Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Đặt \(log_5\left(x+5\right)=a\Rightarrow x+5=5^a\)
\(\Rightarrow a^2-\left(m+6\right)log_25^a+m^2+9=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^2-a\left(m+6\right)log_25+m^2+9=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(m+6\right)^2.log^2_25-4\left(m^2+9\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(log^2_25-4\right)m^2+\left(12log_2^25\right).m+36\left(log_2^25-1\right)\ge0\)
Bấm máy BPT trên và lấy số nguyên gần nhất ta được \(m\ge-2\Rightarrow\) có \(20+2+1=23\) giá trị nguyên của m

ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne y\)
\(log_xy=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Leftrightarrow log_x^2y=1\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\left(l\right)\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=log_{x^{-1}}\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+\frac{1}{x}\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-\frac{1}{x^2}=1\Leftrightarrow x^4-x^2-1=0\Rightarrow x^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\Rightarrow y^2=\frac{1}{x^2}=\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+xy+y^2=\frac{1+\sqrt{5}}{2}+1+\frac{-1+\sqrt{5}}{2}=\sqrt{5}+1\)

\(log_xy=log_yx=\frac{1}{log_xy}\Rightarrow\left(log_xy\right)^2=1\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}log_xy=1\\log_xy=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=y\\x=\frac{1}{y}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(log_x\left(x-y\right)\) tồn tại \(\Rightarrow x-y\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne y\Rightarrow x=\frac{1}{y}\)
\(log_x\left(x-y\right)=log_y\left(x+1\right)\Leftrightarrow log_x\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)=-log_x\left(x+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_x\left[\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)\right]=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{x}\right)\left(x+1\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=x\Leftrightarrow x^3+x^2-2x-1=0\)
Pt này nghiệm xấu, đề bài có vấn đề

ĐKXĐ: \(x>0\)
\(log_{a^4}x-log_{a^2}x+log_ax=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{4}log_ax-\frac{1}{2}log_ax+log_ax=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3}{4}log_ax=\frac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_ax=1\)
\(\Rightarrow x=a\)

Lời giải:
a) ĐKXĐ:......
Ta có: \(\log_{2x+1}(3-x^2)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 3-x^2=(2x+1)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 5x^2+4x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{-2+\sqrt{14}}{5}\\x=\dfrac{-2-\sqrt{14}}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Kết hợp với đkxđ suy ra \(x=\frac{-2+\sqrt{14}}{5}\) là nghiệm
b) ĐKXĐ:....
Đặt \(2-x=a\Rightarrow \log_2(2a+1)=a\) (\(a>\frac{-1}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow 2a+1=2^a\)
Xét hàm \(y(a)=2^a-2a-1\)
\(\Rightarrow y'=\ln 2.2^a-2=0\Leftrightarrow a=\log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right)\)
Lập bảng biến thiên của $y(a)$ với $a>\frac{-1}{2}$ ta thấy đồ thì của $y(a)$ cắt đường thẳng \(y=0\) tại hai điểm, tức là pt có hai nghiệm. Trong đó một nghiệm thuộc \((-\frac{1}{2}; \log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right))\) và nghiệm khác thuộc \((\log_2\left(\frac{2}{\ln 2}\right);+\infty)\)
Thực hiện shift-solve ta thu được \(a=0\) hoặc \(a\approx 2,66\)
Câu c)
ĐKXĐ: \(x>-1\)
Ta có: \(\log_2(x+1)=4-3x\Leftrightarrow x+1=2^{4-3x}\)
Ta thấy:
\((x+1)'=1>0\) nên hàm vế trái đồng biến trên KXĐ
\((2^{4-3x})'=-3.\ln 2.2^{4-3x}<0\) nên hàm vế phải nghịch biến trên KXĐ
Do đó, PT chỉ có thể có duy nhất một nghiệm
Thấy \(x=1\) thỏa mãn nên $x=1$ là nghiệm duy nhất của phương trình

bài a, nhứ đã giải ở câu trc:
b, ĐK: 0<x, x khác 1.
ta có: log2x64= 6.log2x2= 6( \(\frac{1}{1+log_2x}\))
logx216=2logx2=\(\frac{2}{log_2x}\)
Thay vào pt:
6( \(\frac{1}{1+log_2x}\)) +\(\frac{2}{log_2x}\) =3
đặt T=log2x, ĐK. t>0
<=>6\(\frac{1}{1+t}\) +\(\frac{2}{t}\)=3
.......
<=> t=2( nghiệm -\(\frac{1}{3}\)<0 loại)
.....
<=>x=4(thõa)
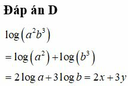
Trắc nghiệm rất lẹ (chắc vài giây), còn tự luận hơi lâu:
Hiển nhiên chỉ cần xét với \(x>2\) (vì vế trái luôn dương). Chú ý rằng \(a^{logx}=x^{loga}\)
Với \(a=10\Rightarrow x+2=x-2\) vô nghiệm (ktm)
- Trắc nghiệm: với \(a>10\Rightarrow\left(x^{loga}+2\right)^{loga}>x+2>x-2\) pt vô nghiệm
Với \(a< 10\) chọn 2 giá trị a=2 và a=9 để kiểm tra hàm \(\left(x^{loga}+2\right)^{loga}-x+2\) thấy đều đổi dấu ở chế độ table \(\Rightarrow a=\left\{2;3;...;9\right\}\) có 8 giá trị nguyên
- Tự luận: xét với \(x>2\), đặt \(loga=m>0\) pt trở thành: \(\left(x^m+2\right)^m=x-2\)
Đặt \(x^m+2=t\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^m=t-2\\t^m=x-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow x^m-t^m=t-x\Rightarrow x^m+x=t^m+t\) (1)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=x^m+x\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=mx^{m-1}+1>0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến
Do đó \(\left(1\right)\Rightarrow x=t\Rightarrow x^m=x-2\Rightarrow x^m-x+2=0\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=x^m-x+2\)
- Với \(m>1\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=m.x^{m-1}-1>1-1\ge0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)>f\left(2\right)=2^m-2+2=2^m>0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) vô nghiệm (ktm)
- Với \(0< m< 1\) ta có:
\(f\left(2\right)=2^m>0\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\left(x^m-x+2\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}x\left(x^{m-1}-1+\dfrac{2}{x}\right)\)
Chú ý rằng \(m< 1\Rightarrow x^{m-1}=\dfrac{1}{x^{1-m}}\rightarrow0\) khi \(x\rightarrow+\infty\Rightarrow x^{m-1}-1+\dfrac{2}{x}\rightarrow-1\Rightarrow\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\left(x^m-x+2\right)=-\infty\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right).\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}f\left(x\right)< 0\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) luôn có ít nhất 1 nghiệm thỏa mãn \(x>2\)
Vậy \(0< m< 1\) hay \(0< loga< 1\Rightarrow2\le a< 10\Rightarrow a=\left\{2;3;...;9\right\}\)