Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Theo giả thiết : \(\begin{cases}xy=3^2\\x^4=y\sqrt{3}\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}y=\frac{9}{x}\\x^4=\frac{9\sqrt{3}}{x}\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}y=\frac{9}{x}\\x^5=9\sqrt{3}\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x=\sqrt[5]{\sqrt{3^5}}\\y=\frac{3^2}{x}\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x=\sqrt{3}\\y=3\sqrt{3}\end{cases}\)

Ba số x, y, z lập thành một cấp số nhân nên:
y = x.q và z = y.q = x.q2 ( q là công bội)
Ba số x, 2y, 3z lậo thành một cấp số cộng nên:
x + 3z = 4y ⇔ x + 3.(xq2) = 4.(x.q)
⇔ x. (1 + 3q2 – 4q) = 0 ⇔ x = 0 hay 3q2 – 4q + 1 = 0
Nếu x = 0 thì x = y= z= 0, q là một số tùy ý
Nếu x ≠ 0 thì 3q2– 4q + 1 = 0 ⇔\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}q=1\\q=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\).
Công bội của cấp số nhân là \(q=1\) hoặc \(q=\dfrac{1}{3}\).

Theo giả thiết ta có : \(\begin{cases}\left(5x-y\right)+\left(x+2y\right)=2\left(2x+3y\right)\\\left(y+1\right)^2\left(x-1\right)^2=\left(xy+1\right)^2\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\x+y=2\end{cases}\) hoặc \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\xy+x+y=0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\x+y=2\end{cases}\) hoặc \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}2x=5y\\y\left(5y\right)+5y+2y=0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x=\frac{10}{3}\\y=\frac{4}{3}\end{cases}\) hoặc \(\begin{cases}x=0,y=0\\x=-\frac{3}{4},y=-\frac{3}{10}\end{cases}\)

Theo đầu bài ta có : \(\cot\frac{A}{2}+\cot\frac{C}{2}=2\cot\frac{B}{2}\Leftrightarrow\frac{\sin\frac{A+C}{2}}{\sin\frac{A}{2}\sin\frac{C}{2}}=2\frac{\cos\frac{B}{2}}{\sin\frac{B}{2}}=2\frac{\sin\frac{A+C}{2}}{\cos\frac{A+C}{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin\left(\frac{A+C}{2}\right)\cos\left(\frac{A+C}{2}\right)=2\sin\frac{A}{2}\sin\frac{C}{2}\sin\frac{A+C}{2}=\left(\cos\frac{A-C}{2}-\cos\frac{A+C}{2}\right)\sin\frac{A+C}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sin\frac{A+C}{2}\cos\frac{A+C}{2}=\cos\frac{A-C}{2}\sin\frac{A+C}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\sin\left(A+C\right)=\frac{1}{2}\left(\sin A+\sin C\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sin A+\sin C=2\sin B\Rightarrow a+c=2b\)
Chứng tỏ 3 cạnh của tam giác lập thành cấp số cộng

\(f\left(x\right)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d\)
a,b,c,d lập thành cấp số nhân công bội q \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}q\ne\left\{0,1\right\}\\a\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=a.q\\c=aq^2\\d=aq^3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(f\left(x\right)=a.x^3+a.q.x^2+a.q^2.x+a.q^3\)(1)
\(f\left(x\right)=a\left[.x^3+q.x^2+q^2.x+q^3\right]\)
\(f\left(x\right)=a.\left[.x^2\left(x+q\right)+q^2\left(.x+q\right)\right]\)
\(f\left(x\right)=a.\left(x+q\right)\left(x^2+q^2\right)\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a,q\ne0\\f\left(x\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Rightarrow x=-q\) là nghiệm duy nhất

Theo giả thiết ta có :
\(u_1+u_2=u_1+\frac{1}{4}\left(u_1\right)=24\)
\(\Rightarrow u_1+\frac{1}{4}u_1^2-24=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_1=-12\) V \(u_1=8\)
Vậy có 2 cấp số nhân tương ứng là : 8,16,32,128 hoặc -12,36,-108,-972
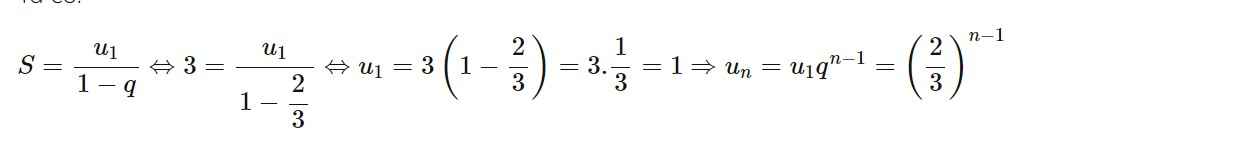
Chọn B
Theo giả thuyết: