Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(y'=1+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\) , gọi \(M\left(m;m-\dfrac{1}{m}\right)\)
Tiếp tuyến d tại M: \(y=\left(1+\dfrac{1}{m^2}\right)\left(x-m\right)+m-\dfrac{1}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1+\dfrac{1}{m^2}\right)x-y-\dfrac{2}{m}=0\)
\(d\left(O;d\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left|\dfrac{2}{m}\right|}{\sqrt{\left(1+\dfrac{1}{m^2}\right)^2+1}}=\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{16}{m^2}=\left(1+\dfrac{1}{m^2}\right)^2+1\Leftrightarrow16t=\left(1+t\right)^2+1\) (với \(t=\dfrac{1}{m^2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow t^2-14t+2=0\)
Sao đề cho nghiệm xấu vậy ta?

\(y'=4x^3-4mx\Rightarrow y'\left(1\right)=4-4m\)
\(A\left(1;1-m\right)\)
Phương trình tiếp tuyến d tại A có dạng:
\(y=\left(4-4m\right)\left(x-1\right)+1-m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4-4m\right)x-y+3m-3=0\)
\(d\left(B;d\right)=\dfrac{\left|\dfrac{3}{4}\left(4-4m\right)-1+3m-3\right|}{\sqrt{\left(4-4m\right)^2+1}}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{\left(4-4m\right)^2+1}}\le1\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(4-4m=0\Rightarrow m=1\)
y′=4x3−4mx⇒y′(1)=4−4my′=4x3−4mx⇒y′(1)=4−4m
A(1;1−m)A(1;1−m)
Phương trình tiếp tuyến d tại A có dạng:
y=(4−4m)(x−1)+1−my=(4−4m)(x−1)+1−m
⇔(4−4m)x−y+3m−3=0⇔(4−4m)x−y+3m−3=0
d(B;d)=∣∣∣34(4−4m)−1+3m−3∣∣∣√(4−4m)2+1=1√(4−4m)2+1≤1d(B;d)=|34(4−4m)−1+3m−3|(4−4m)2+1=1(4−4m)2+1≤1
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi 4−4m=0⇒m=1

\(y'=\dfrac{3}{\left(x+1\right)^2}\Rightarrow\) phương trình tiếp tuyến tại \(M\left(m;\dfrac{m-2}{m+1}\right)\) có dạng:
\(y=\dfrac{3}{\left(m+1\right)^2}\left(x-m\right)+\dfrac{m-2}{m+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-\left(m+1\right)^2y+m^2-4m-2=0\)
\(P=d\left(I;d\right)=\dfrac{\left|6m+6\right|}{\sqrt{9+\left(m+1\right)^4}}=\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{\left(m+1\right)^2+\dfrac{9}{\left(m+1\right)^2}}}\le\dfrac{6}{\sqrt{2\sqrt{\dfrac{9\left(m+1\right)^2}{\left(m+1\right)^2}}}}=\sqrt{6}\)
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi:
\(\left(m+1\right)^2=\dfrac{9}{\left(m+1\right)^2}\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2=3\Rightarrow m=\) ... lại xấu :)

\(y'=3x^2-6x\)
Do M thuộc (C) nên hệ số góc của tiếp tuyến tại M:
\(k=f\left(a\right)=3a^2-6a\)
\(f'\left(a\right)=6a-6>0;\forall a\in\left[2;3\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(a\right)\) đồng biến trên \(\left[2;3\right]\Rightarrow k_{max}\) khi \(a=3\)
\(\Rightarrow b=a^3-3a^2-1=-1\)
\(S=3-1=2\)

Ý tưởng thế này: tọa độ A, B thỏa mãn:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x^2+6ax=6\\y=2x^3+3ax^2+b\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2=1-ax\\y=2x^3+3ax^2+b\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow y=2x\left(1-ax\right)+3a\left(1-ax\right)+b\)
\(\Rightarrow y=-2ax^2+2x-3a^2x+3a+b\)
\(\Rightarrow y=-2a\left(1-ax\right)+2x-3a^2x+3a+b\)
\(\Rightarrow y=\left(2-a^2\right)x+a+b\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2-a^2\right)x-y+a+b=0\)
Đây chính là pt AB theo a;b
Từ khoảng cách \(\Rightarrow\dfrac{\left|a+b\right|}{\sqrt{\left(2-a^2\right)^2+1}}=1\Leftrightarrow\left(a+b\right)^2=\left(2-a^2\right)^2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(a+b\right)^2=a^4-4a^2+5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2a^2+\left(a+b\right)^2=a^4-2a^2+5=\left(a^2-1\right)^2+4\ge4\)

Khoảng giá trị của x mà đồ thị hàm số \(y = {2^x}\) nằm phía trên đường thẳng y = 4 là \(\left( {2; + \infty } \right)\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \({2^x} > 4\) là \(\left( {2; + \infty } \right)\)

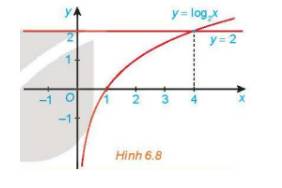
Khoảng giá trị của x mà đồ thị hàm số \(y=log_2x\) nằm phía trên đường thẳng y = 2 là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(log_2x>2\) là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)