Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\dfrac{x-2}{x+1}-\dfrac{3}{x+2}>0.\left(x\ne-1;-2\right).\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-4-3x-3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2-3x-7}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-3x-7}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}>0.\)
Ta có: \(x^2-3x-7=0.\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2}.\\x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x+1=0.\Leftrightarrow x=-1.\\ x+2=0.\Leftrightarrow x=-2.\)
Bảng xét dấu:
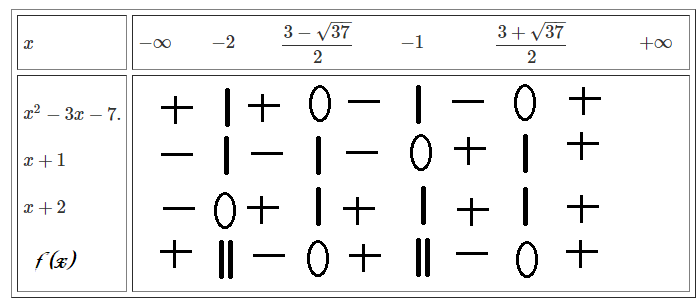
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)>0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left(-\infty-2\right)\cup\left(\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2};-1\right)\cup\left(\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty\right).\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}\ge3.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+2\ge9.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-3x-7\ge0.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}.\\x=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-3x-7.\)
\(f\left(x\right)=x^2-3x-7.\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\in(-\infty;\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}]\cup[\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty).\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{x^2-3x+2}\ge3\Leftrightarrow x\in(-\infty;\dfrac{3-\sqrt{37}}{2}]\cup[\dfrac{3+\sqrt{37}}{2};+\infty).\)

Nhân 2 vế của giả thiết với \(\sqrt{x^2+3}-x\) và rút gọn ta được:
\(y+\sqrt{y^2+3}=\sqrt{x^2+3}-x\) (1)
Nhân 2 vế của giả thiết với \(\sqrt{y^2+3}-y\) và rút gọn ta được:
\(x+\sqrt{x^2+3}=\sqrt{y^2+3}-y\) (2)
Cộng vế với vế (1) và (2) và rút gọn:
\(\Rightarrow x+y=0\Rightarrow y=-x\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\left(\sqrt{x^2+3}-x\right)\left(\sqrt{x^2+3}+x\right)=3\)


\(1)\sqrt{x^2+1}< 3.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+1< 9.\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2< 8.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x< 2\sqrt{2}.\\x>-2\sqrt{2}.\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\sqrt{2}< x< 2\sqrt{2}.\)
\(2)\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{x^2-4}< 0.\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x^2-4x+3}{x^2-4}.\)
\(x^2-4=0.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2.\\x=-2.\end{matrix}\right.\\ x^2-4x+3=0.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3.\\x=1.\end{matrix}\right.\)
Bảng xét dấu:
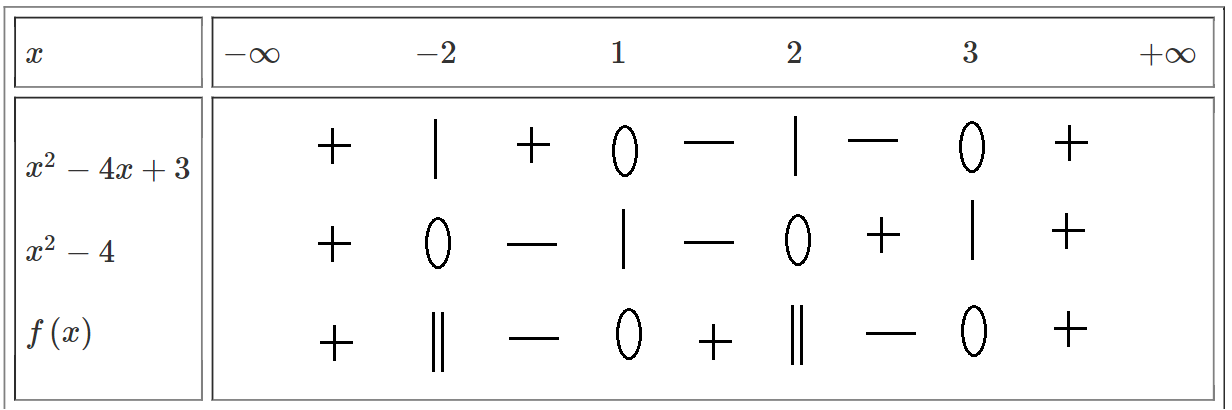
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)< 0\Leftrightarrow x\in\left(-2;1\right)\cup\left(2;3\right).\)
Lời giải:
1.
$\sqrt{x^2+1}<3$
$\Leftrightarrow 0\leq x^2+1<9$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+1<9$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2<8$
$\Leftrightarrow -2\sqrt{2}< x< 2\sqrt{2}$
2.
Xét 2 TH:
TH1: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x^2-4x+3<0\\ x^2-4>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} (x-1)(x-3)<0\\ (x-2)(x+2)>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} 1< x< 3\\ x>2 \text{hoặc} x<-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 2< x<3\)
TH2: \(\left\{\begin{matrix} x^2-4x+3>0\\ x^2-4<0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} (x-1)(x-3)>0\\ (x-2)(x+2)<0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} x>3 \text{hoặc} x<1\\ -2< x< 2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow -2< x< 1\)
Kết hợp 2 TH suy ra tập nghiệm \(S=(2;3)\cup (-2;1)\)

1:
ĐKXĐ: x<>3
\(\dfrac{x-1}{x-3}>1\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-1-\left(x-3\right)}{x-3}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{x-1-x+3}{x-3}>0\)
=>\(\dfrac{2}{x-3}>0\)
=>x-3>0
=>x>3
2: ĐKXĐ: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x>=3\\x< =-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\sqrt{x^2+x-12}< 8-x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}8-x>=0\\x^2+x-12< \left(8-x\right)^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =8\\x^2+x-12-x^2+16x-64< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x< =8\\17x-76< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(x< \dfrac{76}{17}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được: \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}3< =x< \dfrac{76}{17}\\x< =-4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đầu kiện:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ge0\\3-x\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge1\\x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow x\in[1;3]\)
Ta có: \(-x^2+4x-3=\left(x-1\right)\left(3-x\right)\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{3-x}=t;t\ge0\)
\(t^2=x-1+3-x+2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(3-x\right)}\\ \Rightarrow2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(3-x\right)}=t^2-2\left(1\right)\)
Thay vào phương trình đã cho ta được:
\(3t-2\left(t^2-2\right)-2=0\\ \Leftrightarrow-2t^2+3t+2=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=2\\t=-\dfrac{1}{2}< 0.loại\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay t=2 vào (1) ta có:
\(-x^2+4x-4=0;\Delta=0\Rightarrow x=2\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho có nghiệm x = 2