Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1.
Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2-4x+5}=t\ge1\Rightarrow x^2-4x=t^2-5\)
Pt trở thành:
\(4t=t^2-5+2m-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-4t+2m-6=0\) (1)
Pt đã cho có 4 nghiệm pb khi và chỉ khi (1) có 2 nghiệm pb đều lớn hơn 1
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta'=4-\left(2m-6\right)>0\\\left(t_1-1\right)\left(t_2-1\right)>0\\\dfrac{t_1+t_2}{2}>1\\\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}10-2m>0\\t_1t_2-\left(t_1+t_1\right)+1>0\\t_1+t_2>2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< 5\\2m-6-4+1>0\\4>2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9}{2}< m< 5\)
2.
Để pt đã cho có 2 nghiệm:
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne3\\\Delta'=1+4\left(m-3\right)\ge0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne3\\m\ge\dfrac{11}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó:
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=4\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{\left(m-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{8}{m-3}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(m-3\right)^2}+\dfrac{2}{m-3}-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{m-3}=-1-\sqrt{2}\\\dfrac{1}{m-3}=-1+\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4-\sqrt{2}< \dfrac{11}{4}\left(loại\right)\\m=4+\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Xét với \(x>1\)
\(\sqrt{2x+m}=x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+m=x^2-2x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4x+1=m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=x^2-4x+1\) với \(x>1\)
\(-\dfrac{b}{2a}=2\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=-2\) ; \(f\left(2\right)=-3\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt có 2 nghiệm pb lớn hơn 1 khi \(-3< m< -2\)

Đặt \(\sqrt{1-x^2}=t\Rightarrow t\in\left[0;1\right]\)
Pt trở thành:
\(1-t^2+t=m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)=-t^2+t+1\) trên \(\left[0;1\right]\)
\(-\dfrac{b}{2a}=\dfrac{1}{2}\in\left[0;1\right]\)
\(f\left(0\right)=1\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=1\); \(f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow1\le f\left(t\right)\le\dfrac{5}{4}\Rightarrow\) pt có nghiệm khi \(m\in\left[1;\dfrac{5}{4}\right]\)

Đặt \(-x^2+2x=t\Rightarrow0\le t\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow-t^2+t-3+m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-t+3=m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)=t^2-t+3\) trên \(\left[0;1\right]\)
\(-\dfrac{b}{2a}=\dfrac{1}{2}\in\left[0;1\right]\)
\(f\left(0\right)=3\) ; \(f\left(1\right)=3\) ; \(f\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)=\dfrac{11}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{11}{4}\le f\left(t\right)\le3\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt có nghiệm khi và chỉ khi \(\dfrac{11}{4}\le m\le3\)

Đặt \(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{5-x}=t\)
\(t\ge\sqrt{x-1+5-x}=2\)
\(t\le\sqrt{2\left(x-1+5-x\right)}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(t^2=4+2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(5-x\right)}\Rightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(5-x\right)}=\dfrac{t^2-4}{2}\)
Pt trở thành:
\(t+\dfrac{3\left(t^2-4\right)}{2}=m\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}t^2+t-6=m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}t^2+t-6\) với \(t\in\left[2;2\sqrt{2}\right]\)
\(-\dfrac{b}{2a}=-\dfrac{1}{3}\notin\left[2;2\sqrt{2}\right]\)
\(f\left(2\right)=2\) ; \(f\left(2\sqrt{2}\right)=6+2\sqrt{2}\) \(\Rightarrow2\le f\left(t\right)\le6+2\sqrt{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt có nghiệm khi \(2\le m\le6+2\sqrt{2}\)

Xét phương trình hoành độ giao điểm\(x^2\)+4x-m=0 <=> x^2+4x=m, đây là kết hợp của 2 hàm số (P):y=\(x^2\)+4x và (d):y=m.
Khi vẽ đồ thị ta thấy parabol đồng biến trên khoảng (-2;+∞)=> Điểm giao giữa parabol và đồ thị y=m là điểm duy nhất thỏa mãn phương trình có duy nhất 1 nghiệm thuộc khoảng (-3;1).Vậy để phương trình có 1 nghiệm duy nhất <=> delta=0 <=>16+4m=0<=>m=-4.
mình trình bày hơi dài mong bạn thông cảm 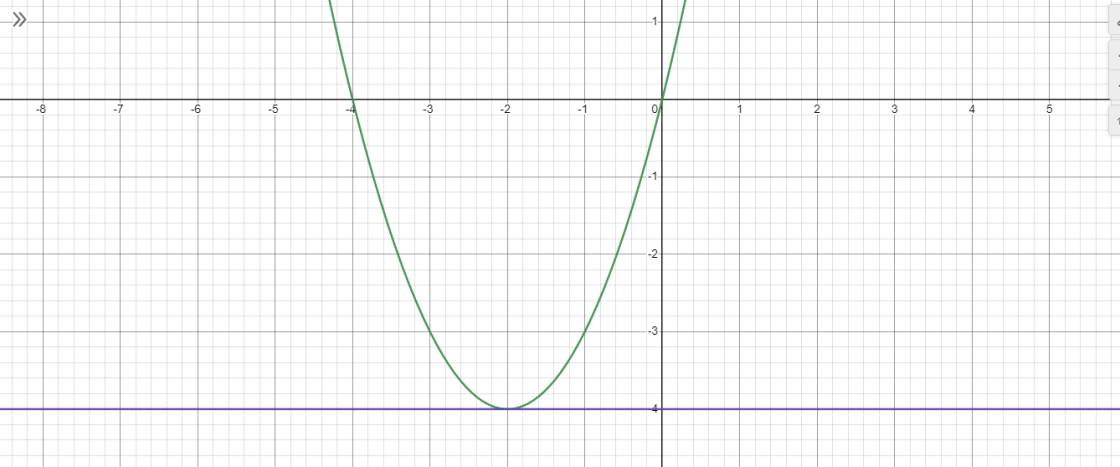

Đặt \(t=2^x>0\).
Phương trình ban đầu trở thành: \(t^2-2t+m=0\) (*)
Để phương trình ban đầu có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì (*) phải có 2 nghiệm phân biệt dương: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta'>0\\t_1+t_2>0\\t_1t_2>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}1-m>0\\2>0\left(đúng\right)\\m>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow0< m< 1\)

