
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Xét phương trình tiếp tuyến tổng quát có dạng:
\(y=\left(6x_0+3x_0^2\right)\left(x-x_0\right)+3x_0^2+x_0^3\)
có 3 tiếp tuyến đi qua A(a,0) nên phương trình \(\left(6x_0+3x_0^2\right)\left(a-x_0\right)+3x_0^2+x_0^3=0\) có 3 nghiệm
\(PT\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x_0=0\\2x_0^2+3\left(1-a\right)x_0+6a=0\end{cases}}\)
Vậy có 1 pttt là y=0
do đó để có hai tiếp tuyến vuông góc thì \(2x_0^2+3\left(1-a\right)x_0+6a=0\) có hia nghiệm \(x_1,x_2\text{ thỏa mãn}\)
\(\left(6x_1+3x_1^2\right)\left(6x_2+3x_2^2\right)=-1\)mà áp dung Viet ta có \(\hept{\begin{cases}x_1+x_2=\frac{3a-3}{2}\\x_1x_2=3a\end{cases}}\)
Nên \(36x_1x_2+18x_1x_2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+9x_1^2x_2^2=-1\Leftrightarrow126a+81a\left(a-1\right)+81a^2=-1\)
từ đây mình giải được a nhé
Xét phương trình tiếp tuyến tổng quát có dạng:
y=(6x0+3x02)(x−x0)+3x02+x03
có 3 tiếp tuyến đi qua A(a,0) nên phương trình (6x0+3x02)(a−x0)+3x02+x03=0 có 3 nghiệm
PT⇔[
| x0=0 |
| 2x02+3(1−a)x0+6a=0 |
Vậy có 1 pttt là y=0
do đó để có hai tiếp tuyến vuông góc thì 2x02+3(1−a)x0+6a=0 có hia nghiệm x1,x2 thỏa mãn
(6x1+3x12)(6x2+3x22)=−1mà áp dung Viet ta có {
| x1+x2=3a−32 |
| x1x2=3a |
Nên 36x1x2+18x1x2(x1+x2)+9x12x22=−1⇔126a+81a(a−1)+81a2=−1

a) 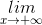 (x4 – x2 + x - 1) =
(x4 – x2 + x - 1) = 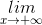 x4(1 -
x4(1 - 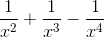 ) = +∞.
) = +∞.
b) 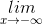 (-2x3 + 3x2 -5 ) =
(-2x3 + 3x2 -5 ) = 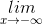 x3(-2 +
x3(-2 + 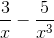 ) = +∞.
) = +∞.
c) 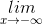
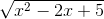 =
= 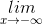
 = +∞.
= +∞.
d) 
 =
= 

= 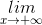
 =
= 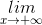
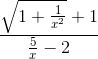 = -1.
= -1.


1.
\(\lim\left(\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}-3^n+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}-3^n\right)\left(\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}+3^n\right)}{\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}+3^n}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{-2.3^n}{\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}+3^n}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{-2.3^n}{3^n\left(\sqrt{1-\dfrac{2}{3^n}}+1\right)}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{1-\dfrac{2}{3^n}}+1}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{-2}{1+1}+\dfrac{1}{2021}=-\dfrac{2020}{2021}\)
2.
\(AP=4PB=4\left(AB-AP\right)=4AB-4AP\)
\(\Rightarrow5AP=4AB\Rightarrow AP=\dfrac{4}{5}AB\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AP}=\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}\)
\(CD=5CQ=5\left(CD-DQ\right)\Rightarrow5DQ=4CD\Rightarrow DQ=\dfrac{4}{5}CD\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{DQ}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}\)
Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow{PQ}=\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{AD}+\overrightarrow{DQ}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}\)
\(=-\dfrac{4}{5}\left(\overrightarrow{AD}+\overrightarrow{DB}\right)+\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{DB}+\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\left(\overrightarrow{CD}+\overrightarrow{DB}\right)=\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}+\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{BC}\)
Mà \(\overrightarrow{AD};\overrightarrow{BC}\) không cùng phương\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AD};\overrightarrow{BC};\overrightarrow{PQ}\) đồng phẳng


1.
\(u_{n+1}=4u_n+3.4^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_{n+1}-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(n+1\right).4^{n+1}=4\left[u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n\right]\)
Đặt \(u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n=v_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}v_1=2-\dfrac{3}{4}.4=-1\\v_{n+1}=4v_n\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow v_n=-1.4^{n-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow u_n=\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n-4^{n-1}=\left(3n-1\right)4^{n-1}\)
2.
\(a_n=\dfrac{a_{n-1}}{2n.a_{n-1}+1}\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=2n+\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}-\left(n-1\right)^2-\left(n-1\right)\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=b_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b_1=2-1-1=0\\b_n=b_{n-1}=...=b_1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=n^2+n\Rightarrow a_n=\dfrac{1}{n^2+n}\)

ĐKXĐ: \(-2\le x\le3\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{x+2}+2\sqrt{3-x}=a\Rightarrow4\sqrt{6+x-x^2}-3x=a^2-14\)
Mặt khác \(a^2=\left(\sqrt{x+2}+2\sqrt{3-x}\right)^2\le5\left(x+2+3-x\right)=25\)
\(\Rightarrow a\le5\)
Và \(\sqrt{x+2}+\sqrt{3-x}+\sqrt{3-x}\ge\sqrt{5}+\sqrt{3-x}\ge\sqrt{5}\) \(\Rightarrow a\ge\sqrt{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\sqrt{5}\le a\le5\)
Phương trình trở thành:
\(a^2-14=ma\Leftrightarrow\frac{a^2-14}{a}=m\) với \(a\in\left[\sqrt{5};5\right]\)
\(f\left(a\right)=\frac{a^2-14}{a}\Rightarrow f'\left(a\right)=\frac{2a^2-a^2+14}{a^2}=\frac{a^2+14}{a^2}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)\) đồng biến \(\Rightarrow f\left(\sqrt{5}\right)\le f\left(a\right)\le5\)
\(\Rightarrow-\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{5}\le f\left(a\right)\le\frac{11}{5}\Rightarrow-\frac{9\sqrt{5}}{5}\le m\le\frac{11}{5}\)

a.
\(sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{\pi}{8}+k\pi\) (1)
\(-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\le x\le\dfrac{7\pi}{3}\Rightarrow-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\le-\dfrac{\pi}{8}+k\pi\le\dfrac{7\pi}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{5}{24}\le k\le\dfrac{59}{24}\Rightarrow k=\left\{0;1;2\right\}\)
Thế vào (1) \(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-\dfrac{\pi}{8};\dfrac{7\pi}{8};\dfrac{15\pi}{8}\right\}\)









\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{\left|x\right|+\sqrt{x^2+x}}{x+10}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{-x+\sqrt{x^2+x}}{x+10}\)
\(=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-\infty}\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{1+\dfrac{1}{x}}}{1+\dfrac{10}{x}}=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{1}}{1}=\dfrac{-1+1}{1}=0\)