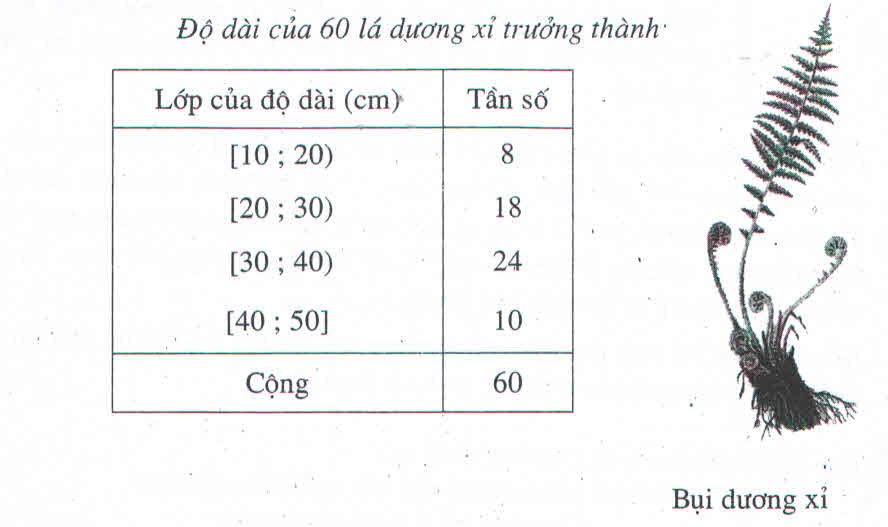
b) Số trung bình về chiều dài lá cây dương xỉ trong bài tập 2 trong là:
.(8x15 + 18x25 + 24x35 + 10x45) = 31 (cm).

a) Phương sai và độ lệch chuẩn trong bài tập 1. Bảng phân bố tần số viết lại là
![]()
Số trung bình: \(\overline{x} = 1170\)
Phương sai: \(S_{x}^{2}=\frac{1}{30}(3x1150^{2}+6x1160^{2}+12x1170^{2}+6x1180^{2}+3x1190^{2})-1170^{2} = 120\)
Độ lệch chuẩn: Sx.= \(\sqrt{S_{x}^{2}}=\sqrt{120} ≈ 10,9545\)
b) Phương sai và độ lệch chuẩn, bảng thống kê trong bài tập 2 \(\S 1.\)
\(S_{x}^{2}=\frac{1}{60}(8x15^{2}+18x25^{2}+24x35^{2}+10x45^{2}) - 312 = 84 \)
Sx ≈ 9,165.

11:
a: \(BD=AC=\sqrt{\left(3a\right)^2+\left(4a\right)^2}=5a\)
|vecto AB+vecto AD|
=|vecto AB+vecto BC|
=|vecto AC|
=5a
b: Gọi M là trung điểm của BC
=>BM=CM=BC/2=2a
\(AM=\sqrt{AB^2+BM^2}=a\sqrt{13}\)
Xét ΔABC có AM là trung tuyến
nên vecto AB+vecto AC=2*vecto AM
=>|vecto AB+vecto AC|=2|vecto AM|
=>\(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right|=2\cdot AM=2a\sqrt{13}\)

12:

a: Gọi M là trung điểm của BC
trên tia đối của tia MA, lấy D sao cho M là trung điểm của AD
Xét tứ giác ABDC có
M là trung điểm chung của AD và BC
góc BAC=90 độ
=>ABDC là hình chữ nhật
=>\(\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}=\overrightarrow{AD}\)
=>\(\overrightarrow{v}=\overrightarrow{AD}\)
b: \(\left|\overrightarrow{v}\right|=\left|\overrightarrow{AD}\right|=AD=2\cdot AM=2\cdot\dfrac{BC}{2}=BC=\sqrt{\left(6a\right)^2+\left(8a\right)^2}=10a\)
hình như đó đâu phải là câu 12 đâu ạ 🤔🤔🤔 trong đề câu 12 có chi tiết nào liên quan tới M đâu 🤔











Câu 1:
1: \(\overrightarrow{OM}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{OA}+\overrightarrow{OD}}{2}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{BO}+\overrightarrow{OA}}{2}=\dfrac{\overrightarrow{BA}}{2}=-\dfrac{1}{2}\overrightarrow{AB}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\overrightarrow{BD}=2\cdot\overrightarrow{BO}=-2\cdot\overrightarrow{OB}\)
nên y=-2
2: \(2\cdot\overrightarrow{ON}=\overrightarrow{OB}+\overrightarrow{OC}=\overrightarrow{DO}+\overrightarrow{OC}=\overrightarrow{DC}=\overrightarrow{AB}\)
Vậy: Các vecto u thỏa mãn là vecto DC và vecto AB